Freedom of speech is a fundamental human right that allows individuals to express their thoughts and opinions without fear of censorship or retaliation. This essential liberty supports democratic societies by encouraging open dialogue and the exchange of diverse ideas. Explore the rest of the article to understand how freedom of speech shapes your rights and responsibilities in today's world.
Table of Comparison
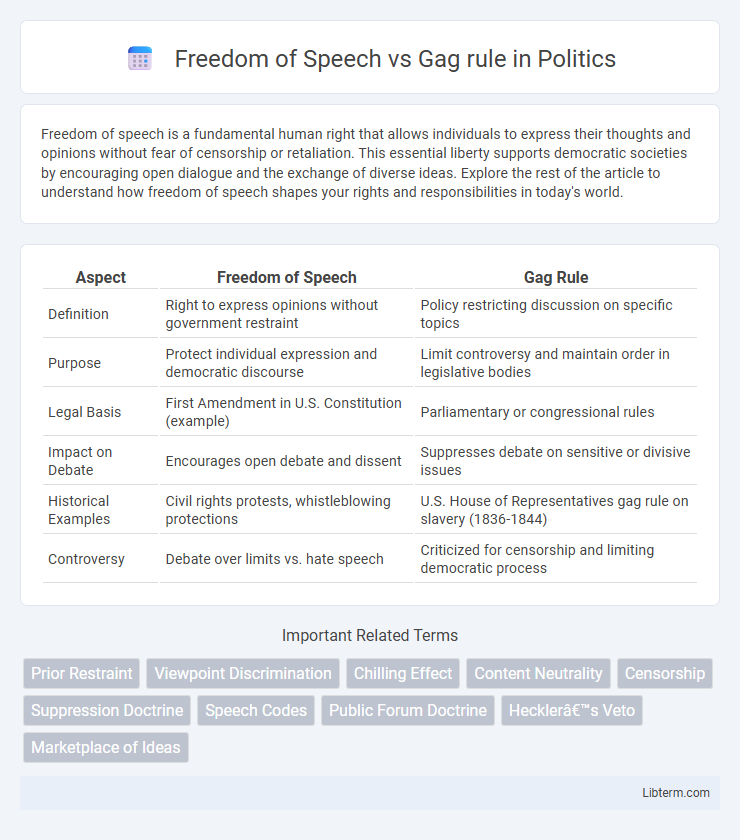
| Aspect | Freedom of Speech | Gag Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Right to express opinions without government restraint | Policy restricting discussion on specific topics |
| Purpose | Protect individual expression and democratic discourse | Limit controversy and maintain order in legislative bodies |
| Legal Basis | First Amendment in U.S. Constitution (example) | Parliamentary or congressional rules |
| Impact on Debate | Encourages open debate and dissent | Suppresses debate on sensitive or divisive issues |
| Historical Examples | Civil rights protests, whistleblowing protections | U.S. House of Representatives gag rule on slavery (1836-1844) |
| Controversy | Debate over limits vs. hate speech | Criticized for censorship and limiting democratic process |
Introduction: Defining Freedom of Speech and Gag Rule
Freedom of speech is a fundamental right protected by the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, allowing individuals to express opinions without government interference. The gag rule refers to regulations that restrict or prohibit discussion on specific topics, often imposed to maintain order or privacy. Understanding the tension between these concepts highlights the balance between open expression and limitations imposed for legal or ethical reasons.
Historical Context of Freedom of Speech
Freedom of speech has deep roots in historical documents such as the Magna Carta and the English Bill of Rights, evolving through Enlightenment ideals that championed individual liberty and democratic governance. The First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, ratified in 1791, explicitly protects freedom of speech, symbolizing a foundational principle against government censorship. In contrast, gag rules, historically used in legislative bodies to suppress discussion on contentious issues like slavery in the 19th century, highlight tensions between governmental control and freedom of expression.
Origins and Evolution of the Gag Rule
The gag rule originated in the early 19th century as a congressional measure to prohibit discussion or debate on the issue of slavery, particularly in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1836 to 1844. This rule aimed to suppress abolitionist petitions and maintain political order by restricting freedom of speech on contentious topics. The eventual repeal of the gag rule marked a pivotal moment in the expansion of free speech rights and legislative transparency in American democracy.
Key Legal Frameworks Governing Expression
The First Amendment of the United States Constitution serves as the cornerstone protecting freedom of speech, restricting government actions that inhibit expression, while the Gag Rule, historically applied in legislative and judicial contexts, imposes limitations on discussing certain topics to prevent bias or protect confidentiality. Legal frameworks such as the Communications Decency Act and Supreme Court rulings like Brandenburg v. Ohio further delineate the boundaries between protected speech and regulatory restrictions. Balancing these frameworks requires careful interpretation of free speech rights against interests like national security, public order, and fair trial rights.
Major Controversies and Landmark Cases
The tension between freedom of speech and gag rules has sparked major controversies such as the landmark Supreme Court case *Miami Herald Publishing Co. v. Tornillo* (1974), which struck down a state law forcing newspapers to provide equal space to political candidates, affirming editorial freedom under the First Amendment. Other significant disputes include the Pentagon Papers case (*New York Times Co. v. United States*, 1971), where prior restraint imposed by gag orders was ruled unconstitutional, reinforcing the press's right to publish sensitive information without government censorship. These cases highlight ongoing debates over balancing national security, individual expression, and government-imposed speech restrictions.
Societal Impacts of Gag Rules
Gag rules, which restrict open discussion and dissent, significantly undermine freedom of speech by limiting public access to diverse viewpoints and stifling democratic debate. The societal impacts include increased misinformation, reduced transparency, and weakened civic engagement, which can erode trust in institutions and hinder social progress. By suppressing critical dialogue, gag rules often facilitate authoritarianism and polarize communities, ultimately damaging social cohesion.
Freedom of Speech: Benefits and Risks
Freedom of speech empowers individuals to express ideas, foster creativity, and promote social progress by allowing open dialogue and debate. It supports democratic governance by ensuring transparency and holding authorities accountable, but unchecked speech can lead to misinformation, hate speech, and social unrest. Balancing freedom of speech with regulations is essential to protect public safety while preserving individual rights.
Balancing Security and Individual Liberties
Balancing security and individual liberties involves carefully navigating the tension between freedom of speech and gag rules, which restrict communication to protect public safety or confidentiality. Governments implement gag rules to prevent the dissemination of sensitive information that could threaten national security or ongoing investigations, while courts often prioritize free expression as a cornerstone of democracy. Achieving this equilibrium requires nuanced policies that safeguard security interests without unduly infringing on fundamental rights to open discourse and dissent.
Global Perspectives: Gag Rules Around the World
Gag rules, which restrict individuals or media from discussing certain topics, vary significantly across the globe, reflecting diverse legal and cultural attitudes toward freedom of speech. In countries like China and Russia, stringent gag rules limit political dissent and control information flow, whereas many Western democracies uphold broader free speech protections despite some content restrictions. The global landscape shows a tension between maintaining public order and safeguarding free expression, with international human rights organizations advocating against gag rules that suppress fundamental freedoms.
Future Challenges and Policy Recommendations
Emerging digital platforms amplify the complexity of balancing freedom of speech with gag rules, necessitating adaptive legislation that protects expression while preventing misinformation. Policymakers should implement transparent content moderation frameworks incorporating AI-driven analysis to uphold democratic values without stifling dissent. Future regulations must prioritize user privacy, platform accountability, and equitable access to ensure resilient communication ecosystems amid evolving political and technological landscapes.
Freedom of Speech Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com