Liberalism emphasizes individual freedoms, equal rights, and limited government intervention to promote personal and economic liberty. Rooted in Enlightenment ideals, it advocates for democracy, rule of law, and protection of civil liberties as foundations for a just society. Explore the rest of this article to understand how liberalism shapes modern political landscapes and influences your daily life.
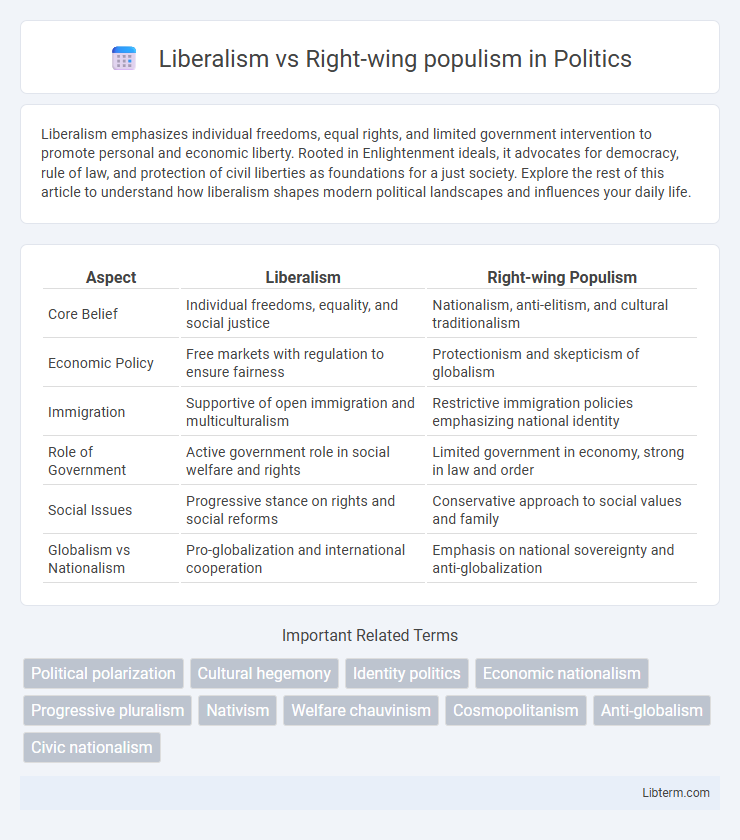
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Liberalism | Right-wing Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Individual freedoms, equality, and social justice | Nationalism, anti-elitism, and cultural traditionalism |
| Economic Policy | Free markets with regulation to ensure fairness | Protectionism and skepticism of globalism |
| Immigration | Supportive of open immigration and multiculturalism | Restrictive immigration policies emphasizing national identity |
| Role of Government | Active government role in social welfare and rights | Limited government in economy, strong in law and order |
| Social Issues | Progressive stance on rights and social reforms | Conservative approach to social values and family |
| Globalism vs Nationalism | Pro-globalization and international cooperation | Emphasis on national sovereignty and anti-globalization |
Defining Liberalism: Core Principles and Values
Liberalism centers on individual freedoms, equal rights, and democratic governance, emphasizing the protection of civil liberties such as freedom of speech, religion, and the press. It advocates for a rule of law framework and promotes social justice through inclusive policies that aim to reduce inequality. Economic liberalism supports market economies balanced by government intervention to ensure fairness and prevent monopolies.
Understanding Right-Wing Populism: Key Characteristics
Right-wing populism is characterized by its emphasis on nationalism, anti-elitism, and a strong stance against immigration, positioning itself as a defender of the "common people" against perceived threats from globalization and multiculturalism. This political ideology often combines conservative social values with a skepticism toward established political institutions and mainstream media. Understanding these key attributes highlights the contrast with liberalism, which prioritizes individual rights, multiculturalism, and institutional trust.
Historical Evolution of Liberalism and Right-Wing Populism
The historical evolution of liberalism traces back to the Enlightenment, emphasizing individual rights, limited government, and free markets as foundational principles. In contrast, right-wing populism emerged primarily in the late 20th century as a reaction to globalization, immigration, and perceived threats to national identity, advocating for strong nationalist policies and skepticism toward elite institutions. The ideological divergence became pronounced as liberalism championed multiculturalism and international cooperation, while right-wing populism prioritized sovereign control and cultural homogeneity.
Liberalism vs Right-Wing Populism: Political Ideologies Compared
Liberalism emphasizes individual rights, democratic governance, and free-market economies, advocating for equality and social justice through inclusive policies. Right-wing populism centers on nationalism, anti-elitism, and immigration restriction, often promoting traditional values and skepticism toward global institutions. The ideological divide lies in liberalism's emphasis on pluralism and progressive reform versus right-wing populism's focus on cultural homogeneity and protectionism.
Economic Policies: Contrasts and Consequences
Liberalism advocates for free-market economies with minimal government intervention, emphasizing individual entrepreneurship, open trade, and regulatory frameworks that promote competition and innovation. Right-wing populism often supports protectionist economic policies, including tariffs, state intervention, and welfare measures aimed at protecting domestic industries and workers from global market disruptions. These contrasting approaches influence economic outcomes such as growth rates, income distribution, and labor market dynamics, with liberalism typically fostering globalization benefits and right-wing populism focusing on national economic sovereignty.
Social Issues: Approaches to Diversity and Inclusion
Liberalism champions diversity and inclusion through policies promoting equal rights, anti-discrimination laws, and multiculturalism to ensure social equity across all groups. Right-wing populism often rejects multiculturalism, advocating for nationalist values and prioritizing majority cultural identity, which can lead to restrictive immigration policies and resistance to minority rights. These contrasting approaches shape societal cohesion and influence public debates on identity, social justice, and integration.
Immigration and National Identity: Diverging Perspectives
Liberalism advocates for inclusive immigration policies emphasizing multiculturalism and the protection of individual rights, fostering a diverse society grounded in universal human values. Right-wing populism prioritizes strict immigration controls and emphasizes preserving national identity through cultural homogeneity and sovereignty. These diverging perspectives reflect fundamental differences in balancing openness with security and cultural cohesion in policy-making.
Media Influence and Public Opinion
Liberalism often promotes a media landscape that values pluralism, fact-based reporting, and open discourse, fostering informed public opinion through diverse perspectives. Right-wing populism leverages media channels to amplify nationalist rhetoric, framing narratives that resonate emotionally with specific demographics, often challenging mainstream media credibility. The contrasting media strategies significantly shape public opinion by influencing trust levels, agenda-setting, and the polarization of political views across societies.
Impact on Democracy and Democratic Institutions
Liberalism champions pluralism, individual rights, and institutionally protected civil liberties that strengthen democratic governance and promote inclusive political participation. Right-wing populism often challenges established democratic institutions by promoting majoritarianism, skepticism of elites, and centralized authority, which can undermine checks and balances and marginalized minority rights. The tension between these ideologies shapes democratic resilience, with liberalism supporting institutional integrity and right-wing populism risking democratic erosion through populist mobilization.
The Future of Liberalism and Right-Wing Populism in Global Politics
The future of liberalism faces challenges from the rising influence of right-wing populism, which often capitalizes on nationalist rhetoric and appeals to socio-economic grievances. As global politics evolve, liberalism must adapt by reinforcing commitments to democratic institutions, human rights, and inclusive policies to counteract populist narratives that undermine these values. The ongoing ideological contest will shape governance models worldwide, impacting policy decisions on immigration, trade, and international cooperation.
Liberalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com