A repealable clause allows a specific section of a contract or law to be officially revoked or annulled at a later date. This provision ensures flexibility in agreements or legislation, enabling parties or lawmakers to adapt to changing circumstances without discarding the entire document. Explore the rest of the article to understand how repealable clauses impact your agreements and legal frameworks.
Table of Comparison
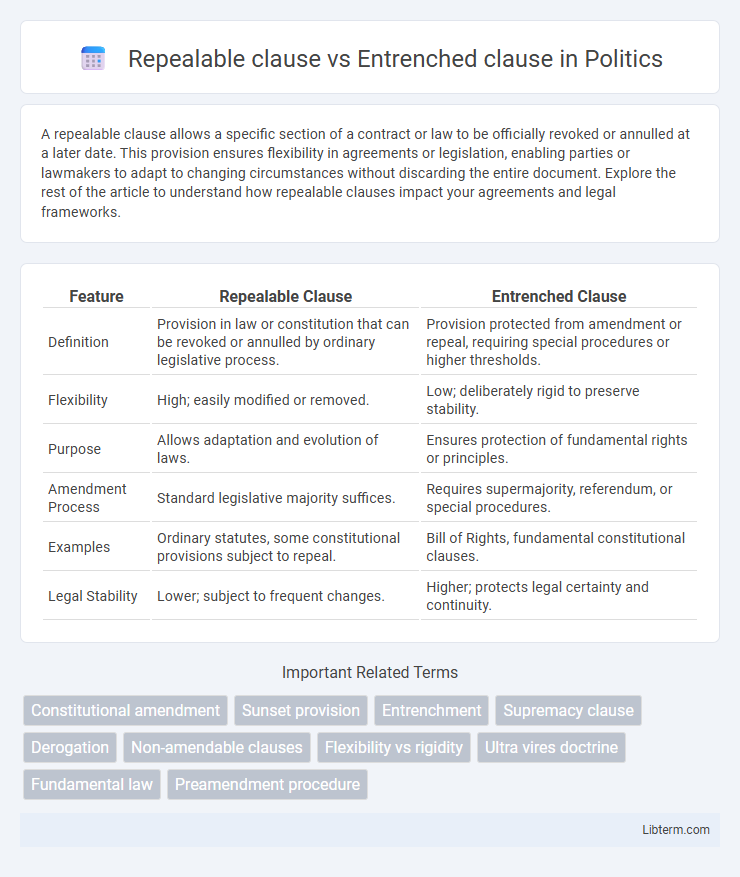
| Feature | Repealable Clause | Entrenched Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Provision in law or constitution that can be revoked or annulled by ordinary legislative process. | Provision protected from amendment or repeal, requiring special procedures or higher thresholds. |
| Flexibility | High; easily modified or removed. | Low; deliberately rigid to preserve stability. |
| Purpose | Allows adaptation and evolution of laws. | Ensures protection of fundamental rights or principles. |
| Amendment Process | Standard legislative majority suffices. | Requires supermajority, referendum, or special procedures. |
| Examples | Ordinary statutes, some constitutional provisions subject to repeal. | Bill of Rights, fundamental constitutional clauses. |
| Legal Stability | Lower; subject to frequent changes. | Higher; protects legal certainty and continuity. |
Introduction to Constitutional Clauses
Repealable clauses in constitutional law allow certain provisions to be amended or revoked through standard legislative processes, providing flexibility in governance. Entrenched clauses, by contrast, are safeguarded against easy alteration, requiring stringent procedures such as supermajority votes or referenda to amend, ensuring foundational principles remain stable over time. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing constitutional durability and the balance between adaptability and rigidity in legal frameworks.
Defining Repealable Clauses
Repealable clauses refer to provisions in a legal document or constitution that can be altered or revoked through a regular legislative process without special procedures. These clauses maintain flexibility, allowing lawmakers to adapt laws as societal needs evolve. Unlike entrenched clauses, repeatable clauses do not require supermajority votes or special amendment processes for modification or repeal.
Understanding Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses are constitutional provisions designed to be resistant to amendment or repeal, often requiring a supermajority or special procedure for any changes. These clauses protect fundamental principles or rights by preventing transient political majorities from altering core aspects of the constitution easily. Understanding entrenched clauses is crucial for grasping how constitutional stability and continuity are maintained in various legal systems.
Key Differences Between Repealable and Entrenched Clauses
Repealable clauses are provisions in a constitution or statute that can be amended or abolished by ordinary legislative processes, allowing flexibility and adaptability in the legal framework. Entrenched clauses require more rigorous procedures for amendment, such as supermajority votes, referendums, or approval by multiple legislative bodies, safeguarding essential constitutional principles from easy alteration. Key differences lie in their amendment thresholds and protective mechanisms, with repealable clauses promoting legislative agility and entrenched clauses preserving constitutional stability and continuity.
Legal Significance of Repealable Clauses
Repealable clauses hold legal significance as they empower legislative bodies to amend or revoke specific provisions without the need for constitutional amendments, ensuring flexibility in adapting laws to evolving societal needs. Unlike entrenched clauses, which require rigorous procedures such as supermajority votes or referenda to amend, repealable clauses facilitate more straightforward legal modifications. This distinction impacts the stability and adaptability of legal frameworks, influencing how quickly laws respond to political and social changes.
Legal Significance of Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses hold significant legal importance as they are designed to be resistant to ordinary legislative amendments, often requiring special procedures or supermajority votes for any changes. This legal rigor ensures stability and protection of fundamental principles within a constitution or legal framework. Unlike repealable clauses that can be altered or removed through regular legislative processes, entrenched clauses safeguard rights, governance structures, and essential rules from transient political shifts.
Examples of Repealable Clauses in Constitutions
Repealable clauses in constitutions allow for amendments or abolition through a prescribed legislative process, exemplified by Article 368 of the Indian Constitution, which permits Parliament to amend any part of the document except the basic structure. Another example is Section 128 of the Australian Constitution, outlining the referendum process to change constitutional provisions. These clauses contrast with entrenched clauses, which require more rigorous procedures or are protected from amendment to preserve core constitutional principles.
Examples of Entrenched Clauses in Constitutions
Entrenched clauses in constitutions are provisions that require a special amendment procedure, making them difficult to repeal or alter, such as the U.S. Constitution's Article V, which mandates a supermajority for amendments. The German Basic Law includes entrenched clauses protecting human dignity and the federal structure, preventing changes through ordinary legislative processes. In contrast, repealable clauses can be modified or repealed through standard legislative enactments without heightened requirements.
Impact on Constitutional Amendments
Repealable clauses allow constitutional amendments to be made more flexibly since they can be altered or abolished by the legislature or through a simpler amendment process, facilitating adaptive legal frameworks. Entrenched clauses require a more rigorous process, often involving supermajority votes or referendums, to ensure stability and protect fundamental constitutional principles from frequent changes. The presence of entrenched clauses significantly limits the ease of amendments, safeguarding core rights and structures from transient political pressures.
Comparative Analysis: Which Clause Protects Democracy Better?
A repealable clause allows legislative bodies to amend or repeal constitutional provisions, promoting flexibility and adaptability in democracy, while an entrenched clause imposes strict hurdles for changes, safeguarding fundamental democratic principles from transient political shifts. Entrenched clauses better protect democracy by preventing arbitrary alterations that could undermine constitutional stability and individual rights, ensuring long-term adherence to democratic norms. However, repealable clauses offer responsiveness to evolving societal values, which may risk instability but allow periodic democratic renewal.
Repealable clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com