Anarchy represents the absence of a governing authority, often leading to a state of disorder and lawlessness. Understanding the causes and effects of anarchy can provide insight into political systems and social stability. Explore the article to learn how anarchy influences societies and what it means for your perspective on governance.
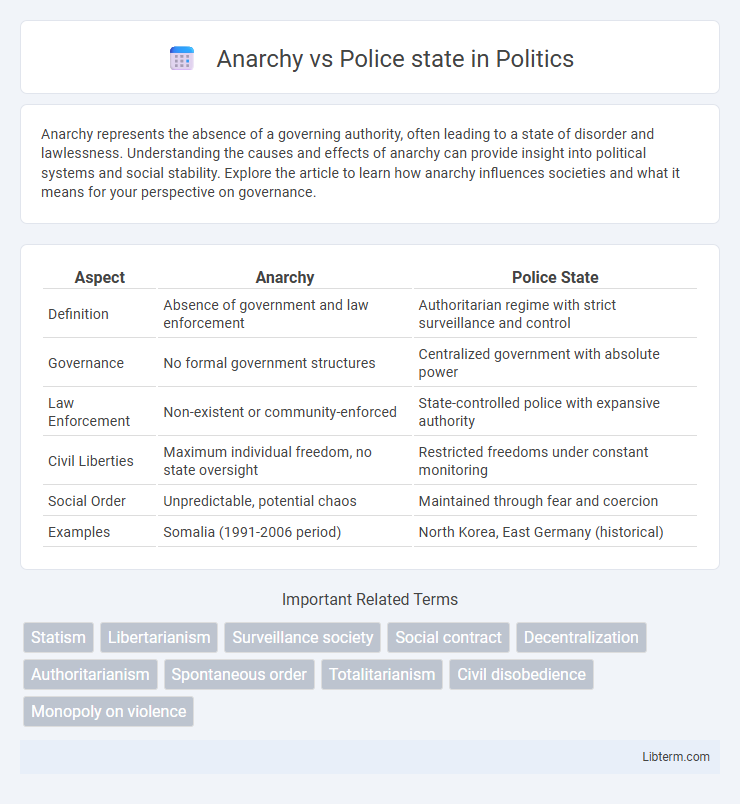
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Anarchy | Police State |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Absence of government and law enforcement | Authoritarian regime with strict surveillance and control |
| Governance | No formal government structures | Centralized government with absolute power |
| Law Enforcement | Non-existent or community-enforced | State-controlled police with expansive authority |
| Civil Liberties | Maximum individual freedom, no state oversight | Restricted freedoms under constant monitoring |
| Social Order | Unpredictable, potential chaos | Maintained through fear and coercion |
| Examples | Somalia (1991-2006 period) | North Korea, East Germany (historical) |
Understanding Anarchy: Definition and Principles
Anarchy is defined as the absence of centralized government or authority, emphasizing voluntary cooperation and self-governance among individuals or communities. It operates on principles of autonomy, mutual aid, and non-coercion, rejecting hierarchical structures and oppressive control. Understanding anarchy involves recognizing its advocacy for decentralized decision-making and the empowerment of individuals to organize society based on consensus and shared responsibility.
What Constitutes a Police State?
A police state is characterized by an authoritarian government that exercises strict control over citizens through pervasive surveillance, arbitrary enforcement of laws, and limited personal freedoms. It relies heavily on a centralized police force empowered to suppress dissent, restrict free speech, and monitor public and private life to maintain order. Key indicators include censorship, lack of judicial independence, and systematic violations of human rights.
Historical Examples of Anarchic Societies
Historical examples of anarchic societies include the Free Territory during the Russian Civil War, where anarchist principles guided social organization without central authority. The Paris Commune of 1871 showcased a brief anarchist-influenced government emphasizing decentralized decision-making and worker self-management. These cases illustrate the challenges and potential of stateless societies in maintaining order and mutual aid without hierarchical policing structures.
Police States Through the Ages
Police states have historically emerged as governments centralize authority to maintain strict social control and enforce laws through extensive surveillance, repression, and militarization. From the secret police of Tsarist Russia to the Gestapo in Nazi Germany and the Stasi in East Germany, these regimes utilize coercion and fear to suppress dissent and preserve power. Modern police states often rely on advanced technology for mass monitoring, illustrating a persistent evolution of authoritarian control methods across centuries.
Key Differences: Anarchy vs Police State
Anarchy is characterized by the absence of formal government, leading to a lack of centralized authority and legal enforcement, resulting in potential social disorder and individual freedom without state control. In contrast, a police state features a highly centralized government authority with extensive surveillance, strict law enforcement, and limited personal freedoms to maintain order and control. The key difference lies in anarchy's absence of governance versus the police state's oppressive governmental oversight.
Individual Freedoms: Anarchy Versus Police Control
Individual freedoms in anarchy emphasize absolute personal autonomy without government-imposed restrictions, allowing individuals to act according to their will. In contrast, police states prioritize control and order through strict law enforcement, often restricting civil liberties such as free speech, movement, and privacy. The tension between these systems lies in balancing unchecked freedom with security and societal stability.
Social Order and Public Safety in Both Systems
Anarchy lacks centralized authority, resulting in minimal social order and heightened risks to public safety due to the absence of law enforcement and regulatory mechanisms. Police states maintain strict control over society through pervasive surveillance and enforcement, often prioritizing order and security at the expense of individual freedoms. Public safety in police states is typically enforced through authoritative measures, while social cohesion in anarchic systems relies heavily on voluntary cooperation and mutual agreements among individuals.
Economic Impacts: Anarchy vs Police State
Anarchy often leads to severe economic instability due to the absence of legal frameworks that protect property rights and enforce contracts, resulting in disrupted trade and decreased investment. In contrast, police states maintain economic order through strict law enforcement and centralized control, which can stabilize markets but may also stifle innovation and discourage entrepreneurship due to excessive regulation and repression. The economic output under police states may appear steady but tends to suffer from inefficiencies and reduced economic freedoms compared to more open societies.
Human Rights: Protection and Violations
Anarchy often leads to widespread human rights violations due to the absence of enforced laws and protection mechanisms, resulting in chaos and lawlessness. Police states enforce strict control over citizens, which can suppress civil liberties and lead to systematic abuses such as arbitrary detention and torture. Effective human rights protection requires a balanced governance system that upholds the rule of law while safeguarding individual freedoms.
Future Implications: Choosing Between Anarchy and Police State
The future implications of choosing between anarchy and a police state hinge on the balance between freedom and security, with anarchy potentially leading to social chaos and lawlessness, while a police state risks oppressive surveillance and restricted civil liberties. Societal stability, economic development, and human rights dynamically interact depending on the degree of governance control or lack thereof. Advances in technology, especially in surveillance and law enforcement tools, will profoundly shape how these systems evolve and impact individual autonomy.
Anarchy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com