Political participation encompasses activities such as voting, attending rallies, engaging in discussions, and contacting representatives to influence government decisions and policies. This involvement is essential for a functioning democracy, empowering citizens to voice their concerns and shape the future of their communities. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective ways to enhance your political engagement and impact.
Table of Comparison
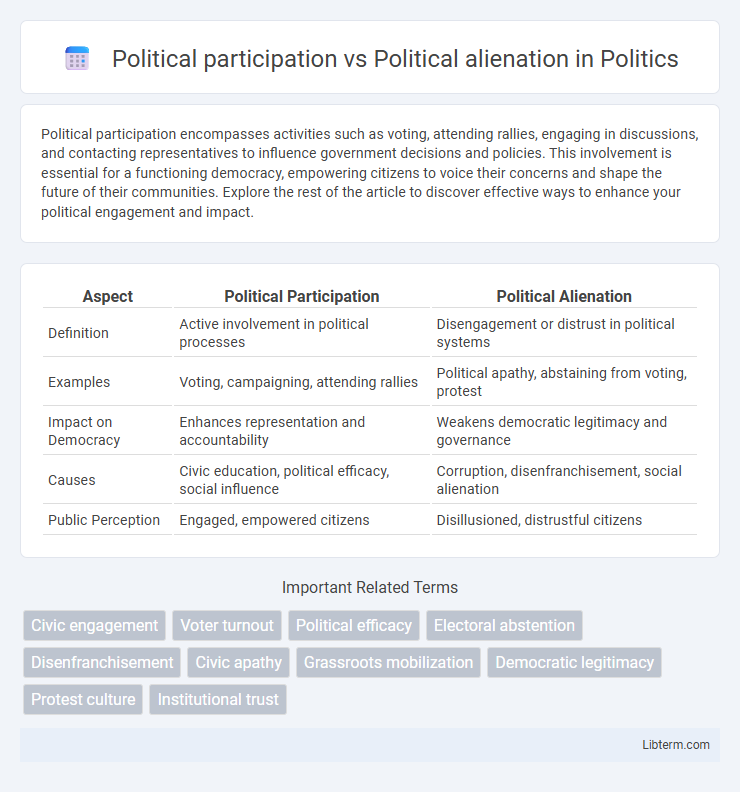
| Aspect | Political Participation | Political Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active involvement in political processes | Disengagement or distrust in political systems |
| Examples | Voting, campaigning, attending rallies | Political apathy, abstaining from voting, protest |
| Impact on Democracy | Enhances representation and accountability | Weakens democratic legitimacy and governance |
| Causes | Civic education, political efficacy, social influence | Corruption, disenfranchisement, social alienation |
| Public Perception | Engaged, empowered citizens | Disillusioned, distrustful citizens |
Defining Political Participation and Political Alienation
Political participation refers to the various activities through which citizens engage in the political process, such as voting, attending political meetings, or joining interest groups, enhancing democratic representation. Political alienation describes the feeling of estrangement or disconnection from political institutions and processes, often resulting in political apathy or withdrawal from civic duties. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing citizen engagement and the health of democratic societies.
Historical Evolution of Political Engagement
Political participation has evolved from limited suffrage and elite control in early democracies to widespread voting rights and diverse forms of civic engagement, reflecting expanded inclusivity and democratization over centuries. Political alienation historically arises during periods of social upheaval or perceived government unresponsiveness, evident in events like the 1960s U.S. civil rights protests and declining voter turnout in late 20th-century Western democracies. The shift from exclusive electoral participation to broader, issue-based activism marks the dynamic interplay between engagement and alienation in shaping contemporary political landscapes.
Factors Influencing Political Participation
Socioeconomic status, education levels, and political efficacy are key factors influencing political participation, as individuals with higher income and education tend to engage more actively in voting and civic activities. Conversely, political alienation often stems from feelings of powerlessness, distrust in government institutions, and perceived lack of meaningful impact, which reduce motivation to participate. Media exposure and social networks also shape political engagement by either empowering citizens with information or reinforcing disengagement through skepticism.
Causes and Symptoms of Political Alienation
Political alienation arises from causes such as perceived government corruption, lack of political efficacy, and social exclusion, leading individuals to feel disconnected from political processes. Symptoms include voter apathy, distrust in political institutions, and reduced engagement in civic activities. This alienation contrasts with active political participation, where citizens feel empowered and involved in shaping governance.
The Role of Media in Shaping Political Attitudes
Media plays a critical role in shaping political attitudes by influencing public awareness and engagement levels, directly impacting political participation versus alienation. Exposure to diverse media sources fosters informed voting behavior and civic involvement, while biased or sensationalist coverage can contribute to political disillusionment and alienation. Social media platforms amplify these effects by enabling both inclusive dialogues and echo chambers that reinforce political apathy or activism.
Socioeconomic Impacts on Civic Involvement
Socioeconomic status significantly influences political participation, with higher income and education levels correlating to increased voter turnout and civic engagement. Conversely, economic hardship and limited educational opportunities often lead to political alienation, reducing trust in governmental institutions and decreasing involvement in political processes. These disparities in socioeconomic factors contribute to uneven civic participation, impacting democratic representation and social equity.
Political Participation Trends in Different Democracies
Political participation trends in different democracies reveal varying levels of voter turnout, civic engagement, and activism influenced by factors such as electoral systems, political culture, and socio-economic conditions. Established democracies like Sweden and Germany exhibit high levels of political participation through voting and organized civil society involvement, while newer or struggling democracies, such as Brazil or South Africa, often face challenges with political alienation and lower engagement due to corruption and trust deficits. Comparative studies highlight that inclusive institutions and transparent governance correlate strongly with increased citizen involvement and reduced political alienation.
Consequences of Political Alienation for Governance
Political alienation leads to decreased voter turnout, diminished public trust in government institutions, and weakened democratic legitimacy. Low political participation resulting from alienation can cause ineffective policy-making and reduced accountability among elected officials. Prolonged political disengagement risks fostering social unrest and undermining stable governance structures.
Strategies to Enhance Political Engagement
Implementing targeted civic education programs increases political awareness and reduces feelings of alienation by empowering citizens with knowledge of their rights and the political process. Creating inclusive platforms for dialogue and community involvement fosters a sense of belonging and representation, directly countering political disengagement. Utilizing digital tools and social media campaigns effectively reaches younger demographics, encouraging active participation and mitigating the impact of political alienation.
Bridging the Gap: Solutions to Political Disenfranchisement
Increasing voter education and accessibility, such as implementing online registration and extended voting hours, effectively addresses political disenfranchisement by reducing barriers to participation. Community engagement initiatives, including town halls and civic workshops, foster a sense of belonging and counteract political alienation among marginalized groups. Policymakers must prioritize inclusive reforms that promote trust in democratic institutions to bridge the gap between political participation and alienation.
Political participation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com