Suppression involves the conscious effort to inhibit unwanted thoughts, emotions, or behaviors, often as a coping mechanism during stressful situations. While it can provide temporary relief, prolonged suppression may lead to increased anxiety and emotional distress. Explore the rest of the article to understand how managing suppression effectively can improve your mental well-being.
Table of Comparison
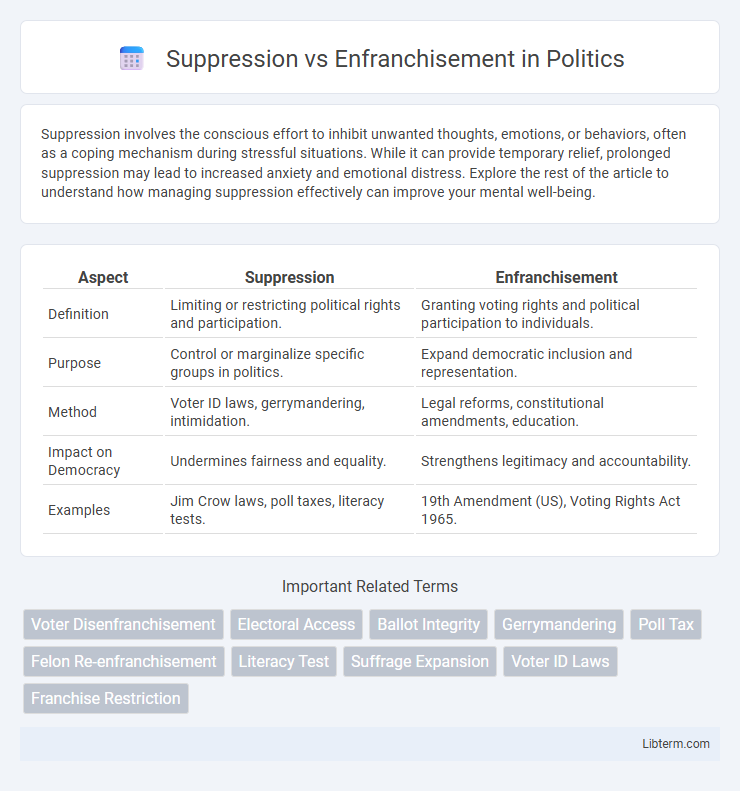
| Aspect | Suppression | Enfranchisement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Limiting or restricting political rights and participation. | Granting voting rights and political participation to individuals. |
| Purpose | Control or marginalize specific groups in politics. | Expand democratic inclusion and representation. |
| Method | Voter ID laws, gerrymandering, intimidation. | Legal reforms, constitutional amendments, education. |
| Impact on Democracy | Undermines fairness and equality. | Strengthens legitimacy and accountability. |
| Examples | Jim Crow laws, poll taxes, literacy tests. | 19th Amendment (US), Voting Rights Act 1965. |
Understanding Suppression and Enfranchisement
Suppression refers to the systematic restriction or denial of rights and freedoms, often targeting specific groups to maintain control or power imbalances. Enfranchisement involves granting individuals or groups the legal rights and privileges of citizenship, most notably the right to vote, thereby promoting participation and inclusion in democratic processes. Understanding suppression and enfranchisement is essential to recognizing the dynamics of political power and the ongoing struggle for civil rights and social justice.
Historical Contexts of Voting Rights
Suppression and enfranchisement of voting rights have shaped political landscapes throughout history, reflecting power dynamics and social hierarchies. Historical suppression tactics include literacy tests, poll taxes, and intimidation aimed at disenfranchising African Americans and other marginalized groups, particularly in the post-Reconstruction United States. Enfranchisement milestones such as the 15th Amendment (1870), the 19th Amendment (1920), and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 represent significant legal victories that expanded suffrage and sought to dismantle institutional barriers.
Key Tactics of Voter Suppression
Voter suppression employs tactics such as strict voter ID laws, purging voter rolls, and limiting early voting or absentee ballot access to disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Gerrymandering and misinformation campaigns further undermine voter turnout by confusing or discouraging eligible voters from participating. These methods collectively erode democratic participation and skew election outcomes by restricting who can effectively cast their ballots.
Major Movements for Enfranchisement
Major movements for enfranchisement such as the women's suffrage movement, civil rights movement, and labor union campaigns played pivotal roles in expanding voting rights and political participation. The women's suffrage movement led to the 19th Amendment in the United States, granting women the right to vote, while the civil rights movement resulted in the Voting Rights Act of 1965, eliminating racial barriers to voting. Labor unions also pushed for broader enfranchisement by advocating for workers' rights and fair representation in democratic processes.
Legal Frameworks Shaping Access to Voting
Legal frameworks governing voting access vary significantly, with suppression tactics often embedded in restrictive voter ID laws, felony disenfranchisement policies, and limited polling locations that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Conversely, enfranchisement initiatives include automatic voter registration, restoration of voting rights for formerly incarcerated individuals, and expanded early voting options designed to increase electoral participation. These contrasting legal mechanisms critically influence the inclusivity and fairness of democratic processes across jurisdictions.
Socioeconomic Impacts of Suppression
Suppression of voting rights disproportionately affects marginalized communities by limiting access to political representation and perpetuating economic inequalities. Reduced political participation hinders the ability to influence policies that address poverty, education, and healthcare disparities. These socioeconomic impacts create cycles of disadvantage, deepening poverty and limiting upward mobility for suppressed populations.
Technology’s Role in Voting Rights
Technology plays a crucial role in enfranchisement by improving access through online voter registration, electronic voting systems, and real-time voter information updates. Conversely, technology can facilitate suppression via targeted misinformation campaigns on social media, algorithmic biases that hinder minority voter outreach, and cybersecurity threats compromising election integrity. The dual impact of technology on voting rights underscores the need for robust digital safeguards and equitable access to ensure fair democratic participation.
Case Studies: Notable Suppression and Enfranchisement Examples
The landmark case of Shelby County v. Holder (2013) exemplifies suppression by invalidating key parts of the Voting Rights Act, leading to new voting restrictions in states like Alabama and Texas. Conversely, the 1965 Voting Rights Act's enforcement in Selma, Alabama, showcases enfranchisement by significantly increasing Black voter registration and participation through federal oversight. These cases highlight the contrasting legal and social impacts on voter access, where suppression limits electoral power while enfranchisement promotes inclusive democracy.
Advocacy Groups and Their Influence
Advocacy groups play a pivotal role in enfranchisement efforts by mobilizing resources, shaping public opinion, and lobbying policymakers to expand voting rights and reduce suppression tactics such as restrictive ID laws and gerrymandering. Organizations like the NAACP and the ACLU actively challenge voter suppression through litigation and grassroots campaigns, emphasizing equitable access to the ballot. Their influence is evident in legislative reforms and court rulings that protect electoral participation for marginalized communities.
The Path Forward: Empowerment and Equity
Suppression undermines democratic participation by limiting access to voting rights, whereas enfranchisement promotes empowerment and equity through inclusive policies that ensure all citizens can engage in the political process. Empowerment arises when systemic barriers are dismantled, enabling marginalized communities to influence decisions affecting their lives. Equity requires sustained efforts in education, legal reforms, and community engagement to create a fair and representative democracy for the future.
Suppression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com