Outgoing individuals thrive in social settings, easily forming connections and energizing those around them with their enthusiasm. Their natural charisma often opens doors to new opportunities and collaborative experiences that enrich personal and professional life. Discover more about how embracing your outgoing nature can transform your interactions and success in the following article.
Table of Comparison
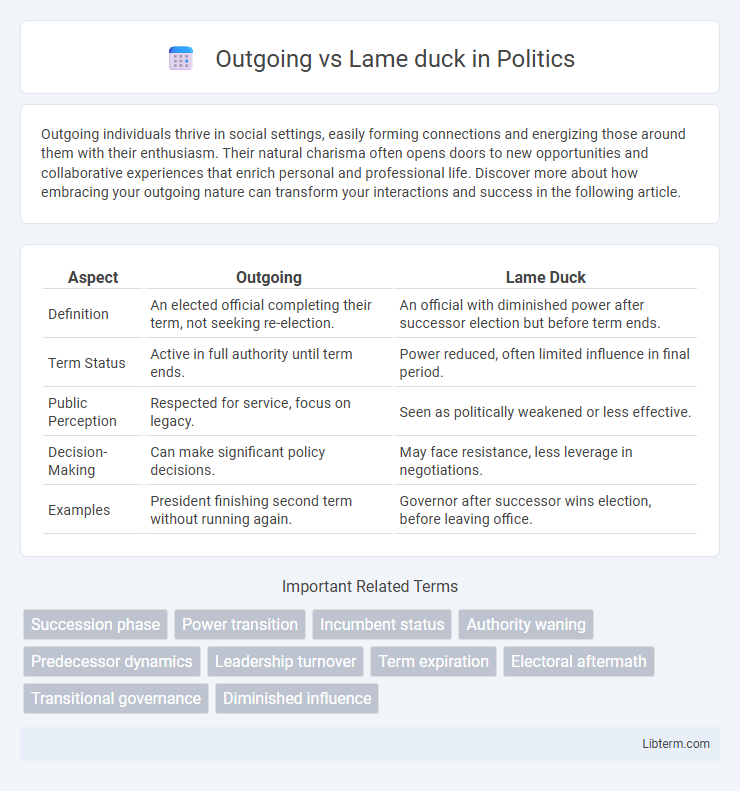
| Aspect | Outgoing | Lame Duck |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An elected official completing their term, not seeking re-election. | An official with diminished power after successor election but before term ends. |
| Term Status | Active in full authority until term ends. | Power reduced, often limited influence in final period. |
| Public Perception | Respected for service, focus on legacy. | Seen as politically weakened or less effective. |
| Decision-Making | Can make significant policy decisions. | May face resistance, less leverage in negotiations. |
| Examples | President finishing second term without running again. | Governor after successor wins election, before leaving office. |
Understanding the Terms: Outgoing vs Lame Duck
Outgoing refers to an official who is leaving office at the end of their term, often continuing to perform duties until a successor is sworn in. Lame duck specifically describes an outgoing official whose power is weakened because their successor has already been elected or designated. Understanding these terms clarifies the transitional period in political offices, highlighting differences in authority and influence during the handover phase.
Key Differences Between Outgoing and Lame Duck
Outgoing and lame duck both describe transitional political periods, but outgoing refers to any official leaving office after election results, while lame duck specifically denotes an elected official continuing to serve after losing re-election or choosing not to run again. The key difference lies in influence; outgoing officials typically maintain authority until their term ends, whereas lame ducks experience reduced political power and diminished effectiveness. Understanding this distinction clarifies the impact on legislative processes and executive decisions during transitions.
Historical Origins of ‘Lame Duck’ in Politics
The term "lame duck" in politics originated in the 18th century London Stock Exchange, referring to investors who defaulted on debts. By the early 19th century, American political discourse adopted "lame duck" to describe elected officials who completed their terms after losing re-election, highlighting their diminished influence. This historical evolution underscores the term's metaphorical shift from financial failure to political impotence during a transitional period.
The Role of an Outgoing Leader
An outgoing leader plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition by actively supporting their successor and maintaining organizational stability. They leverage their experience to mentor new leadership while wrapping up key initiatives and preserving stakeholder confidence. Effective outgoing leaders foster continuity and uphold the institution's mission during periods of change.
Lame Duck Period: What It Means for Governance
The lame duck period refers to the time between an election and the inauguration of a new officeholder, during which the outgoing official retains power but typically has diminished authority. This phase often leads to reduced policy influence and limited legislative productivity, as the incumbent's ability to enact significant changes is constrained by the anticipation of leadership transition. Governance during the lame duck period can face challenges due to unclear mandates, shifting priorities, and potential strategic delays in decision-making.
Political Implications of Lame Duck Status
Lame duck status significantly limits a politician's influence and ability to enact policies due to their impending departure from office. This period often triggers strategic shifts among legislators, reducing cooperation with outgoing officials perceived as less accountable to voters. Political opponents may exploit lame duck sessions to pass controversial measures, knowing the departing leader has diminished political leverage.
Outgoing Office Holders and Transition of Power
Outgoing office holders play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition of power, facilitating continuity and stability within government operations. Their cooperation with incoming officials allows for effective transfer of critical information, resources, and responsibilities, minimizing disruptions during changes in administration. Efficient transitions bolster public confidence and uphold democratic principles by enabling new leaders to quickly assume their duties.
Effects on Policy and Decision-Making
Outgoing administrations often face diminished authority, leading to a slowdown in policy implementation and cautious decision-making to avoid constraining successors. Lame duck officials experience reduced political capital, limiting their capacity to introduce bold initiatives or influence legislative agendas effectively. This transitional period typically results in a focus on routine governance rather than transformative policy changes.
Public Perception: Outgoing vs Lame Duck Leaders
Outgoing leaders often maintain public respect by emphasizing achievements and a clear transition plan, reinforcing their legacy and competence. Lame duck leaders, perceived as less effective due to diminished political power, frequently face skepticism and reduced public confidence. This perception impacts their ability to influence policy and public opinion during their final term.
Lessons Learned: Managing the Transition Period
Managing the transition period between outgoing and lame duck leadership requires clear communication, defined roles, and strategic planning to maintain organizational stability. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of early stakeholder engagement and maintaining momentum on key initiatives to avoid operational disruptions. Establishing a structured handover process ensures continuity and prepares the incoming leadership for immediate effectiveness.
Outgoing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com