The ruling party holds the principal authority in government, shaping policies and legislative agendas that impact a nation's direction. Understanding its structure and influence helps you grasp the broader political landscape and societal changes. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how ruling parties affect your daily life and global affairs.
Table of Comparison
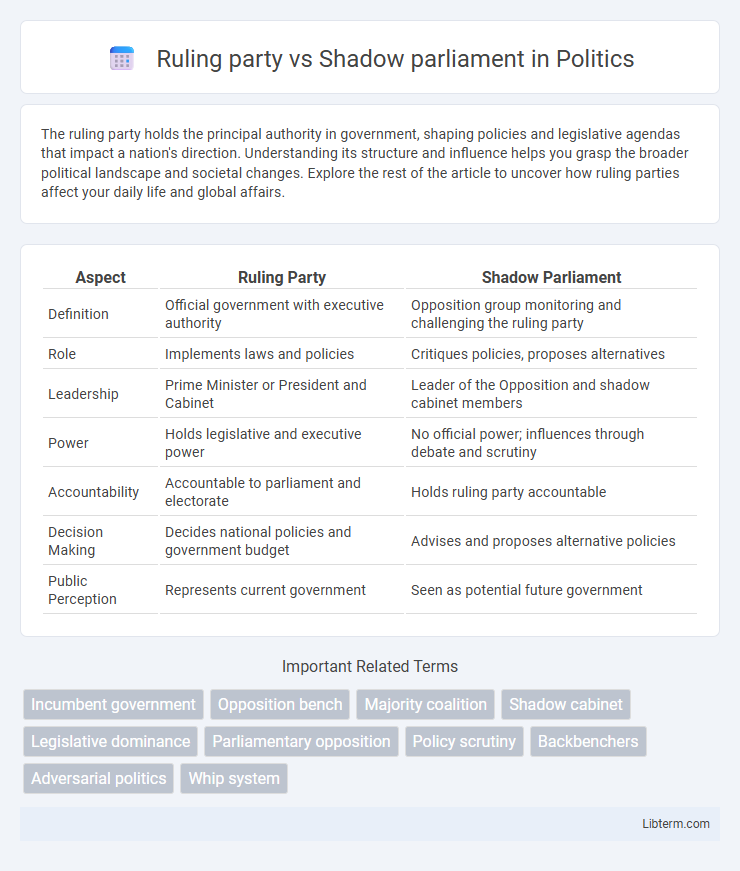
| Aspect | Ruling Party | Shadow Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official government with executive authority | Opposition group monitoring and challenging the ruling party |
| Role | Implements laws and policies | Critiques policies, proposes alternatives |
| Leadership | Prime Minister or President and Cabinet | Leader of the Opposition and shadow cabinet members |
| Power | Holds legislative and executive power | No official power; influences through debate and scrutiny |
| Accountability | Accountable to parliament and electorate | Holds ruling party accountable |
| Decision Making | Decides national policies and government budget | Advises and proposes alternative policies |
| Public Perception | Represents current government | Seen as potential future government |
Introduction to Ruling Party and Shadow Parliament
The ruling party holds the majority of seats in the parliament, enabling it to form the government and implement policies. The shadow parliament consists of opposition members who monitor and challenge the ruling party's decisions, often forming a "shadow cabinet" that mirrors government ministries. This system enhances democratic accountability and provides alternative policy proposals.
Historical Evolution of Political Oppositions
The historical evolution of political oppositions reveals the emergence of the ruling party as the dominant force shaping governance, while the shadow parliament developed as a structured counterbalance providing critical scrutiny and alternative policies. Originating in the British parliamentary system, shadow cabinets formalized political opposition by mirroring government roles to hold the ruling party accountable. Over time, this dynamic institutionalized competitive democracy, ensuring a continuous dialogue between power holders and opposition voices in modern legislatures worldwide.
Structure and Functions: Ruling Party Explained
The ruling party controls the government and holds the majority of seats in the legislature, enabling it to implement policies and pass laws effectively. Its structure includes key leadership roles such as the Prime Minister or President, cabinet members, and party whips, who coordinate legislative agendas and ensure party discipline. Functions of the ruling party involve setting national policy, managing public administration, and responding to legislative challenges while maintaining public support.
Understanding the Role of Shadow Parliament
The Shadow Parliament functions as a critical component in democratic governance by scrutinizing the ruling party's policies and holding them accountable through alternative proposals and debates. It provides a structured framework for opposition parties to challenge government decisions, ensuring transparency and encouraging policy improvement. By mirroring the official parliament, the Shadow Parliament enhances political dialogue and prepares its members for potential future governance.
Power Dynamics: Governance vs Oversight
The ruling party holds executive power, directing governance through policy implementation and legislative control, shaping national agendas and public administration. The shadow parliament functions as an essential oversight body, scrutinizing government actions, proposing alternative policies, and holding the ruling party accountable. Power dynamics center on balancing decisive governance with effective checks and balances to maintain democratic integrity.
Policy Development: Initiatives and Alternatives
The ruling party drives policy development by formulating and implementing government initiatives that align with their legislative agenda and public commitments, ensuring effective governance and socio-economic progress. The shadow parliament, led by opposition parties, scrutinizes these initiatives and proposes alternative policies, enhancing democratic accountability and fostering diverse solutions to national issues. This dynamic interaction between ruling and shadow entities strengthens policy robustness and addresses a broader spectrum of public interests.
Accountability Mechanisms and Transparency
The ruling party exercises executive power while being subject to accountability mechanisms such as parliamentary oversight, committee reviews, and public audits to ensure transparency in governance. The shadow parliament, often composed of opposition members, serves as a critical body that scrutinizes government actions, promoting transparency through questioning, debate, and alternative policy proposals. Both entities contribute to a system of checks and balances, enhancing democratic accountability and fostering open access to information for citizens.
Impact on Democratic Processes
The ruling party holds legislative authority, shaping policies and laws that directly influence democratic governance, while the shadow parliament provides critical oversight and alternative policies, ensuring accountability and transparency. This dynamic fosters a balance of power, preventing authoritarianism and promoting diverse political representation within democratic processes. Effective interaction between the ruling party and shadow parliament strengthens public trust and enhances the responsiveness of democratic institutions.
Case Studies: Global Examples and Lessons
Examining case studies from the United Kingdom and India reveals how ruling parties maintain legislative control while shadow parliaments challenge policies and offer alternative governance visions. In the UK, the Shadow Cabinet systematically scrutinizes government decisions, enhancing democratic accountability through structured opposition. India's vibrant parliamentary democracy showcases a dynamic interplay where shadow parties influence policy debates, demonstrating the importance of an active opposition in policy refinement and political stability.
Future Trends in Political Opposition and Governance
The ruling party maintains executive power and policy implementation, while the shadow parliament functions as a critical opposition body scrutinizing government actions and proposing alternatives. Future trends indicate increased digital engagement and data-driven strategies by shadow parliaments to enhance transparency and accountability in governance. Emerging technologies and social media platforms will empower opposition parties to mobilize support and influence public discourse more effectively.
Ruling party Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com