Whips are versatile tools historically used for animal training, sport, and performance arts, designed to create a sharp cracking sound through rapid motion. Understanding the different types of whips, such as bullwhips, stockwhips, and riding crops, can enhance your appreciation of their practical and cultural significance. Explore the rest of the article to discover the craftsmanship, uses, and safety tips for whips.
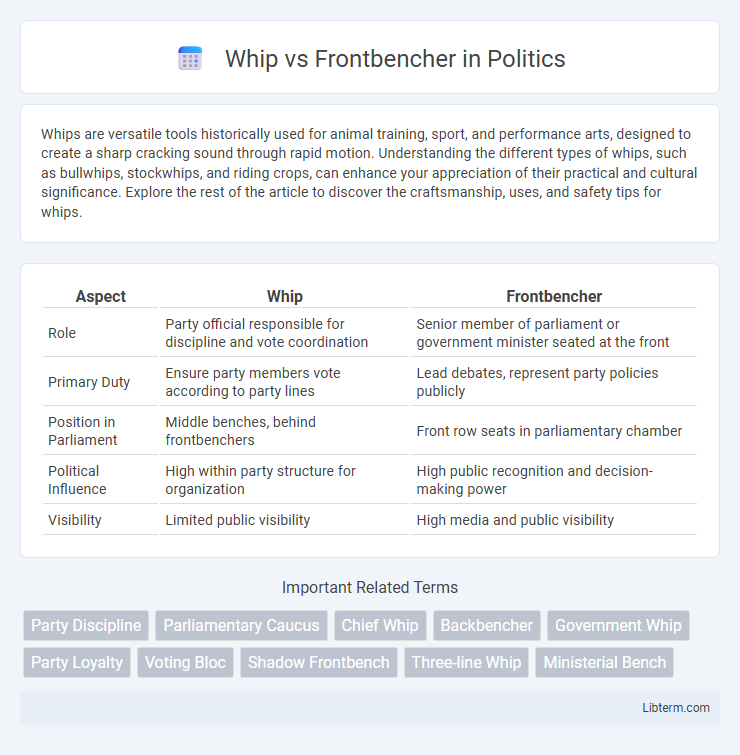
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Whip | Frontbencher |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Party official responsible for discipline and vote coordination | Senior member of parliament or government minister seated at the front |
| Primary Duty | Ensure party members vote according to party lines | Lead debates, represent party policies publicly |
| Position in Parliament | Middle benches, behind frontbenchers | Front row seats in parliamentary chamber |
| Political Influence | High within party structure for organization | High public recognition and decision-making power |
| Visibility | Limited public visibility | High media and public visibility |
Introduction to Whips and Frontbenchers
Whips and frontbenchers play crucial roles in parliamentary systems, with whips responsible for party discipline and ensuring member attendance during key votes, while frontbenchers are senior party members who hold official positions such as ministers or shadow ministers. Whips manage communication between party leadership and legislators, coordinating strategies to maintain voting cohesion. Frontbenchers represent their party's policy positions and lead debates, influencing legislative priorities and governance.
Defining the Whip: Role and Responsibilities
The Whip plays a crucial role in maintaining party discipline by ensuring members attend and vote according to party lines during legislative sessions. Responsibilities include managing communication between party leadership and members, organizing attendance for key votes, and persuading or enforcing voting behavior to secure legislative success. This role contrasts with Frontbenchers, who are primarily focused on policy leadership and representing the party in parliamentary debates and committees.
Who are Frontbenchers?
Frontbenchers are senior members of a parliamentary party who hold key positions either in the government or opposition, typically sitting on the front benches in the legislative chamber. They include ministers, shadow ministers, and party spokespersons responsible for specific policy areas, playing a central role in shaping and communicating party policies. Frontbenchers work closely with whips, who manage party discipline and ensure members vote according to party lines.
Key Differences Between Whips and Frontbenchers
Whips are party officials responsible for discipline and ensuring party members vote according to party lines, whereas frontbenchers are senior politicians who hold ministerial or shadow ministerial positions and actively participate in policy-making. Whips manage party organization and communication within the legislature, while frontbenchers lead debates and represent their party's stance on major issues. The key difference lies in whips focusing on party cohesion and voting strategy, whereas frontbenchers focus on governance and political leadership.
Historical Evolution of Whips and Frontbenchers
The historical evolution of whips and frontbenchers reflects their distinct roles in parliamentary systems, with whips originating in the British Parliament during the 18th century as enforcers of party discipline, ensuring MPs' attendance and voting alignment. Frontbenchers, historically referred to as leading government or opposition ministers, have evolved from the tradition of seating ministers and shadow cabinet members on the front rows, symbolizing their executive and strategic responsibilities. Over time, the functions of whips and frontbenchers have become more specialized, with whips managing party cohesion while frontbenchers focus on policy-making and legislative leadership.
The Importance of Party Discipline
Whips play a critical role in enforcing party discipline by ensuring members attend voting sessions and adhere to party lines, maintaining cohesion in parliamentary strategies. Frontbenchers, often senior party members or ministers, rely on this discipline to project a unified stance on policies and legislation. Effective party discipline, orchestrated by whips and supported by frontbenchers, is essential for stable governance and the successful passage of government agendas.
Powers and Limitations of Whips
Whips possess significant powers including enforcing party discipline, organizing votes, and communicating party strategies to ensure legislative cohesion, yet their influence is often limited by members' individual autonomy and potential backlash from strict enforcement. Whips can summon members to attend crucial debates and vote according to party lines, but their authority does not extend to overriding personal conscience or dissent within parliamentary procedures. While frontbenchers typically enjoy broader policymaking influence as party leaders or ministers, whips primarily operate as enforcers of party order, balancing persuasion with penalties to maintain majority control.
Frontbenchers in Policy-Making
Frontbenchers hold key positions in government or opposition parties, directly influencing policy-making through the formulation and advocacy of legislative agendas. Their roles in ministries or shadow ministries empower them to shape national priorities, draft legislation, and oversee the implementation of government programs. Unlike whips, whose primary function is party discipline and vote management, frontbenchers contribute strategically to the development and execution of public policy.
Famous Whips and Frontbenchers in History
The role of Whips in parliamentary systems is crucial for maintaining party discipline, with famous figures like Thomas Riley and Cornelia M. Hanisch known for their strategic influence. Frontbenchers, often senior politicians who hold significant ministerial or shadow positions, include renowned leaders such as Winston Churchill and Margaret Thatcher, who shaped major policy decisions. Both Whips and Frontbenchers play pivotal roles in legislative success and party cohesion throughout political history.
Conclusion: Whip vs Frontbencher in Modern Politics
Whips play a crucial role in maintaining party discipline and ensuring legislative cohesion, while frontbenchers act as prominent policymakers and public representatives of their parties. The dynamic interaction between whips and frontbenchers shapes parliamentary strategy and influences government stability. Effective collaboration between these roles is essential for the successful functioning of modern democratic institutions.
Whip Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com