General elections determine the representatives who shape the future of a country, impacting policies and governance at every level. Voter turnout and informed choices play critical roles in ensuring a fair and democratic process that reflects the will of the people. Explore the rest of the article to understand how general elections influence your community and why your participation matters.
Table of Comparison
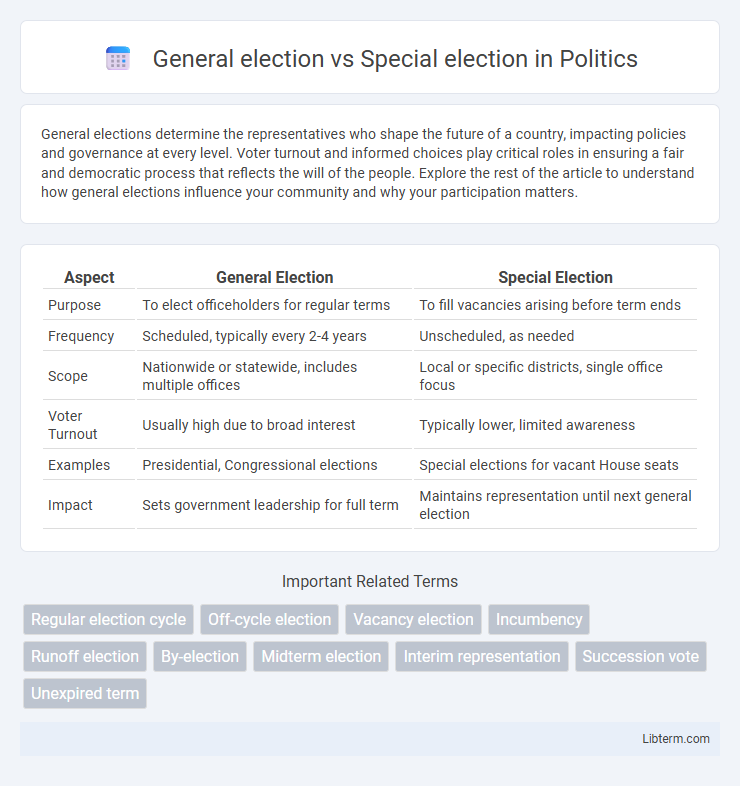
| Aspect | General Election | Special Election |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To elect officeholders for regular terms | To fill vacancies arising before term ends |
| Frequency | Scheduled, typically every 2-4 years | Unscheduled, as needed |
| Scope | Nationwide or statewide, includes multiple offices | Local or specific districts, single office focus |
| Voter Turnout | Usually high due to broad interest | Typically lower, limited awareness |
| Examples | Presidential, Congressional elections | Special elections for vacant House seats |
| Impact | Sets government leadership for full term | Maintains representation until next general election |
Introduction to General and Special Elections
General elections determine public officials at various government levels, typically held on a fixed schedule, such as the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November in the United States. Special elections occur outside the regular election cycle to fill vacancies or decide specific issues, often prompted by resignations, deaths, or recalls. Both election types play crucial roles in democratic governance by enabling voters to select representatives and address immediate political needs.
Definition of General Election
A general election is a regularly scheduled election where voters choose candidates for public offices, including national, state, and local positions, typically occurring on a fixed date set by law. It determines the political leadership for an entire government term and involves a broad electorate voting across multiple districts or constituencies. This contrasts with a special election, which is held to fill vacancies or address specific issues outside the usual election cycle.
Definition of Special Election
A special election is a type of election held to fill a political office that has become vacant before the incumbent's term has ended, often due to resignation, death, or removal from office. Unlike general elections, which occur at regularly scheduled intervals for all offices, special elections are organized as needed to address specific vacancies or issues. This process ensures continuous representation and the timely filling of essential government roles.
Key Differences between General and Special Elections
General elections occur on a fixed schedule, typically every two or four years, determining public officials for regular terms across various government levels. Special elections are held to fill vacancies caused by resignation, death, or removal of an officeholder before the term expires, often with a condensed timeline and limited candidate pool. Voter turnout tends to be higher in general elections due to broader awareness, while special elections focus on specific, localized contests with potentially lower participation.
Purposes of General Elections
General elections serve the purpose of selecting public officials for regular government terms, determining leadership across executive, legislative, and sometimes local offices. These elections establish the political direction for a defined period and reflect the electorate's broad policy preferences. Unlike special elections, which fill unexpected vacancies or specific issues, general elections provide a comprehensive mandate that influences governance and public policy implementation.
Purposes of Special Elections
Special elections serve to fill vacancies in office that occur between general elections, ensuring continuous representation in government. They are called for specific purposes such as addressing urgent legal issues, ratifying local ballot measures, or resolving recall efforts, which general elections cannot immediately accommodate. Unlike general elections that follow a fixed schedule, special elections provide a timely and targeted mechanism to maintain electoral accountability and operational governance.
Voting Process Comparison
General elections feature a standardized voting process where all eligible voters participate to elect officials for regular terms, often involving multiple races and ballot measures. Special elections have a more targeted voting process, focusing on specific offices or issues with a shorter campaign period and typically lower voter turnout. Both processes use similar methods such as paper ballots, electronic voting machines, or absentee ballots but differ mainly in scale and frequency.
Impact on Voter Turnout
General elections typically see higher voter turnout due to widespread awareness and participation in deciding major offices such as the presidency or Congress. Special elections, often held to fill unexpected vacancies or on specific issues, tend to have lower voter engagement because of limited media coverage and voter interest. The difference in turnout significantly impacts electoral outcomes, with general elections reflecting broader public opinion compared to the more localized and sometimes disproportionate voter influence in special elections.
Legal Framework and Scheduling
General elections operate under established legal frameworks defined by national constitutions or electoral laws, typically scheduled at fixed intervals, such as every four or five years. Special elections arise from specific legal provisions triggered by unforeseen vacancies or extraordinary circumstances and are scheduled irregularly to fill positions before the next general election cycle. Election commissions or relevant authorities enforce strict timelines and procedural rules to ensure compliance and legitimacy for both election types.
Importance of Understanding Election Types
Understanding the distinction between general elections, which determine leadership for scheduled terms, and special elections, held to fill unexpected vacancies, is crucial for informed voter participation. This knowledge enhances civic engagement by clarifying the timing, purpose, and impact of each election type on local and national governance. Recognizing these differences improves election preparedness and ensures voters exercise their rights effectively across diverse electoral scenarios.
General election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com