Unipartisan approaches focus on the support or involvement of a single political party, which can streamline decision-making and policy implementation. This method often leads to quicker legislative outcomes but may lack diverse perspectives. Discover how unipartisan strategies impact governance and what they mean for your political understanding in the full article.
Table of Comparison
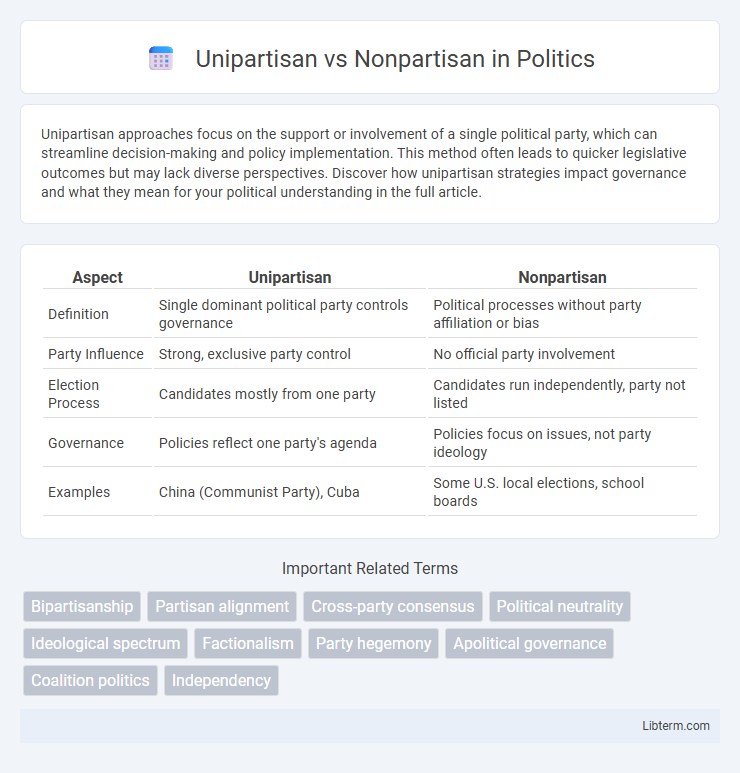
| Aspect | Unipartisan | Nonpartisan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single dominant political party controls governance | Political processes without party affiliation or bias |
| Party Influence | Strong, exclusive party control | No official party involvement |
| Election Process | Candidates mostly from one party | Candidates run independently, party not listed |
| Governance | Policies reflect one party's agenda | Policies focus on issues, not party ideology |
| Examples | China (Communist Party), Cuba | Some U.S. local elections, school boards |
Understanding Unipartisan and Nonpartisan Concepts
Unipartisan refers to actions or policies supported by a single political party, reflecting a unified stance within that group, often seen in legislative processes where only one party drives decisions. Nonpartisan denotes a lack of affiliation with any political party, emphasizing impartiality or neutrality, commonly applied to elections, organizations, or discussions aimed at minimizing party influence. Understanding these concepts clarifies the distinction between party-driven agendas (unipartisan) and independent, unbiased approaches (nonpartisan) in political and social contexts.
Historical Roots of Unipartisanship
Unipartisanship traces its historical roots to political systems dominated by a single party, often emerging in post-colonial or authoritarian states where opposition is limited or suppressed. Unlike nonpartisanship, which avoids formal party affiliations to maintain neutrality, unipartisanship reflects a structured political alignment centered around a dominant party's ideology and governance. This approach historically facilitated political stability in certain regimes but frequently limited pluralism and electoral competitiveness.
The Rise of Nonpartisan Governance
Nonpartisan governance has gained prominence as it emphasizes decision-making based on community interests rather than party affiliations. This approach fosters collaboration among elected officials by minimizing partisan conflicts, resulting in more pragmatic and inclusive policies. The rise of nonpartisan systems reflects growing public demand for transparency and accountability in local government structures.
Key Differences Between Unipartisan and Nonpartisan Systems
Unipartisan systems feature a single political party that dominates governance, limiting electoral competition and often restricting political pluralism. Nonpartisan systems remove party affiliations from elections, emphasizing candidate qualifications and individual merit over party loyalty, which can foster more diverse representation. The key difference lies in the presence or absence of party influence, with unipartisan systems maintaining strict party control and nonpartisan systems promoting decision-making free from formal party alignment.
Political Implications of Unipartisan Approaches
Unipartisan approaches concentrate power within a single political party, often marginalizing opposition voices and reducing policy debate diversity. This consolidation can lead to rapid legislative action but risks fostering polarization and undermining democratic checks and balances. The political implications include decreased accountability and potential erosion of public trust in governance structures.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Nonpartisan Structures
Nonpartisan structures promote unbiased decision-making by removing party affiliations, which can enhance cooperation and focus on community needs rather than political agendas. However, the absence of party labels may lead to lower voter engagement and difficulty in identifying candidates' policy positions, potentially reducing accountability. Nonpartisan systems often require voters to be more informed, placing a greater emphasis on candidate qualifications and local issues instead of party loyalty.
Impact on Voter Representation and Democracy
Unipartisan systems concentrate political power within a single party, often limiting voter choice and reducing diverse representation, which can weaken democratic accountability. Nonpartisan frameworks eliminate party labels, encouraging candidates to focus on local issues and individual qualifications, potentially enhancing voter engagement and more accurately reflecting community interests. The contrast between these systems significantly influences voter representation, with nonpartisan models fostering inclusivity and unipartisan models risking political homogeneity.
Case Studies: Unipartisan vs Nonpartisan in Practice
Case studies of unipartisan versus nonpartisan systems highlight significant differences in legislative dynamics and policy outcomes. Unipartisan systems, often seen in dominant-party states like Singapore, enable streamlined decision-making with minimal opposition, resulting in rapid policy implementation but potential risks of limited debate and reduced accountability. Nonpartisan models, exemplified by some municipal governments in the United States, foster collaboration across diverse groups, enhancing consensus-building and reducing party polarization, yet sometimes facing challenges in achieving swift legislative action.
Criticisms and Challenges Facing Both Models
Unipartisan systems often face criticism for limiting political diversity and marginalizing minority voices, leading to reduced policy innovation and democratic representation. Nonpartisan models encounter challenges such as voter confusion due to lack of clear party cues, which can decrease electoral engagement and accountability. Both frameworks struggle with fostering transparent policymaking and ensuring balanced power dynamics in increasingly complex political environments.
Future Trends in Political System Evolution
Unipartisan political models, characterized by dominant single-party control, may face challenges in adapting to increasing demands for diversity and representation, potentially leading to calls for hybrid governance structures. Nonpartisan systems, which emphasize candidate qualifications over party affiliation, are projected to gain traction in local governance and independent commissions to reduce polarization and enhance decision-making transparency. Future political evolution is likely to see a blend of unipartisan efficiency and nonpartisan inclusivity as technology enables more direct citizen engagement and data-driven policy formation.
Unipartisan Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com