A sunset clause is a provision in a contract or legislation that sets an expiration date for certain terms or regulations unless renewed or extended. This mechanism ensures that laws or agreements are reviewed and reconsidered periodically, preventing outdated or unnecessary provisions from continuing indefinitely. Discover how understanding sunset clauses can protect your interests and why they matter by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
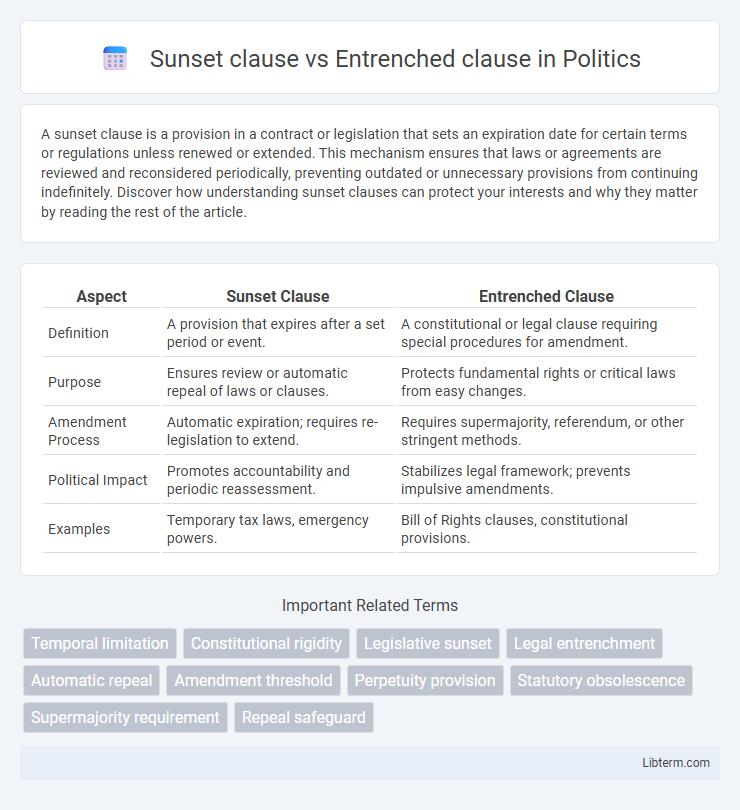
| Aspect | Sunset Clause | Entrenched Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A provision that expires after a set period or event. | A constitutional or legal clause requiring special procedures for amendment. |
| Purpose | Ensures review or automatic repeal of laws or clauses. | Protects fundamental rights or critical laws from easy changes. |
| Amendment Process | Automatic expiration; requires re-legislation to extend. | Requires supermajority, referendum, or other stringent methods. |
| Political Impact | Promotes accountability and periodic reassessment. | Stabilizes legal framework; prevents impulsive amendments. |
| Examples | Temporary tax laws, emergency powers. | Bill of Rights clauses, constitutional provisions. |
Introduction to Legal Clauses
A Sunset clause specifies a predetermined expiration date for a law or contract, ensuring automatic termination unless renewed, promoting temporal limits on legal provisions. An Entrenched clause, by contrast, protects certain constitutional or contractual provisions from amendment or repeal without a supermajority or special procedure, securing their permanence. Both clauses serve crucial roles in legal frameworks by balancing flexibility and stability within legislative or contractual systems.
Defining Sunset Clause
A Sunset Clause is a legal provision that sets an automatic expiration date for a law, policy, or regulation unless it is explicitly renewed or extended by legislative action. This mechanism ensures periodic review and prevents outdated or unnecessary laws from remaining indefinitely in effect. In contrast, an Entrenched Clause is designed to make certain laws or constitutional provisions difficult to amend or repeal, providing long-term stability and protection against frequent changes.
Defining Entrenched Clause
An entrenched clause is a specific legal provision designed to protect certain parts of a contract or constitution from amendment or repeal without meeting stringent requirements, often involving supermajority approval or referendums. In contrast, a sunset clause automatically terminates a law or policy after a predetermined period unless officially renewed, ensuring temporal limitations. Entrenched clauses provide stability by safeguarding foundational rules, while sunset clauses ensure adaptability by introducing automatic expiration.
Key Differences Between Sunset and Entrenched Clauses
Sunset clauses automatically terminate a law or contract after a specified period unless renewed, ensuring periodic review and preventing permanence, whereas entrenched clauses are designed to be difficult or impossible to amend, providing stability and protection against changes. Sunset clauses promote legislative flexibility and accountability by requiring explicit reauthorization, while entrenched clauses safeguard fundamental provisions, often needing supermajorities or special procedures for modification. The key difference lies in their purpose: sunset clauses encourage expiration and reassessment, whereas entrenched clauses secure longevity and resistance to alteration.
Legal Implications of Sunset Clauses
Sunset clauses impose a predetermined expiration date on laws or regulations, ensuring periodic legislative review and preventing outdated or ineffective statutes. These clauses limit long-term legal uncertainty by mandating reassessment, which can impact the stability and predictability of legal frameworks. In contrast, entrenched clauses provide rigidity by requiring special procedures for amendments, emphasizing constitutional permanence over temporary legal measures.
Legal Implications of Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses have significant legal implications as they create provisions within a constitution or contract that require a more stringent process for amendment, often needing supermajorities or referendums, thereby ensuring stability and protection against arbitrary changes. These clauses can limit legislative flexibility and must be carefully interpreted by courts to balance constitutional rigidity with democratic adaptability. In contrast, sunset clauses impose automatic expiration of certain provisions after a set period, affecting temporary legal authority rather than permanent governance structures.
Practical Examples of Sunset Clauses
Sunset clauses specify that certain laws or regulations will automatically expire after a predetermined period unless renewed, such as the USA PATRIOT Act provisions that required periodic reauthorization by Congress. Entrenched clauses, by contrast, are constitutional provisions designed to be resistant to amendment or repeal, often requiring supermajority votes or referenda, like the protection of fundamental rights in various constitutions. Practical examples of sunset clauses include temporary tax cuts, emergency public health measures, and trial periods for new legislation, ensuring periodic legislative review and preventing indefinite extension without scrutiny.
Practical Examples of Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses protect specific provisions within legal documents, such as a company's articles of association, preventing amendments without a supermajority vote, often seen in takeover defenses or constitutional charters of organizations. For instance, a company may include an entrenched clause requiring a 75% shareholder approval for altering dividend policies or board composition, ensuring stability and minority protection. Practical examples extend to constitutional law, where entrenched clauses safeguard fundamental rights or procedural rules, as observed in the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which requires substantial legislative consensus to amend.
Sunset vs Entrenched Clause: Which is Appropriate?
A sunset clause sets a predefined expiration date for a law or regulation, ensuring automatic repeal unless renewed, which promotes legislative review and adaptability. An entrenched clause, by contrast, safeguards certain constitutional provisions from amendment without stringent procedures, providing stability and protection against transient political changes. Selecting between a sunset clause and an entrenched clause depends on balancing flexibility for legal evolution with the need for constitutional permanence in governance.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Sunset clauses provide automatic expiration dates for laws or provisions, ensuring periodic legislative review and adaptability, while entrenched clauses require supermajority or special procedures for amendment, protecting fundamental rules from easy changes. Best practices recommend using sunset clauses for regulatory measures prone to obsolescence, allowing flexibility, whereas entrenched clauses should safeguard constitutional or foundational elements, promoting legal stability. Balancing both clauses enhances governance by combining necessary adaptability with protection against arbitrary alterations.
Sunset clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com