A standing committee is a permanent panel established within a legislative body to oversee specific areas such as finance, health, or education. These committees play a crucial role in shaping policy by reviewing bills, conducting hearings, and providing expert recommendations. Explore the full article to understand how standing committees influence governance and impact your community.
Table of Comparison
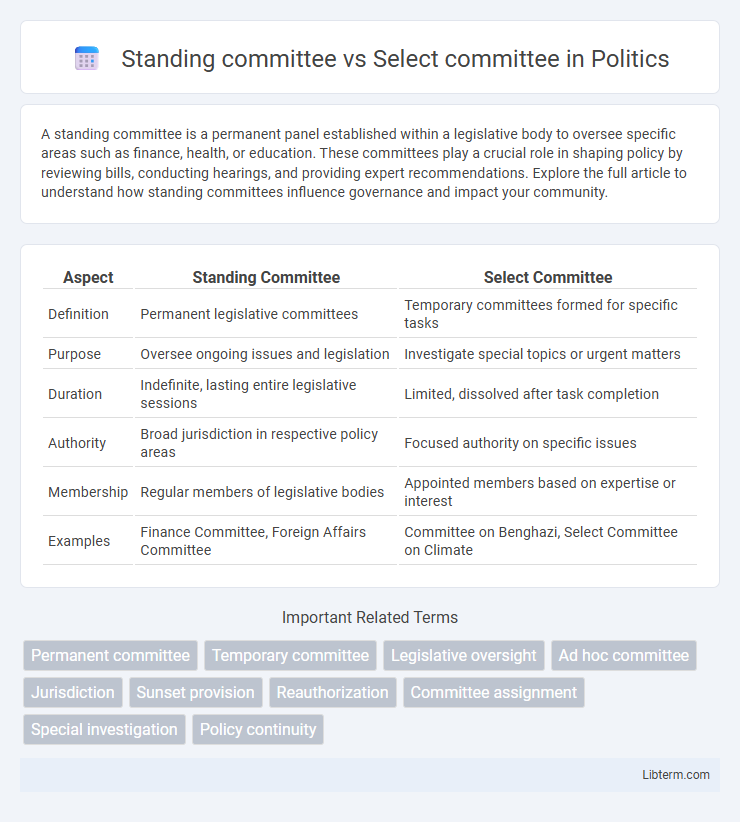
| Aspect | Standing Committee | Select Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent legislative committees | Temporary committees formed for specific tasks |
| Purpose | Oversee ongoing issues and legislation | Investigate special topics or urgent matters |
| Duration | Indefinite, lasting entire legislative sessions | Limited, dissolved after task completion |
| Authority | Broad jurisdiction in respective policy areas | Focused authority on specific issues |
| Membership | Regular members of legislative bodies | Appointed members based on expertise or interest |
| Examples | Finance Committee, Foreign Affairs Committee | Committee on Benghazi, Select Committee on Climate |
Introduction to Legislative Committees
Standing committees are permanent panels established within legislative bodies to oversee specific areas such as finance, defense, or education, allowing continuous review and development of legislation. Select committees are temporary groups formed to address particular issues or investigations, disbanding after completing their assigned tasks. Both types of committees play crucial roles in managing legislative workload, conducting detailed analysis, and shaping policy outcomes.
Definition of Standing Committee
A Standing Committee is a permanent legislative panel established to oversee specific areas such as finance, health, or education, ensuring continuous scrutiny and expertise development within its jurisdiction. Unlike Select Committees, which are temporary and created to address particular issues or investigations, Standing Committees hold ongoing authority and play a crucial role in the legislative process by reviewing bills, conducting hearings, and monitoring government operations. Their enduring nature allows for consistent policy oversight and detailed evaluation of long-term legislative matters.
Definition of Select Committee
A Select Committee is a temporary legislative body established to investigate specific issues or conduct particular tasks not covered by Standing Committees, which are permanent. Unlike Standing Committees, Select Committees often have a limited duration and focus on detailed examination of specialized topics or emerging concerns. Their role is to provide targeted analysis, gather evidence, and make recommendations on matters requiring urgent or specialized attention.
Key Differences Between Standing and Select Committees
Standing committees are permanent panels established by legislative rules, responsible for handling a broad range of ongoing governmental functions and legislation within specific policy areas, such as finance or education. Select committees are temporary and created for a specific purpose or investigation, often disbanded after completing their assigned tasks; they address issues not covered by standing committees or require specialized focus. Key differences include their duration, with standing committees being permanent and select committees temporary, and their scope, where standing committees have continuous jurisdiction while select committees have limited, specific objectives.
Functions and Responsibilities
Standing committees are permanent legislative bodies responsible for reviewing bills, overseeing government agencies, and conducting ongoing policy evaluation within their specific subject areas. Select committees are temporary and formed to investigate or address particular issues, often producing specialized reports or recommendations for legislative action. While standing committees maintain continuous jurisdiction, select committees focus on targeted inquiries and usually dissolve after completing their assigned tasks.
Duration and Permanence
Standing committees are permanent legislative panels established to handle ongoing governmental functions, maintaining continuous jurisdiction over specific policy areas. Select committees are temporary, created to address particular issues or investigations and dissolve once their assigned tasks are completed. The duration of standing committees spans multiple sessions of a legislature, whereas select committees have limited lifespans tied explicitly to their investigative or special assignments.
Examples of Standing Committees
Standing committees such as the House Ways and Means Committee and the Senate Judiciary Committee play a continuous role in legislating and overseeing government functions, contrasting with select committees formed for specific investigations or temporary purposes. The House Ways and Means Committee handles taxation and revenue-related issues, making it one of the most powerful standing committees. The Senate Judiciary Committee oversees judicial appointments and federal law enforcement matters, exemplifying the ongoing oversight responsibilities of standing committees.
Examples of Select Committees
Select committees in the U.S. Congress, such as the House Select Committee on the January 6 Attack, are established for specific purposes and investigations that do not fall within the jurisdiction of standing committees. Examples include the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, which oversees national intelligence activities, and the House Select Committee on Energy Independence and Global Warming, created to address climate change issues. These committees are typically temporary, unlike standing committees that have permanent legislative responsibilities.
Importance in Legislative Process
Standing committees play a crucial role in the legislative process by handling bills related to specific policy areas, ensuring continuity and expertise in reviewing legislation. Select committees are important for addressing specialized issues or investigations that fall outside the purview of standing committees, providing detailed scrutiny and recommendations. Both types of committees enhance legislative efficiency and accountability by facilitating thorough examination and expert input on proposed laws.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Committee Structure
Standing committees provide ongoing oversight and expertise in permanent legislative areas, ensuring stability and deep knowledge, while select committees offer flexibility for addressing specific, temporary issues with focused investigation. Selecting the appropriate committee depends on the legislative goals, with standing committees suited for continuous policy management and select committees ideal for targeted inquiries or emergent topics. Optimal committee structure balances the need for sustained oversight and specialized investigation to enhance legislative effectiveness.
Standing committee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com