Royal assent is the formal approval by a monarch required to make a bill passed by parliament into law. This constitutional step signifies the final stage in the legislative process and ensures the bill's legitimacy and authority. Discover how royal assent functions within your government and its impact on the legislative system in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
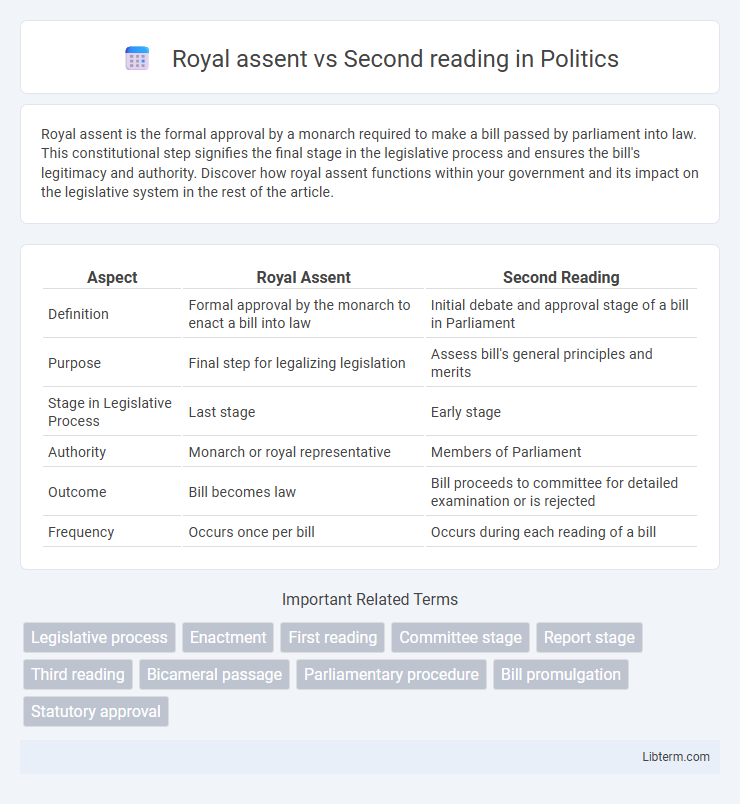
| Aspect | Royal Assent | Second Reading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal approval by the monarch to enact a bill into law | Initial debate and approval stage of a bill in Parliament |
| Purpose | Final step for legalizing legislation | Assess bill's general principles and merits |
| Stage in Legislative Process | Last stage | Early stage |
| Authority | Monarch or royal representative | Members of Parliament |
| Outcome | Bill becomes law | Bill proceeds to committee for detailed examination or is rejected |
| Frequency | Occurs once per bill | Occurs during each reading of a bill |
Understanding Royal Assent
Royal Assent is the formal approval by the monarch or their representative that enacts a bill into law, marking the final stage in the legislative process. Unlike the Second Reading, which involves parliamentary debate on the general principles of the bill, Royal Assent signifies legal validation and the completion of a bill's journey through Parliament. Understanding Royal Assent is crucial for comprehending how proposed legislation officially becomes statute in constitutional monarchies like the United Kingdom.
The Role of the Second Reading
The Second Reading serves as the initial opportunity for Parliament to debate the general principles and purpose of a bill, ensuring thorough scrutiny of its content before it advances. Following successful debate and approval during the Second Reading, the bill proceeds to detailed examination in subsequent stages, unlike Royal Assent, which is the final formal approval by the monarch that enacts the bill into law. The Second Reading plays a crucial legislative role by shaping the bill's trajectory and securing parliamentary consensus before the formal enactment process begins.
Legislative Process Overview
The legislative process begins with the Second Reading, where the general principles and purpose of a bill are debated and voted upon by the legislature, determining whether it progresses to detailed examination. Royal Assent marks the final stage in the legislative process, where the monarch or their representative formally approves the bill, transforming it into law. Understanding the distinct roles of the Second Reading and Royal Assent is crucial for comprehending how legislation moves from proposal to enforceable statute.
Key Differences: Royal Assent vs Second Reading
Royal Assent is the formal approval by a monarch or their representative, marking the final step for a bill to become law. The Second Reading occurs earlier in the legislative process and involves debating the general principles and purpose of the bill. Unlike Royal Assent, which is a procedural formality, the Second Reading is a critical stage for parliamentary scrutiny and discussion.
Historical Background of Both Stages
Royal assent, originating from the medieval period, represents the monarch's formal approval required to enact legislation passed by Parliament, reflecting the historical power balance between the Crown and the legislature. The second reading, rooted in the traditions of the English Parliament since the 14th century, serves as the initial substantive debate on a bill's general principles, marking the transition from proposal to detailed legislative scrutiny. Both stages illustrate the evolution of the UK's constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy, highlighting the gradual shift of legislative authority from the sovereign to elected representatives.
Importance in Parliamentary Procedure
Royal assent is the final step in the legislative process where the monarch formally approves a bill, making it law and ensuring the authority of Parliament is upheld. The second reading provides an essential opportunity for members of Parliament to debate the general principles and purpose of the bill, shaping its direction and legitimacy early in the process. Both stages are critical in parliamentary procedure, with the second reading enabling democratic scrutiny and Royal assent granting legal validity.
Legal Implications of Royal Assent
Royal Assent constitutes the final legal approval by the monarch or their representative, transforming a bill into enforceable law, thereby granting it full legislative authority. Unlike the Second Reading, which involves parliamentary debate on the bill's principles, Royal Assent solidifies the statute's validity within the legal system. This step is crucial as it marks the formal enactment necessary for the bill's provisions to have binding legal effect.
Debate and Discussion at Second Reading
The Second Reading is a pivotal stage in the legislative process where members of parliament engage in detailed debate and discussion on the general principles and purpose of a bill. This stage allows legislators to express support or opposition, propose amendments, and scrutinize the bill's objectives before it advances further. In contrast, Royal Assent is the formal approval by the monarch or their representative, signaling the final step for a bill to become law without further debate.
Timeline from Second Reading to Royal Assent
The timeline from Second Reading to Royal Assent typically spans several weeks to months, depending on the complexity of the bill and parliamentary schedule. After the Second Reading, the bill undergoes committee scrutiny, report stage, and third reading before being sent to the other house for a similar process. Once both houses agree on the bill's final text, it proceeds to the Governor-General or monarch for Royal Assent, officially becoming law.
Comparative Analysis: Impact on Lawmaking
Royal assent represents the final step in the legislative process, where the monarch formally approves a bill, transforming it into law and ensuring legal authority. The second reading occurs earlier, involving parliamentary debate on the general principles, shaping the bill's direction and public agenda influence. Compared to the second reading's role in policymaking and scrutiny, royal assent's impact is procedural, marking the formal completion rather than substantive lawmaking.
Royal assent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com