Pluralism embraces diverse perspectives within societies, enabling coexistence and mutual respect among different cultural, religious, and social groups. This approach fosters democratic engagement, promotes social cohesion, and encourages inclusive dialogue to address complex challenges. Discover how pluralism shapes your community and why it is essential for a harmonious future in the full article.
Table of Comparison
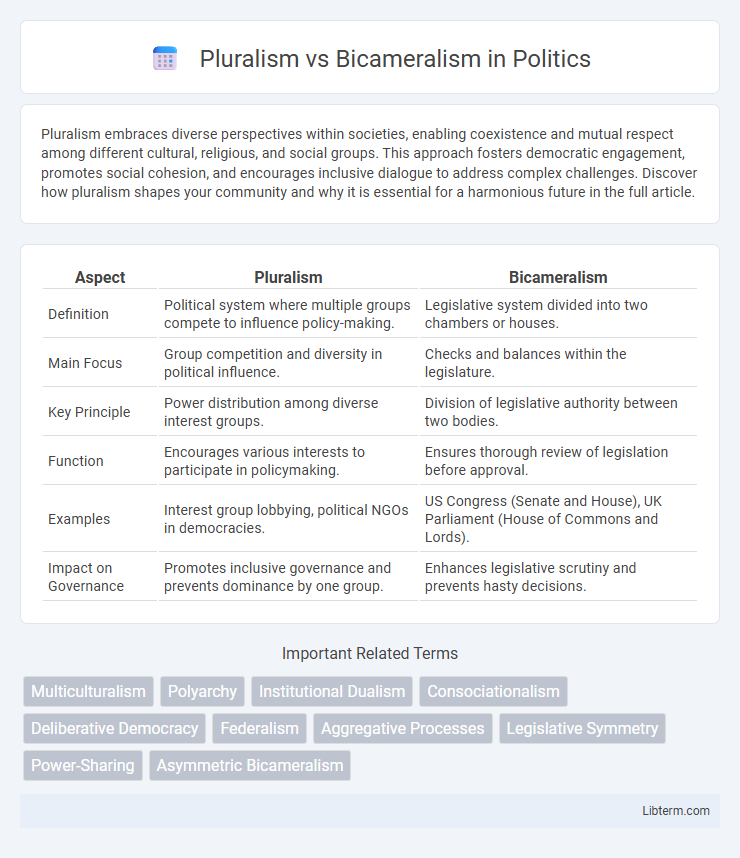
| Aspect | Pluralism | Bicameralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political system where multiple groups compete to influence policy-making. | Legislative system divided into two chambers or houses. |
| Main Focus | Group competition and diversity in political influence. | Checks and balances within the legislature. |
| Key Principle | Power distribution among diverse interest groups. | Division of legislative authority between two bodies. |
| Function | Encourages various interests to participate in policymaking. | Ensures thorough review of legislation before approval. |
| Examples | Interest group lobbying, political NGOs in democracies. | US Congress (Senate and House), UK Parliament (House of Commons and Lords). |
| Impact on Governance | Promotes inclusive governance and prevents dominance by one group. | Enhances legislative scrutiny and prevents hasty decisions. |
Introduction to Pluralism and Bicameralism
Pluralism emphasizes diverse group interests influencing policy-making, reflecting a decentralized power structure where multiple organizations compete for influence. Bicameralism involves a legislative body divided into two separate chambers, typically designed to balance representation and prevent unilateral decisions. Both concepts shape democratic governance, with pluralism highlighting interest group competition and bicameralism focusing on institutional checks within legislatures.
Defining Pluralism in Political Systems
Pluralism in political systems refers to the recognition and active coexistence of diverse interest groups, organizations, and social factions that influence policy-making through negotiation and compromise. It emphasizes the diffusion of power across multiple actors rather than concentration in a single legislative body, contrasting sharply with bicameralism, which relies on two distinct chambers within the legislature to balance authority. Defining pluralism highlights the importance of decentralized power structures that facilitate representation and competition among varied political, social, and economic groups.
Understanding Bicameralism: Structure and Function
Bicameralism refers to a legislative system divided into two separate chambers, typically an upper and a lower house, designed to provide checks and balances within the legislative process. The structure of bicameral legislatures allows for more deliberate lawmaking by requiring approval from both chambers, which often represent different interests or constituencies. This dual-chamber system enhances the depth of debate, improves scrutiny of legislation, and helps prevent hasty or unilateral policy decisions.
Historical Evolution of Pluralism and Bicameralism
Pluralism historically emerged as a response to the concentration of power, emphasizing diverse interest groups' roles in policymaking to balance societal demands. Bicameralism evolved from medieval bicameral legislative practices, designed to provide checks and balances within government by dividing legislative authority between two chambers. Both systems reflect distinct approaches to governance, with pluralism focusing on interest group competition and bicameralism institutionalizing power separation for legislative scrutiny.
Key Differences: Pluralism vs Bicameralism
Pluralism emphasizes the distribution of power among diverse interest groups competing within a political system, ensuring no single group dominates decision-making. Bicameralism refers to a legislative structure with two separate chambers or houses, designed to provide checks and balances within the lawmaking process. The key difference lies in pluralism being a theory of power distribution across societal groups, while bicameralism is a structural feature of government institutions.
Advantages of Pluralistic Governance
Pluralistic governance enhances democratic participation by incorporating diverse interest groups, leading to more balanced policy outcomes. It fosters transparency and accountability as multiple stakeholders engage in decision-making processes. This inclusivity prevents the concentration of power, reducing the risk of authoritarianism and promoting social stability.
Benefits and Challenges of Bicameral Legislatures
Bicameral legislatures provide benefits such as enhanced checks and balances, preventing hasty lawmaking by requiring approval from two chambers, and representing diverse interests through separate bodies often reflecting different constituencies or expertise. Challenges include slower legislative processes, potential deadlocks between chambers, and increased complexity that can hinder efficient governance. While bicameralism promotes thorough debate and accountability, it may reduce responsiveness and increase political gridlock compared to unicameral systems.
Comparative Analysis: Case Studies Worldwide
Pluralism emphasizes multiple groups influencing political decision-making, as seen in the United States, where interest groups compete within a unicameral House of Representatives balanced by a Senate, reflecting diverse societal interests. Bicameralism, exemplified by the United Kingdom, divides legislative authority between two chambers--the House of Commons and the House of Lords--ensuring regional representation and checks on legislative power, which contrasts with pluralism's group-based influence model. Comparative analysis reveals that pluralism fosters broad participation in policy formulation, while bicameralism institutionalizes representation diversity and legislative scrutiny across different political systems.
Impact on Policy-Making and Representation
Pluralism fosters diverse interest group participation, enhancing representation and producing policy outcomes reflecting multiple societal voices. Bicameralism structurally divides legislative power between two chambers, creating checks that can either improve policy deliberation or cause gridlock. The interaction between pluralist influences and bicameral institutional design significantly shapes the balance between inclusive representation and effective policy-making.
Future Trends in Political Organization
Future trends in political organization suggest increased integration of pluralism and bicameralism to balance diverse societal interests and enhance legislative efficiency. Emerging democratic systems emphasize multi-layered representation, leveraging bicameral structures to accommodate pluralistic voices from varied ethnic, regional, and social groups. Technological advancements and global interconnectedness drive reforms toward more inclusive political frameworks that combine pluralist participation with bicameral oversight for stable governance.
Pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com