Framework legislation provides a broad legal structure that guides policy development and implementation across various sectors while allowing flexibility for specific regulations. This type of legislation ensures consistency in governance and supports coordinated efforts to address complex issues efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to understand how framework legislation impacts your industry and legal landscape.
Table of Comparison
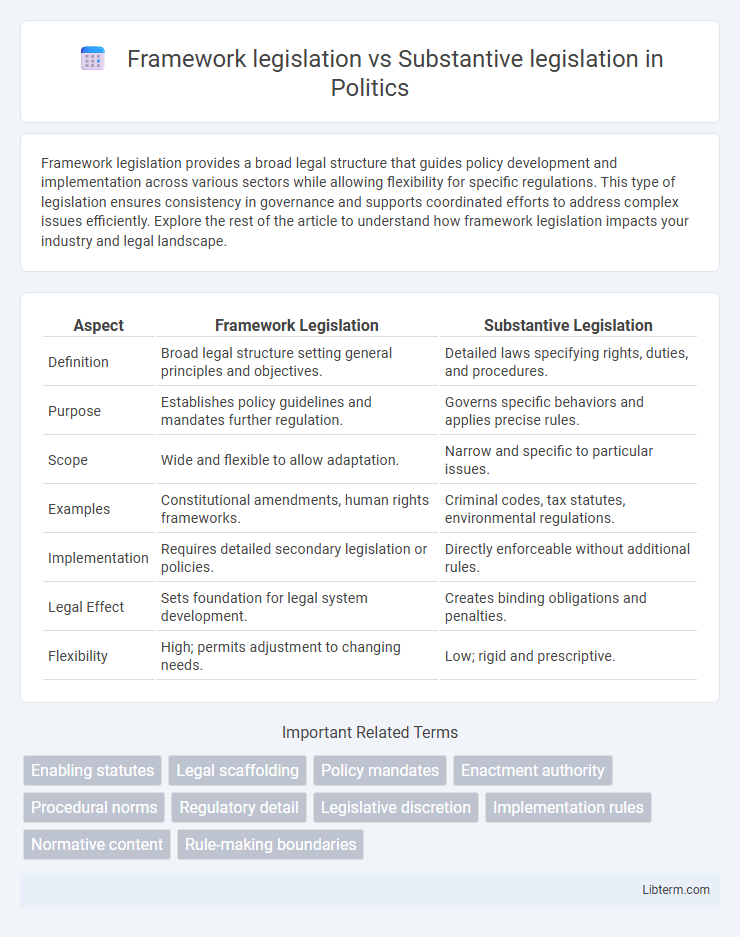
| Aspect | Framework Legislation | Substantive Legislation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad legal structure setting general principles and objectives. | Detailed laws specifying rights, duties, and procedures. |
| Purpose | Establishes policy guidelines and mandates further regulation. | Governs specific behaviors and applies precise rules. |
| Scope | Wide and flexible to allow adaptation. | Narrow and specific to particular issues. |
| Examples | Constitutional amendments, human rights frameworks. | Criminal codes, tax statutes, environmental regulations. |
| Implementation | Requires detailed secondary legislation or policies. | Directly enforceable without additional rules. |
| Legal Effect | Sets foundation for legal system development. | Creates binding obligations and penalties. |
| Flexibility | High; permits adjustment to changing needs. | Low; rigid and prescriptive. |
Definition of Framework Legislation
Framework legislation establishes broad principles and guidelines that set the foundation for more detailed laws and regulations within a specific area. It provides a flexible structure allowing for adaptation and detailed rules to be developed through subordinate legislation or policies. Unlike substantive legislation, which addresses specific rights and obligations, framework legislation outlines general objectives and procedural foundations.
Definition of Substantive Legislation
Substantive legislation defines the rights, duties, and liabilities of individuals and entities, forming the core legal obligations and protections within a jurisdiction. It encompasses laws that regulate behavior and prescribe penalties or remedies, such as criminal codes, contract laws, and property laws. Unlike framework legislation, substantive laws provide specific rules that govern real-world transactions and conduct.
Key Distinctions Between Framework and Substantive Laws
Framework legislation establishes broad principles and guidelines that set the foundation for detailed rules, whereas substantive legislation outlines specific rights, duties, and procedures. Framework laws often delegate authority to agencies for rule-making, providing flexibility in implementation, while substantive laws are concrete and directly enforceable by courts. The key distinction lies in framework laws serving as a structural base, facilitating the development and evolution of more detailed substantive regulations.
Purposes and Objectives of Framework Legislation
Framework legislation establishes broad principles and general guidelines designed to shape and guide future detailed laws, providing consistency and flexibility across legal systems. Its purposes include setting overarching policy goals, ensuring coherence among related laws, and creating a legal environment conducive to balanced governance and adaptation to evolving circumstances. Unlike substantive legislation that dictates specific rights, duties, or penalties, framework legislation aims to facilitate systematic development and coordination of multiple legislative instruments.
Purposes and Objectives of Substantive Legislation
Substantive legislation establishes legal rights, duties, and obligations, defining the core principles and standards that govern conduct within society. Its primary purpose is to create enforceable rules that determine how individuals and entities interact, ensuring justice, protection, and order in areas such as criminal law, contract law, and property law. By contrast, framework legislation provides the procedural structure and guidelines for implementing and administering substantive laws, facilitating regulatory oversight and consistent application.
Examples of Framework Legislation in Practice
Framework legislation establishes broad principles and guidelines that direct subsequent detailed laws, commonly used in environmental protection statutes such as the Clean Air Act in the United States. This type of legislation sets overarching goals and frameworks for policy implementation, allowing flexibility for future regulations, unlike substantive legislation which directly prescribes specific rules. Examples include the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) framework that outlines data privacy principles without detailing every procedural element, enabling member states to adapt implementation accordingly.
Examples of Substantive Legislation in Practice
Substantive legislation directly establishes rights, duties, and legal relationships, such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits discrimination and enforces equal treatment across numerous sectors. Another example includes the Affordable Care Act, which mandates healthcare coverage standards and consumer protections within the health insurance market. These laws create concrete legal obligations and protections, contrasting with framework legislation that primarily outlines procedural or institutional structures.
Advantages of Framework Legislation
Framework legislation offers significant advantages by providing flexible, broad guidelines that facilitate adaptation to evolving policy needs without frequent legal amendments. It enables efficient coordination across various sectors and levels of government, promoting consistent implementation while allowing detailed rules to be tailored through subsidiary legislation. This approach enhances legal clarity and stability, reducing legislative complexity and expediting policy responses to emerging challenges.
Advantages of Substantive Legislation
Substantive legislation offers clear, detailed rules that directly define rights and obligations, reducing ambiguities in legal interpretation. It provides specific guidance for enforcement agencies and courts, ensuring consistent application of the law. This clarity minimizes disputes and promotes legal certainty for individuals and businesses.
Choosing Between Framework and Substantive Legislation
Choosing between framework legislation and substantive legislation depends on the need for flexibility versus specificity in legal regulation. Framework legislation establishes broad principles and guidelines adaptable to future developments, making it ideal for areas requiring ongoing interpretation and adjustment. Substantive legislation provides detailed, precise rules designed to address specific issues directly, suitable for contexts demanding clear, enforceable standards.
Framework legislation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com