Term limits restrict the number of terms an elected official can serve in a particular office, aiming to prevent the concentration of political power and encourage fresh leadership. Advocates argue term limits promote accountability and reduce the potential for corruption, while opponents claim they can lead to a loss of experienced governance. Explore the full article to understand how term limits impact democracy and your representation.
Table of Comparison
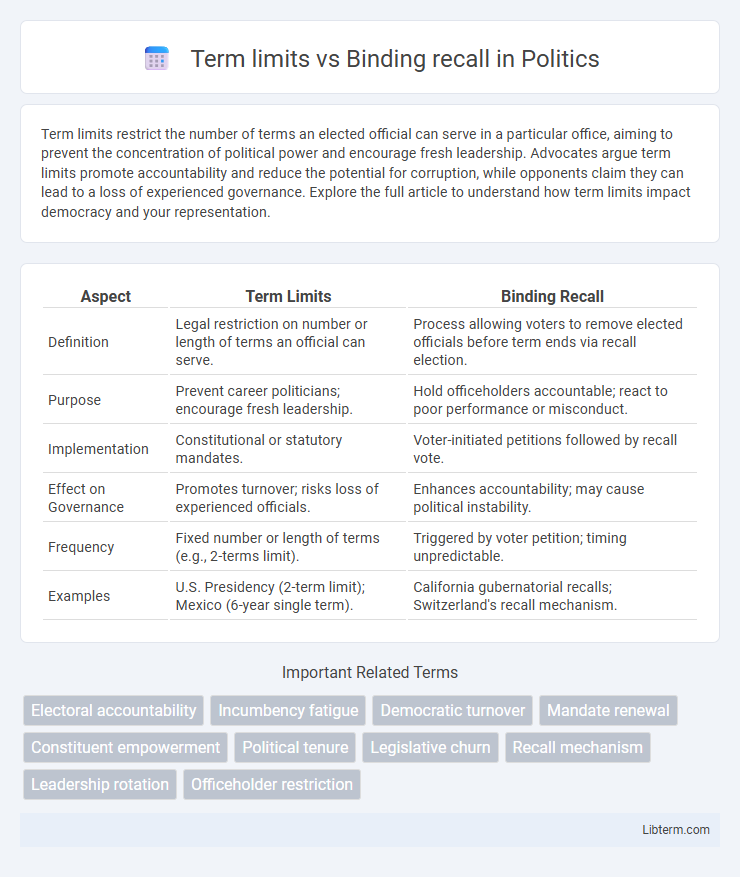
| Aspect | Term Limits | Binding Recall |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal restriction on number or length of terms an official can serve. | Process allowing voters to remove elected officials before term ends via recall election. |
| Purpose | Prevent career politicians; encourage fresh leadership. | Hold officeholders accountable; react to poor performance or misconduct. |
| Implementation | Constitutional or statutory mandates. | Voter-initiated petitions followed by recall vote. |
| Effect on Governance | Promotes turnover; risks loss of experienced officials. | Enhances accountability; may cause political instability. |
| Frequency | Fixed number or length of terms (e.g., 2-terms limit). | Triggered by voter petition; timing unpredictable. |
| Examples | U.S. Presidency (2-term limit); Mexico (6-year single term). | California gubernatorial recalls; Switzerland's recall mechanism. |
Understanding Term Limits: Definition and Purpose
Term limits restrict the number of terms an elected official can serve to promote political turnover and prevent entrenched incumbency, ensuring fresh perspectives in governance. Binding recall allows voters to remove an elected official before the end of their term through a direct vote, serving as a mechanism for accountability between elections. Understanding the definition and purpose of term limits highlights their role in fostering democratic renewal and preventing power consolidation.
Exploring Binding Recall: What It Means
Binding recall enables voters to remove elected officials from office before the end of their term through a direct vote, increasing political accountability and responsiveness. Unlike term limits, which restrict the number of terms an official can serve, binding recall empowers constituents to respond immediately to misconduct or poor performance. This mechanism fosters a dynamic democratic process by allowing active citizen participation in holding public officials accountable.
Historical Context of Term Limits and Recall Mechanisms
Term limits have historically emerged to prevent prolonged concentration of power, notably seen in U.S. presidential and legislative roles since the 18th century, establishing structured political turnover. Binding recall mechanisms, rooted in early 20th-century progressive reforms, empower voters to remove elected officials before term completion, reflecting a push for direct democratic control. Both tools address political accountability but stem from different historical contexts emphasizing preventive succession versus reactive removal.
Pros and Cons of Term Limits in Government
Term limits in government restrict the number of terms an elected official can serve, promoting political diversity and reducing the risk of entrenched incumbency and corruption. They can enhance accountability by ensuring regular turnover and encourage fresh ideas, but also lead to a loss of experienced lawmakers and disrupt long-term policy continuity. Opponents argue term limits weaken voter choice and empower unelected bureaucrats or lobbyists who remain constant.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Binding Recall
Binding recall allows citizens to remove elected officials before the end of their term, increasing government accountability and responsiveness to public dissatisfaction. However, it can lead to political instability, frequent disruptions in governance, and the potential misuse of recall efforts for partisan or personal reasons. Unlike term limits, which provide a fixed tenure, binding recall introduces uncertainty that may hinder long-term policy planning and governance continuity.
Impact on Political Accountability and Representation
Term limits constrain the duration elected officials can serve, fostering political accountability by preventing entrenchment and encouraging regular infusion of fresh perspectives in representation. Binding recall empowers voters to remove officials before their term ends, directly holding politicians accountable for performance and responsiveness to constituents. Both mechanisms enhance political accountability, but recall offers more immediate corrective action while term limits promote long-term renewal in representation.
Effects on Political Stability and Continuity
Term limits impose fixed durations for elected officials, preventing prolonged incumbency and encouraging political renewal, which can enhance stability by reducing power monopolies. Binding recall mechanisms allow voters to remove officials before term ends, increasing accountability but potentially causing abrupt leadership changes and political uncertainty. The interplay between term limits and binding recall shapes governance continuity by balancing stability with responsiveness to public dissatisfaction.
Case Studies: Term Limits and Recall in Action
Case studies of term limits reveal a significant impact on political dynamics, such as in California, where term limits have reshaped legislative experience and policy continuity. Binding recall mechanisms, exemplified by the 2003 California gubernatorial recall of Governor Gray Davis, demonstrate direct voter influence to remove officials before their term ends, affecting political accountability and campaign strategies. Comparative analysis shows term limits often stabilize leadership succession, while binding recalls enable rapid public intervention in governance crises.
Public Opinion and Support for Political Reforms
Public opinion on term limits shows strong support as a measure to curb political entrenchment and promote fresh leadership, with polls indicating over 70% approval among voters seeking greater accountability. Conversely, binding recall mechanisms receive mixed reactions, with approximately 55% favoring the ability to remove elected officials before their term ends, reflecting concerns about potential misuse and political instability. Comparative studies reveal that while term limits enjoy more consistent backing across demographics, recall measures gain traction primarily in regions with heightened distrust in incumbents.
Conclusion: Balancing Term Limits and Binding Recall for Better Governance
Balancing term limits and binding recall mechanisms enhances democratic accountability by preventing entrenched power while allowing voters to remove underperforming officials. Term limits ensure regular leadership renewal, promoting fresh ideas and reducing corruption risks, whereas binding recall empowers citizens to hold representatives directly responsible between elections. Integrating both tools creates a dynamic governance system that fosters responsiveness and stability, aligning political leadership more closely with public interests.
Term limits Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com