The private sector drives innovation and economic growth by fostering competition and entrepreneurship within a market economy. Your engagement with private enterprises can influence job creation, technological advancement, and consumer choice. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the private sector impacts your daily life and the broader economy.
Table of Comparison
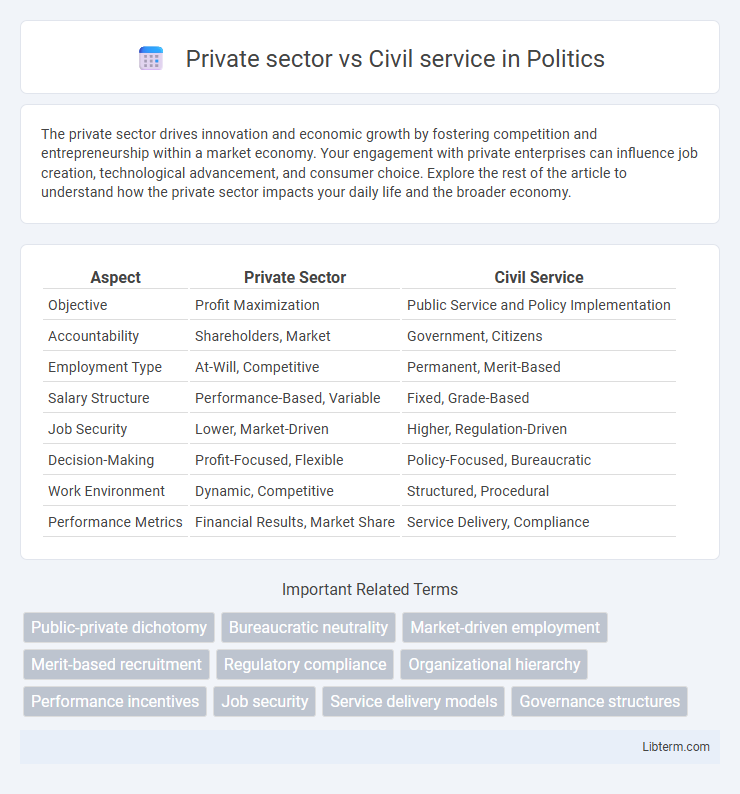
| Aspect | Private Sector | Civil Service |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Profit Maximization | Public Service and Policy Implementation |
| Accountability | Shareholders, Market | Government, Citizens |
| Employment Type | At-Will, Competitive | Permanent, Merit-Based |
| Salary Structure | Performance-Based, Variable | Fixed, Grade-Based |
| Job Security | Lower, Market-Driven | Higher, Regulation-Driven |
| Decision-Making | Profit-Focused, Flexible | Policy-Focused, Bureaucratic |
| Work Environment | Dynamic, Competitive | Structured, Procedural |
| Performance Metrics | Financial Results, Market Share | Service Delivery, Compliance |
Overview of Private Sector and Civil Service
The private sector comprises businesses and corporations driven by profit and innovation, encompassing industries like technology, finance, and manufacturing with a dynamic workforce focused on market competitiveness and customer satisfaction. Civil service involves government-employed professionals dedicated to public administration, policy implementation, and delivering essential public services, emphasizing job stability, regulatory compliance, and serving the common good. Key distinctions include funding sources, operational goals, and accountability frameworks, with the private sector relying on revenue generation and the civil service focusing on public interest and governmental mandates.
Key Differences in Organizational Structure
The private sector features a hierarchical organizational structure driven by profit motives, with flexible management layers aimed at innovation and market competitiveness. In contrast, the civil service operates within a bureaucratic framework characterized by rigid hierarchies and defined roles to ensure policy implementation and public accountability. Private companies prioritize dynamic decision-making processes, while civil service organizations emphasize procedural consistency and adherence to regulations.
Recruitment and Selection Processes
Recruitment and selection processes in the private sector emphasize speed, flexibility, and skill-specific criteria to quickly adapt to market demands and maintain competitive advantage. Civil service recruitment relies on rigorous standardized assessments, merit-based evaluations, and transparent procedures to ensure fairness, accountability, and adherence to legal frameworks. Both sectors utilize technology-driven applicant tracking systems, but civil service processes often involve multi-stage examinations and public service eligibility lists to uphold equal opportunity and transparency.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Private sector salaries often surpass those in civil service due to competitive market-driven wage structures, especially in high-demand industries like technology and finance. Civil service benefits typically include robust pension plans, job security, and comprehensive healthcare packages, which may offset the lower base salary. While private sector jobs may offer performance bonuses and stock options, civil service roles generally provide greater long-term financial stability through guaranteed incremental pay increases and retirement benefits.
Job Security and Stability
Job security in the civil service is generally higher due to government backing, offering employees protection from layoffs during economic downturns. The private sector, while potentially offering higher salaries, often experiences more volatility, with job stability closely tied to company performance and market conditions. Civil service positions benefit from structured career progression and union protections, which contribute to long-term employment stability.
Career Growth and Promotion Opportunities
Career growth in the private sector often features faster promotion opportunities driven by performance metrics and profit incentives, enabling merit-based advancement. The civil service typically offers more structured, time-bound promotion pathways linked to seniority, exams, and standardized evaluations that ensure job security and steady progression. Private sector roles emphasize skill diversification and entrepreneurial initiatives, while civil service careers prioritize stability and incremental hierarchical advancement.
Workplace Culture and Environment
The private sector emphasizes a competitive workplace culture driven by innovation, performance metrics, and profit generation, often featuring flexible work arrangements and dynamic team structures. In contrast, civil service environments prioritize stability, adherence to formal policies, and public accountability, fostering a culture of procedure and consistency. Employee motivation in the private sector is frequently linked to financial incentives, while civil service rewards focus on job security, benefits, and community service impact.
Performance Evaluation and Accountability
Performance evaluation in the private sector typically emphasizes quantitative metrics such as sales targets, profitability, and customer satisfaction to drive business outcomes. In contrast, the civil service prioritizes compliance with regulations, adherence to public policies, and service delivery standards, often measured through formal appraisals and 360-degree feedback. Accountability mechanisms differ, with private companies relying on shareholder oversight and performance-based incentives, while civil servants are held accountable through bureaucratic audits, legislative oversight, and public transparency requirements.
Skills and Experience Requirements
The private sector demands specialized skills such as advanced marketing, financial analysis, and technological proficiency, emphasizing results-driven experience that showcases innovation and profitability. The civil service prioritizes comprehensive understanding of public policies, regulatory compliance, and administrative skills, valuing experience in government operations and community service. Both sectors require strong communication, leadership, and problem-solving abilities, but the private sector favors adaptability to market trends while civil service stresses adherence to legal frameworks and public accountability.
Impact on Society and National Development
The private sector drives economic growth by fostering innovation, creating employment, and generating tax revenue that funds public services, directly influencing national development. Civil service ensures stability and equitable delivery of essential public services, upholding social welfare and regulatory frameworks that protect citizens and maintain public trust. Together, these sectors complement each other by balancing market-driven progress with structured governance, crucial for sustainable societal impact and long-term national advancement.
Private sector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com