Bloc voting refers to a voting system where a group of voters cast their ballots as a unified block, often influencing election outcomes more decisively than individual votes. This method is common in elections with multiple seats available, allowing a cohesive group to maximize their representation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how bloc voting impacts democratic processes and your electoral choices.
Table of Comparison
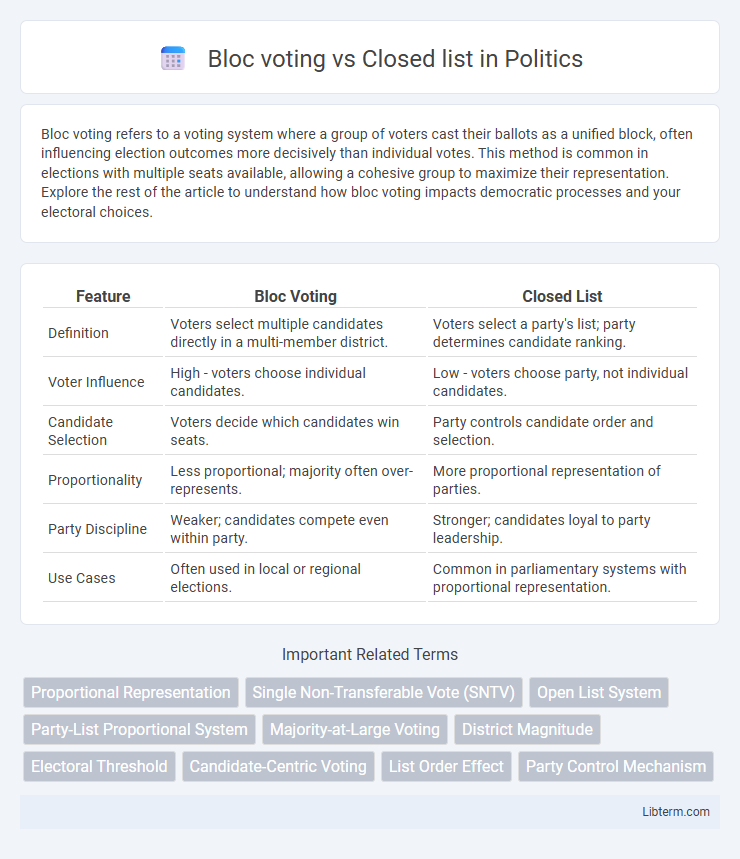
| Feature | Bloc Voting | Closed List |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters select multiple candidates directly in a multi-member district. | Voters select a party's list; party determines candidate ranking. |
| Voter Influence | High - voters choose individual candidates. | Low - voters choose party, not individual candidates. |
| Candidate Selection | Voters decide which candidates win seats. | Party controls candidate order and selection. |
| Proportionality | Less proportional; majority often over-represents. | More proportional representation of parties. |
| Party Discipline | Weaker; candidates compete even within party. | Stronger; candidates loyal to party leadership. |
| Use Cases | Often used in local or regional elections. | Common in parliamentary systems with proportional representation. |
Introduction to Voting Systems
Bloc voting allows voters to select multiple candidates, often equal to the number of available seats, making it suitable for multi-member districts. Closed list systems require voters to choose a party rather than individual candidates, with parties predetermining candidate order on a ranked list. These voting systems influence proportionality, representation, and voter influence in electoral outcomes, with bloc voting typically favoring majorities and closed lists enhancing party control.
Understanding Bloc Voting
Bloc voting allows voters to select multiple candidates, often up to the number of seats available, promoting more proportional representation in multi-member districts. This system contrasts with closed list voting, where voters select a party rather than individual candidates, and party leaders determine the order of candidates on the list. Understanding bloc voting highlights its potential to empower individual candidate choice while maintaining group representation.
Overview of Closed List System
The Closed List system requires voters to select a party rather than individual candidates, with seats allocated based on the party's overall share of the vote. Parties present a ranked list of candidates, and seats are awarded in that specific order, limiting voter influence on individual candidate selection. This method emphasizes party control and promotes proportional representation within legislative bodies.
Key Differences Between Bloc Voting and Closed List
Bloc voting allows voters to select multiple candidates individually, often up to the number of seats available, enabling more personalized choices and potential support for mixed party representation. Closed list systems present voters with a pre-ranked party list, where seats are allocated strictly according to the party's order, emphasizing party control over candidate selection. The key difference lies in voter influence: bloc voting offers choice among individual candidates, while closed lists prioritize party-determined candidate order and limit voter input to a party preference.
Advantages of Bloc Voting
Bloc voting allows voters to select multiple candidates individually, enhancing voter choice and representation compared to the fixed order of candidates in closed list systems. This method promotes greater accountability as candidates must appeal directly to voters, encouraging responsiveness and competition. Bloc voting also reduces party control over candidate selection, empowering minority voices and increasing electoral fairness.
Benefits of Closed List System
The Closed List system enhances party cohesion by allowing political parties to control candidate rankings, ensuring a unified legislative agenda and reducing factionalism. It promotes proportional representation, providing minority groups with better chances of securing seats compared to the majoritarian Bloc Voting system. Voters focus on party platforms rather than individual candidates, simplifying the decision-making process and strengthening party accountability.
Disadvantages of Bloc Voting
Bloc voting often leads to disproportional representation as it tends to favor the majority group, marginalizing minority voices in the electoral process. This voting system can result in "winner-takes-all" outcomes, reducing political diversity and limiting the accountability of elected officials. Compared to closed list systems, bloc voting diminishes voter influence over individual candidates, concentrating power within dominant parties or coalitions.
Drawbacks of Closed List System
The Closed List system limits voter choice by restricting candidates to pre-determined party lists, which often centralizes power within party leadership and diminishes individual accountability. This can lead to reduced voter influence over specific representatives, potentially weakening the connection between elected officials and their constituencies. Furthermore, the lack of candidate differentiation may discourage voter engagement and reduce electoral competitiveness.
Impact on Political Representation
Bloc voting tends to concentrate power among majority groups, often leading to less proportional political representation by allowing dominant parties to win multiple seats. Closed list systems offer more predictable outcomes by enabling parties to rank candidates, which can enhance representation of minorities and smaller parties within legislatures. This often results in a more balanced political landscape, improving inclusivity and reflecting diverse voter preferences.
Choosing the Right System: Bloc Voting vs Closed List
Choosing the right electoral system depends on the desired balance between voter influence and party control. Bloc voting allows voters to select multiple candidates individually, promoting personal accountability and voter choice, while the closed list system prioritizes party coherence by letting voters select a party list rather than individual candidates. Considerations include electoral fairness, representation diversity, and the extent to which the system empowers individual candidates versus party structures.
Bloc voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com