Representative democracy empowers citizens to elect officials who make decisions on their behalf, ensuring government accountability and responsiveness. This system balances direct public participation with efficient governance by allowing elected representatives to debate and enact policies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how representative democracy shapes your political rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
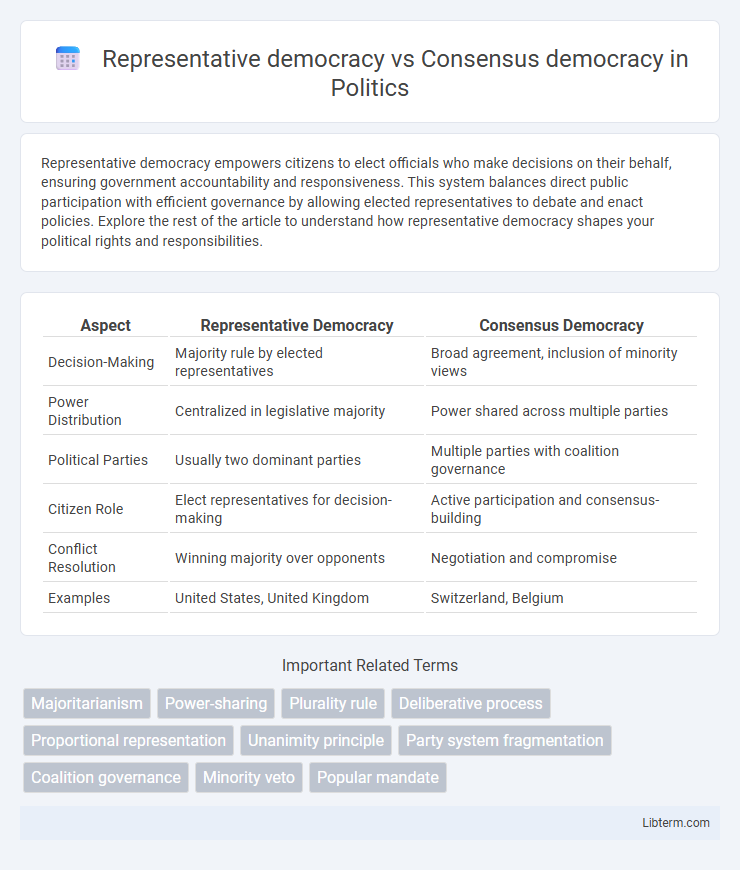
| Aspect | Representative Democracy | Consensus Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Majority rule by elected representatives | Broad agreement, inclusion of minority views |
| Power Distribution | Centralized in legislative majority | Power shared across multiple parties |
| Political Parties | Usually two dominant parties | Multiple parties with coalition governance |
| Citizen Role | Elect representatives for decision-making | Active participation and consensus-building |
| Conflict Resolution | Winning majority over opponents | Negotiation and compromise |
| Examples | United States, United Kingdom | Switzerland, Belgium |
Understanding Representative Democracy
Representative democracy is a political system where citizens elect officials to make decisions on their behalf, emphasizing political accountability and majority rule. This form of democracy enables efficient governance by delegating authority to representatives who reflect the electorate's preferences while balancing competing interests. It contrasts with consensus democracy, which seeks broader agreement among multiple stakeholders, often through power-sharing and coalition-building mechanisms.
Defining Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy emphasizes broad agreement and power-sharing among diverse political groups to ensure inclusive decision-making, contrasting with representative democracy's reliance on majority rule through elected officials. It involves mechanisms such as proportional representation, coalition governments, and minority veto rights to foster cooperation and mitigate conflict. This model seeks to balance interests across society, aiming for policies that reflect collective consensus rather than simple electoral majorities.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Representative democracy originated in ancient Rome and medieval European councils, evolving through the Enlightenment to emphasize elected officials making decisions on behalf of citizens. Consensus democracy emerged notably in post-World War II Western Europe, particularly in countries like Belgium, the Netherlands, and Switzerland, prioritizing power-sharing and broad agreement among diverse groups. The historical evolution of representative democracy centers on majority rule and electoral competition, while consensus democracy developed to manage pluralism and maintain political stability in fragmented societies.
Core Principles and Mechanisms
Representative democracy centers on elected officials making decisions on behalf of citizens, emphasizing competition, majority rule, and periodic elections to ensure accountability. Consensus democracy prioritizes broad agreement among diverse groups, employing power-sharing, proportional representation, and coalition governments to promote inclusiveness and minority rights. Key mechanisms in representative democracy include single-member districts and legislative voting, whereas consensus democracy utilizes negotiation, cross-party collaboration, and constitutional safeguards to achieve collective decision-making.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Representative democracy centralizes decision-making in elected officials who govern based on majority rule, enabling efficient and decisive policy implementation. Consensus democracy emphasizes inclusive decision-making through negotiation and collaboration among diverse political actors, aiming to reflect a broader range of interests and achieve broader legitimacy. These contrasting approaches affect government stability, minority representation, and policy responsiveness in different political systems.
Strengths of Representative Democracy
Representative democracy offers efficient decision-making by delegating authority to elected officials who act on behalf of the populace, ensuring swift legislative processes in complex societies. It facilitates accountability through regular elections, enabling voters to remove underperforming representatives and encouraging responsiveness to public needs. The system also supports diverse political competition, fostering innovation in policy and preventing the concentration of power.
Advantages of Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy fosters inclusive decision-making by incorporating diverse viewpoints, which enhances policy legitimacy and social cohesion. This system often results in more stable governance, as power is shared among multiple parties, reducing the risk of abrupt policy shifts. By promoting compromise and collaboration, consensus democracy minimizes political polarization and supports long-term, broadly acceptable solutions.
Challenges and Criticisms
Representative democracy faces challenges like limited public participation and susceptibility to elite capture, which can lead to voter disenfranchisement and reduced accountability. Consensus democracy, while promoting inclusivity and power-sharing, often encounters difficulties in decision-making efficiency and risks legislative gridlock due to the need for broad agreement among diverse groups. Both systems struggle with balancing effective governance and citizen representation, prompting ongoing debates about legitimacy and responsiveness in democratic processes.
Global Examples and Case Studies
Representative democracy, characterized by elected officials making decisions on behalf of citizens, is exemplified by the United States, where majority rule dominates legislative processes. Consensus democracy, as seen in Switzerland and the Netherlands, emphasizes power-sharing, coalition governments, and broad agreement to ensure minority inclusion and political stability. Case studies reveal that representative democracies often enable swift policy decisions, while consensus democracies foster inclusive governance and higher societal trust.
Future Prospects and Hybrid Models
Future prospects of representative democracy explore integrating digital platforms to enhance participation and transparency, potentially increasing responsiveness to citizens' needs. Consensus democracy's emphasis on inclusive decision-making may inspire hybrid models combining majority rule efficiency with power-sharing mechanisms to reduce polarization. Emerging governance frameworks increasingly adopt hybrid systems blending representative mandates with deliberative elements to balance effectiveness and broad-based legitimacy.
Representative democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com