Liberalism champions individual freedoms, equality, and democratic governance as the foundation of a just society. It emphasizes the protection of civil liberties, free markets tempered by social justice, and the rule of law to ensure opportunity for all. Explore the rest of the article to understand how liberalism shapes modern politics and impacts your life.
Table of Comparison
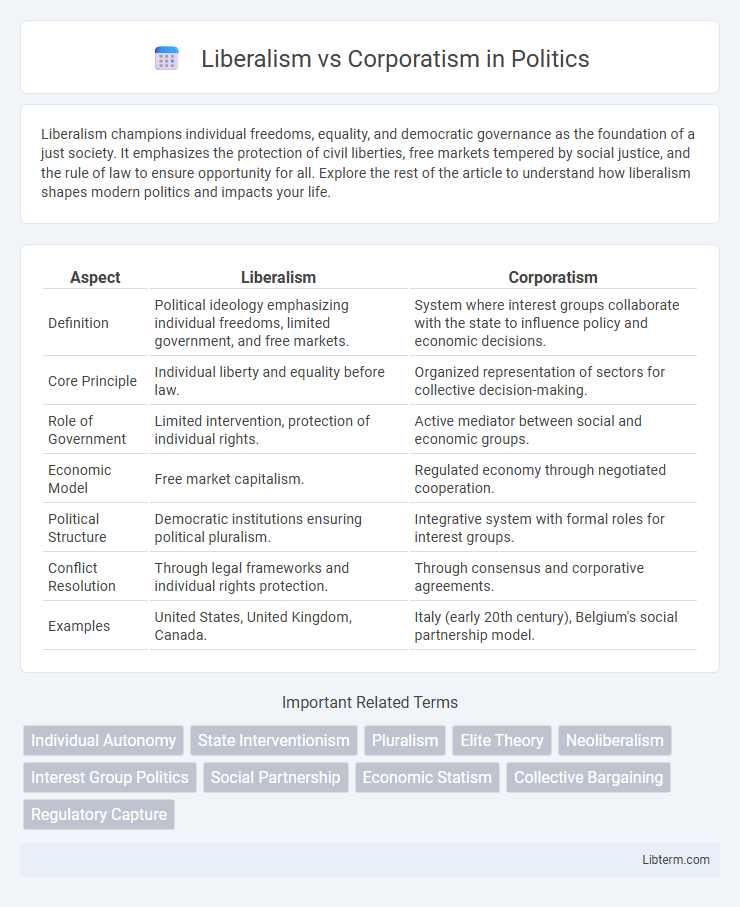
| Aspect | Liberalism | Corporatism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political ideology emphasizing individual freedoms, limited government, and free markets. | System where interest groups collaborate with the state to influence policy and economic decisions. |
| Core Principle | Individual liberty and equality before law. | Organized representation of sectors for collective decision-making. |
| Role of Government | Limited intervention, protection of individual rights. | Active mediator between social and economic groups. |
| Economic Model | Free market capitalism. | Regulated economy through negotiated cooperation. |
| Political Structure | Democratic institutions ensuring political pluralism. | Integrative system with formal roles for interest groups. |
| Conflict Resolution | Through legal frameworks and individual rights protection. | Through consensus and corporative agreements. |
| Examples | United States, United Kingdom, Canada. | Italy (early 20th century), Belgium's social partnership model. |
Introduction to Liberalism and Corporatism
Liberalism emphasizes individual freedom, free markets, and limited government intervention to promote economic growth and personal rights. Corporatism advocates for structured collaboration between government, businesses, and labor groups to manage the economy and social policies through negotiated agreements. These ideological frameworks represent contrasting approaches to governance, economic coordination, and the role of state intervention in society.
Historical Origins of Liberalism and Corporatism
Liberalism originated in the 17th and 18th centuries during the Enlightenment, emphasizing individual freedoms, limited government, and free markets, rooted in philosophers like John Locke and Adam Smith. Corporatism developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a response to industrial capitalism, advocating for organized collaboration between state, business, and labor groups to achieve social harmony. The historical origins of liberalism focus on political and economic liberty, while corporatism centers on structured social cooperation and the integration of various interest groups within the state.
Core Principles of Liberalism
Liberalism emphasizes individual liberty, free markets, and limited government intervention, advocating for equal rights and personal freedoms as fundamental to social and economic order. The core principles include protection of private property, rule of law, and democratic governance to ensure accountability and prevent tyranny. This contrasts with corporatism, which prioritizes coordination between the state, businesses, and interest groups to manage economic and social policies, often limiting individual autonomy for collective goals.
Fundamental Concepts of Corporatism
Corporatism is a socio-political concept advocating for the organization of society by corporate groups, such as agricultural, labor, military, or scientific affiliations, based on common interests. It emphasizes collective negotiation between these organized groups and the state to achieve social harmony and economic coordination, contrasting with the individualistic and market-driven principles of Liberalism. Fundamental to corporatism is the integration of interest groups into the governance process, fostering collaboration and reducing class conflict through structured representation.
Economic Systems: Liberalism vs Corporatism
Liberalism emphasizes free markets, individual entrepreneurship, and limited government intervention, promoting economic efficiency and innovation. Corporatism involves structured collaboration between the state, businesses, and labor organizations to coordinate economic activity, aiming for social stability and equitable distribution of resources. These contrasting economic systems reflect differing approaches to balancing market freedom with centralized control and collective interests.
Political Power and Governance Structures
Liberalism emphasizes individual rights, free markets, and limited government intervention, promoting decentralized political power through democratic institutions and the rule of law. Corporatism centers governance around structured partnerships between the state, corporations, and interest groups, concentrating political power within organized bodies that coordinate economic and social policies. This results in a governance model where power is exercised via negotiated collaboration among elites rather than solely through broadly inclusive democratic processes.
Social Implications and Individual Rights
Liberalism emphasizes the protection of individual rights and freedoms, advocating for limited government intervention in personal and economic affairs to promote equality and social justice. Corporatism prioritizes collective interests through collaboration between government, businesses, and labor groups, often subordinating individual rights to the needs of the community or state. Social implications of liberalism include enhanced personal autonomy and civil liberties, while corporatism can lead to social cohesion but risks marginalizing dissenting voices and restricting individual freedoms.
Liberalism and Corporatism in Modern Societies
Liberalism in modern societies emphasizes individual freedoms, market economy, and limited government intervention to promote personal autonomy and innovation, fostering competitive environments that drive economic growth. Corporatism, conversely, integrates key interest groups such as businesses, labor unions, and government into a cooperative framework to regulate the economy and social policy, aiming to achieve social harmony and reduce conflict. The dynamic between liberalism and corporatism shapes policy-making, labor relations, and economic structures, influencing how contemporary states balance market forces with social stability.
Key Debates and Contemporary Challenges
Liberalism emphasizes individual freedom, market competition, and limited government intervention, while corporatism prioritizes structured cooperation between the state, businesses, and labor groups to manage economic and social policies. Key debates center on the efficiency of market-driven versus coordinated economic systems, the balance of power between private interests and collective governance, and the role of the state in regulating economic activities. Contemporary challenges include addressing income inequality, navigating globalization's impact on labor relations, and responding to crises like climate change that demand coordinated multi-sectoral action.
Conclusion: Future Trends and Impacts
Liberalism, emphasizing individual freedom and market competition, is expected to prioritize innovation and decentralized decision-making in future economic policies. Corporatism's focus on collaboration among government, business, and labor may lead to more regulated markets aiming for stability and social equity. Emerging global challenges such as automation, climate change, and inequality will likely influence the balance between these ideologies, shaping regulatory frameworks and economic governance.
Liberalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com