A flexible clause allows parties to adapt contract terms according to changing circumstances, providing essential versatility in legal agreements. It helps manage unforeseen events without the need for renegotiation, saving time and reducing potential disputes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how incorporating a flexible clause can benefit your contracts.
Table of Comparison
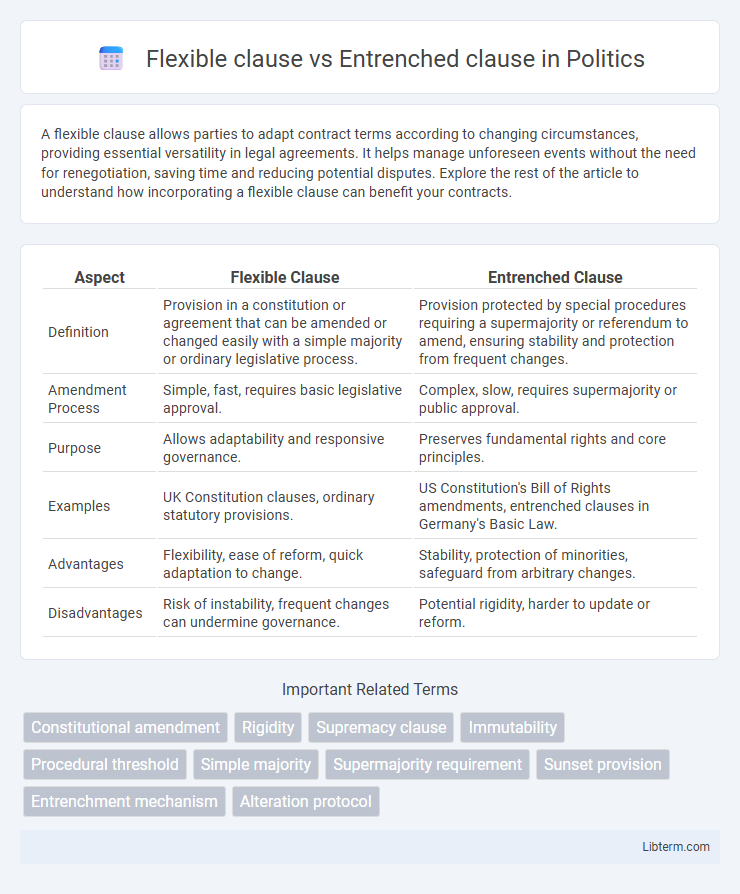
| Aspect | Flexible Clause | Entrenched Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Provision in a constitution or agreement that can be amended or changed easily with a simple majority or ordinary legislative process. | Provision protected by special procedures requiring a supermajority or referendum to amend, ensuring stability and protection from frequent changes. |
| Amendment Process | Simple, fast, requires basic legislative approval. | Complex, slow, requires supermajority or public approval. |
| Purpose | Allows adaptability and responsive governance. | Preserves fundamental rights and core principles. |
| Examples | UK Constitution clauses, ordinary statutory provisions. | US Constitution's Bill of Rights amendments, entrenched clauses in Germany's Basic Law. |
| Advantages | Flexibility, ease of reform, quick adaptation to change. | Stability, protection of minorities, safeguard from arbitrary changes. |
| Disadvantages | Risk of instability, frequent changes can undermine governance. | Potential rigidity, harder to update or reform. |
Introduction to Constitutional Clauses
Flexible clauses in constitutional law allow adaptability and interpretation over time, enabling the constitution to evolve with societal changes. Entrenched clauses, however, are rigid and protected from amendments to preserve fundamental principles and prevent alteration of core constitutional elements. Understanding the distinction between flexible and entrenched clauses is essential for analyzing constitutional stability and transformation.
Definition of Flexible Clause
A flexible clause is a contractual provision designed to allow adjustments or modifications based on changing circumstances or mutual agreement between parties. It contrasts with an entrenched clause, which is fixed and difficult to alter once established, ensuring stability and predictability. Flexible clauses provide adaptability in contracts, essential in dynamic business environments.
Definition of Entrenched Clause
An entrenched clause is a contractual provision designed to be difficult to amend or remove, often requiring a supermajority or specific conditions for modification, thereby protecting certain terms from easy alteration. Unlike flexible clauses, which can be changed with relative ease by ordinary resolutions, entrenched clauses safeguard fundamental aspects of an agreement, ensuring stability and predictability over time. These clauses are commonly used in corporate bylaws, partnership agreements, and constitutions to maintain core governance structures or protections.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Entrenched Clauses
Flexible clauses allow modifications or removals through ordinary legislative procedures, providing adaptability in constitutional or legal documents. Entrenched clauses require special procedures, such as supermajority votes or referendums, to ensure stability and rigidity against easy amendments. The key difference lies in the amendment process, with flexible clauses emphasizing adaptability and entrenched clauses prioritizing protection of core principles.
Examples of Flexible Clauses in Constitutions
Flexible clauses in constitutions allow amendments through ordinary legislative processes, exemplified by the United Kingdom's unwritten constitution where statutes like the Human Rights Act 1998 can be modified by simple parliamentary acts. Similarly, the Indian Constitution features flexible provisions permitting amendments via a special majority in Parliament, as seen in the 42nd Amendment of 1976 that redefined the preamble and fundamental duties. These examples contrast entrenched clauses, which require more rigorous procedures, such as supermajorities or referendums, to ensure constitutional stability.
Examples of Entrenched Clauses in Constitutions
Entrenched clauses in constitutions include provisions such as the U.S. Bill of Rights, which requires supermajority approval for amendments, ensuring durability against ordinary legislative changes. Germany's Basic Law contains an entrenched clause protecting human dignity and the democratic order, preventing any amendment that would compromise these core principles. Similarly, the Indian Constitution's "basic structure doctrine" renders certain fundamental features immutable, safeguarding key aspects of the constitutional framework from amendment.
Advantages of Flexible Clauses
Flexible clauses offer significant advantages in contract management and negotiation due to their adaptability, allowing parties to modify terms as circumstances evolve without requiring formal amendments. These clauses enhance business agility by accommodating unforeseen changes, reducing disputes, and fostering collaborative problem-solving. The ability to tailor obligations and rights dynamically supports long-term relationships and mitigates risks associated with rigid contract terms.
Advantages of Entrenched Clauses
Entrenched clauses provide significant advantages by offering enhanced legal protection against easy amendment or repeal, ensuring stability and predictability in agreements or constitutions. Their rigidity helps maintain long-term commitments, safeguarding critical rights and provisions from transient political or organizational changes. This durability supports trust and consistency in governance and contractual relations, crucial for upholding fundamental principles.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Each Clause
Flexible clauses often lead to ambiguity in contract interpretation, increasing the risk of disputes and inconsistent enforcement. Entrenched clauses can hinder adaptability, causing difficulties in responding to changing circumstances and potentially locking parties into unfavorable terms. The rigidity of entrenched clauses may result in prolonged negotiations and increased legal costs when amendments become necessary.
Impact of Clause Types on Constitutional Amendments
Flexible clauses allow constitutional amendments through relatively simple legislative procedures, facilitating adaptability to evolving political, social, and economic conditions. Entrenched clauses impose stricter amendment requirements, such as supermajority votes or referenda, safeguarding foundational principles from frequent changes. The impact of these clause types significantly shapes a constitution's rigidity or fluidity, influencing the ease with which legal frameworks can respond to societal needs.
Flexible clause Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com