Primary elections serve as critical preliminary contests where political parties select their candidates for the general election, shaping the political landscape well before the major voting day. Understanding the various types of primaries--open, closed, or semi-closed--can enhance your insight into how party affiliations impact candidate selection. Dive deeper into the article to discover how primary elections influence campaign strategies and voter engagement.
Table of Comparison
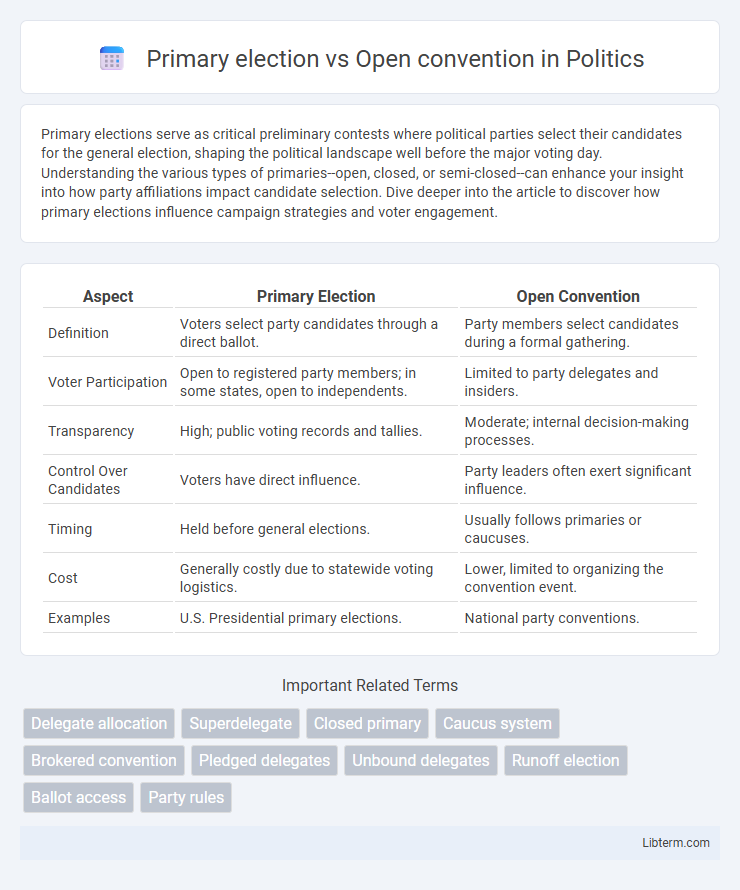
| Aspect | Primary Election | Open Convention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters select party candidates through a direct ballot. | Party members select candidates during a formal gathering. |
| Voter Participation | Open to registered party members; in some states, open to independents. | Limited to party delegates and insiders. |
| Transparency | High; public voting records and tallies. | Moderate; internal decision-making processes. |
| Control Over Candidates | Voters have direct influence. | Party leaders often exert significant influence. |
| Timing | Held before general elections. | Usually follows primaries or caucuses. |
| Cost | Generally costly due to statewide voting logistics. | Lower, limited to organizing the convention event. |
| Examples | U.S. Presidential primary elections. | National party conventions. |
Understanding Primary Elections
Primary elections allow registered party members to vote for their preferred candidate, shaping the party's nomination before the general election. These elections vary by state, with closed primaries limiting voting to registered party members, while open primaries permit independent voters to participate. Understanding primary elections is crucial for recognizing how candidates secure party support and influence the overall electoral process.
What is an Open Convention?
An Open Convention is a political gathering where delegates from various parties and independent members convene to select a party's candidate without restricting participation to registered party members. Unlike a Primary election, which involves a statewide voting process limited to party-affiliated voters, an Open Convention allows for broader representation and deliberation in candidate selection. This method emphasizes direct engagement and debate among representatives, potentially leading to a consensus choice that reflects a wider range of viewpoints within the party.
Key Differences Between Primaries and Open Conventions
Primary elections involve registered voters selecting their preferred candidate within a specific party, often through a secret ballot, ensuring party affiliation influences participation. Open conventions allow delegates or party members to openly discuss and vote on candidates, sometimes including unaffiliated voters, emphasizing transparency and direct engagement. While primaries prioritize individual voter choice in a structured process, open conventions focus on collective decision-making and party consensus-building.
Historical Background of Primary Elections
Primary elections originated in the early 20th century as a reform to reduce party leaders' control over candidate nominations, promoting greater voter participation and democratic selection processes. The first statewide primary election was held in Wisconsin in 1904, establishing a model that gradually replaced caucuses and conventions. This shift marked a pivotal change in American electoral politics by enhancing transparency and expanding the influence of ordinary party members in choosing candidates.
Evolution of Open Conventions
Open conventions evolved as a more transparent alternative to primary elections, allowing party members and delegates to openly discuss and select candidates during a public assembly. Unlike primary elections where voting is private and often limited to registered party members, open conventions encourage broader participation and real-time debate, fostering direct grassroots influence. This evolution reflects efforts to enhance democratic engagement and reduce the disenfranchisement perceived in closed or primary-based systems.
Advantages of Primary Elections
Primary elections offer increased voter participation by allowing a broader electorate to directly select party nominees, enhancing democratic representation. They provide transparency and reduce the influence of party insiders compared to open conventions, which often limit decision-making to a smaller group of delegates. Moreover, primary elections generate clearer mandates for candidates by reflecting the preferences of the general party membership, improving legitimacy and electoral accountability.
Pros and Cons of Open Conventions
Open conventions allow broader voter participation beyond party members, increasing democratic inclusivity and enhancing candidate exposure. However, this openness can lead to strategic voting by non-affiliated or opposition party members, potentially skewing candidate selection away from core party preferences. The lack of preliminary filtering may also result in fragmented delegate support, complicating consensus-building during the convention.
Impact on Party Unity
Primary elections often enhance party unity by allowing a broad base of members to participate in candidate selection, fostering a sense of inclusiveness and legitimacy. Open conventions can sometimes lead to division as they allow delegates to be influenced by shifting alliances and external pressures during the event, potentially marginalizing primary results. The choice between these methods significantly affects party cohesion, with primaries typically promoting stronger grassroots engagement while open conventions may introduce internal conflicts.
Voter Participation: Primary Election vs Open Convention
Voter participation in primary elections typically exceeds that of open conventions due to their broader accessibility, allowing registered party members or, in some cases, all eligible voters to cast ballots directly. Open conventions often see lower turnout as they require attendees to physically participate in meetings or caucuses, limiting involvement to more engaged or available party activists. Data from recent elections show primary voter turnout rates can range from 20% to 40%, whereas open convention attendance seldom surpasses 10% of eligible party members.
Future Trends in Candidate Selection
Future trends in candidate selection indicate a shift towards more inclusive and technology-driven processes, blending the transparency of primary elections with the participatory nature of open conventions. Digital platforms and data analytics increasingly influence voter engagement and candidate vetting, enhancing accessibility and real-time feedback. This hybrid approach aims to balance broad voter input with deliberate party deliberation, shaping democratic participation in modern elections.
Primary election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com