Political lobbying influences legislation by advocating for specific interests and policies through direct interaction with lawmakers and government officials. It plays a crucial role in shaping public policy, impacting sectors such as healthcare, environment, and business regulations. Discover how effective lobbying strategies can empower your voice in the political arena by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
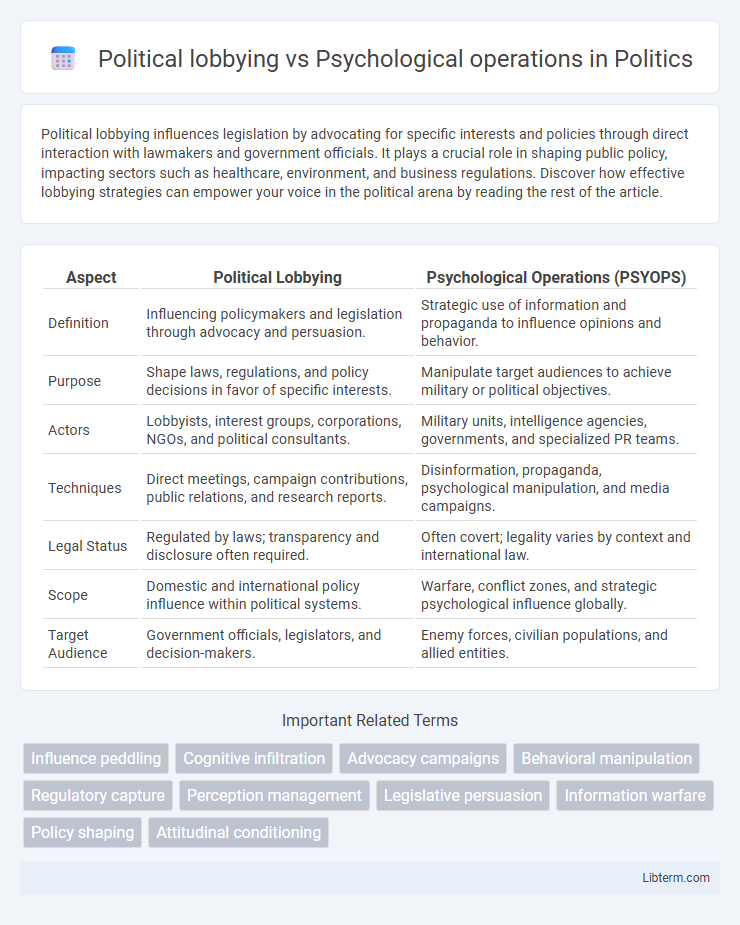
| Aspect | Political Lobbying | Psychological Operations (PSYOPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Influencing policymakers and legislation through advocacy and persuasion. | Strategic use of information and propaganda to influence opinions and behavior. |
| Purpose | Shape laws, regulations, and policy decisions in favor of specific interests. | Manipulate target audiences to achieve military or political objectives. |
| Actors | Lobbyists, interest groups, corporations, NGOs, and political consultants. | Military units, intelligence agencies, governments, and specialized PR teams. |
| Techniques | Direct meetings, campaign contributions, public relations, and research reports. | Disinformation, propaganda, psychological manipulation, and media campaigns. |
| Legal Status | Regulated by laws; transparency and disclosure often required. | Often covert; legality varies by context and international law. |
| Scope | Domestic and international policy influence within political systems. | Warfare, conflict zones, and strategic psychological influence globally. |
| Target Audience | Government officials, legislators, and decision-makers. | Enemy forces, civilian populations, and allied entities. |
Introduction to Political Lobbying and Psychological Operations
Political lobbying involves organized efforts by interest groups to influence government decisions and policies through direct interaction with legislators and officials. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) employ strategic communication techniques to influence the perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors of targeted populations, often in military or intelligence contexts. Both methods aim to shape decision-making but differ fundamentally in approach and ethical considerations.
Defining Political Lobbying: Strategies and Tactics
Political lobbying involves organized efforts to influence legislation or governmental decisions by advocating specific policies through direct interaction with lawmakers and public officials. Strategies include coalition building, drafting policy proposals, and leveraging public opinion, while tactics range from face-to-face meetings and testimony at legislative hearings to targeted communications and campaign contributions. Effective lobbying requires deep understanding of political processes, stakeholder interests, and timing to shape policy outcomes in favor of particular groups or causes.
Understanding Psychological Operations: Methods and Objectives
Psychological operations (PSYOP) utilize strategic communication techniques to influence the emotions, motives, and behavior of targeted audiences, often through misinformation, propaganda, and other psychological tactics. Unlike political lobbying, which seeks to persuade lawmakers and government officials through direct advocacy and relationship-building, PSYOP aims to manipulate public perception and morale to achieve specific military or political objectives. Key methods include disseminating tailored messaging across multiple media platforms to destabilize adversaries or bolster support among allies, emphasizing subtle psychological influence over overt political negotiation.
Historical Evolution of Lobbying and PsyOps
Political lobbying has evolved from informal influence by interest groups in ancient Greece and Rome to highly organized efforts within modern democratic frameworks, involving professional lobbyists and regulatory systems. Psychological operations (PsyOps) originated during World War I as military strategies designed to influence enemy morale and public opinion, expanding in complexity and scope with advancements in communication technologies through the Cold War and modern conflicts. Both practices demonstrate an increasingly sophisticated use of communication tactics to shape political outcomes and public perception over time.
Key Differences Between Lobbying and PsyOps
Political lobbying involves influencing lawmakers and government officials through advocacy, campaign contributions, and direct communication to shape public policy and legislation. Psychological operations (PsyOps) target the emotions, motives, and reasoning of individuals or groups using misinformation, propaganda, and psychological tactics to manipulate perceptions and behaviors in favor of strategic objectives. Lobbying operates openly within legal frameworks to advocate policy changes, while PsyOps often employ covert, deceptive methods to influence populations without transparent disclosure.
Overlapping Techniques: Where Lobbying Meets PsyOps
Political lobbying and psychological operations (PsyOps) both employ strategic messaging and influence tactics to shape public perception and decision-making. Techniques such as targeted communication, emotional appeals, and narrative framing overlap, aiming to persuade key audiences, whether policymakers or the general public. These shared methods highlight the blurred lines between lobbying efforts and psychological manipulation in advancing political agendas.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Political lobbying involves advocating for specific legislation or policies within legal frameworks that require transparency, registration, and disclosure to prevent corruption and undue influence. Psychological operations (PSYOPs) are military or governmental actions designed to influence emotions, motives, and behavior, often operating in classified contexts with stricter ethical scrutiny due to potential manipulation and misinformation risks. Both activities raise significant ethical concerns, but lobbying is regulated through laws ensuring accountability, while PSYOPs necessitate rigorous oversight to balance national security interests against moral implications of psychological influence.
Influence on Public Policy and Opinion
Political lobbying directly targets policymakers and legislators to shape public policy through advocacy, campaign contributions, and providing expert information, effectively influencing decision-making processes. Psychological operations (PSYOPs) aim to sway public opinion and behavior using information campaigns, propaganda, and media manipulation, often focusing on large populations rather than specific officials. Both methods impact public policy and opinion, but lobbying works within formal political structures, while PSYOPs operate primarily through psychological influence on the broader public.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Political lobbying involves organized efforts to influence government policy through advocacy, as demonstrated by the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC), which successfully shapes U.S. foreign policy in the Middle East. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) deploy strategic communications and propaganda to alter behaviors, exemplified by the U.S. military's use of leaflet campaigns in Iraq to undermine insurgent morale. Case studies highlight how lobbying targets lawmakers directly for legislative change, while PSYOPS manipulate public perception and enemy combatants in conflict zones.
Future Trends and Implications
Political lobbying increasingly integrates data analytics and AI to refine targeting and influence strategies, enhancing the precision of advocacy efforts. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) leverage advancements in social media algorithms and deepfake technology to manipulate public perception and propagate disinformation with greater subtlety. Future trends suggest a convergence of lobbying and PSYOPS tactics, raising ethical concerns and necessitating stronger regulatory frameworks to mitigate misinformation and protect democratic processes.
Political lobbying Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com