Summit diplomacy plays a crucial role in shaping international relations by facilitating direct dialogue between world leaders, allowing for the swift resolution of complex global issues. These high-level meetings help build trust, foster cooperation, and address emergencies or conflicts that require immediate attention. Discover how summit diplomacy impacts global politics and what it means for Your country's foreign policy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
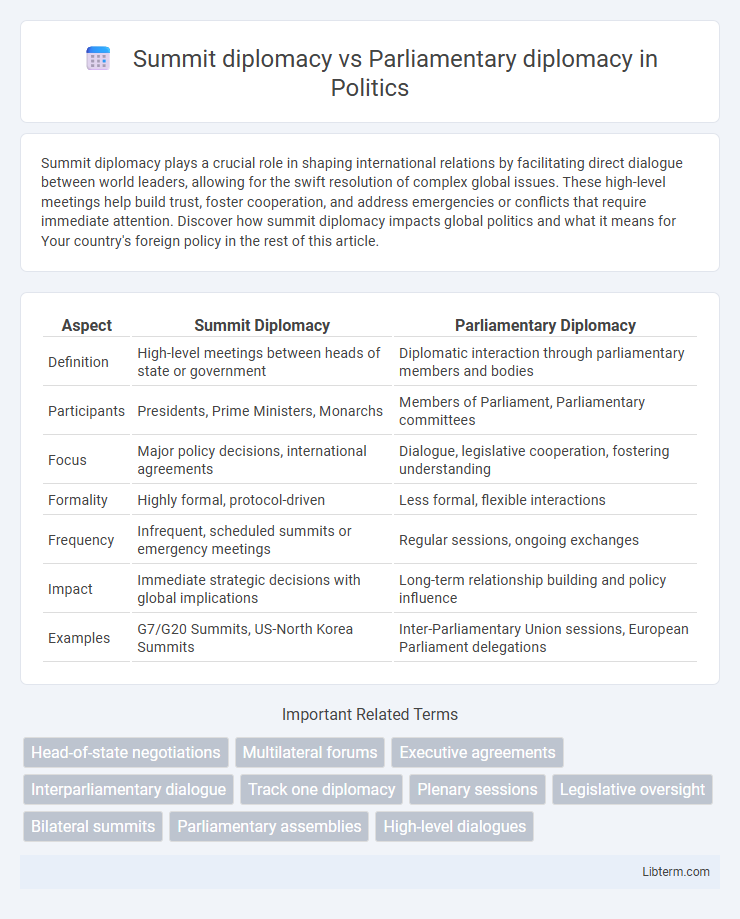
| Aspect | Summit Diplomacy | Parliamentary Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-level meetings between heads of state or government | Diplomatic interaction through parliamentary members and bodies |
| Participants | Presidents, Prime Ministers, Monarchs | Members of Parliament, Parliamentary committees |
| Focus | Major policy decisions, international agreements | Dialogue, legislative cooperation, fostering understanding |
| Formality | Highly formal, protocol-driven | Less formal, flexible interactions |
| Frequency | Infrequent, scheduled summits or emergency meetings | Regular sessions, ongoing exchanges |
| Impact | Immediate strategic decisions with global implications | Long-term relationship building and policy influence |
| Examples | G7/G20 Summits, US-North Korea Summits | Inter-Parliamentary Union sessions, European Parliament delegations |
Defining Summit Diplomacy and Parliamentary Diplomacy
Summit diplomacy involves high-level meetings between heads of state or government to address critical international issues, emphasizing direct negotiation and decision-making at the top political level. Parliamentary diplomacy refers to dialogue and cooperation among legislative bodies or parliamentarians from different countries, fostering mutual understanding, conflict resolution, and norm-setting through legislative collaboration. Both forms enhance international relations but differ in participants and methods, with summit diplomacy centered on executive authority and parliamentary diplomacy on legislative engagement.
Historical Evolution of Diplomatic Practices
Summit diplomacy emerged prominently in the 20th century as a mechanism for direct dialogue between heads of state, accelerating decision-making during critical international crises such as the Cold War. Parliamentary diplomacy has its roots in the growth of representative institutions in the 19th century, evolving as legislative bodies increased their role in shaping foreign policy and fostering international parliamentary cooperation. The historical evolution highlights a shift from exclusive executive negotiations to more inclusive frameworks incorporating both executive summit meetings and parliamentary interactions to enhance transparency and democratic legitimacy in diplomatic practices.
Key Actors: Leaders vs Legislators
Summit diplomacy primarily involves heads of state or government leaders who negotiate and make decisions on critical international issues, leveraging their executive authority and direct communication channels. Parliamentary diplomacy engages legislators who represent diverse political viewpoints, fostering dialogue, oversight, and consensus-building through formal debates and committee work. While summit diplomacy accelerates high-level agreements, parliamentary diplomacy ensures broader democratic legitimacy and accountability in foreign policy-making.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Summit diplomacy centralizes decision-making in high-level meetings involving heads of state or government, enabling swift resolutions on critical international issues through direct negotiation. Parliamentary diplomacy distributes decision-making across elected legislative representatives, fostering more inclusive deliberation and consensus-building over extended periods. This contrast highlights summit diplomacy's efficiency in urgent matters versus parliamentary diplomacy's emphasis on transparency and democratic legitimacy in international policymaking.
Transparency and Accountability in Each Approach
Summit diplomacy often operates behind closed doors, limiting transparency but enabling swift decision-making among top leaders, which can challenge accountability due to less public oversight. Parliamentary diplomacy emphasizes openness through regular debates, committee hearings, and public scrutiny, enhancing transparency and accountability by involving elected representatives. The contrast highlights summit diplomacy's expedited process versus parliamentary diplomacy's rigorous, transparent deliberation mechanisms.
Speed and Flexibility of Diplomatic Responses
Summit diplomacy offers unparalleled speed in decision-making by bringing heads of state together for immediate, high-stakes negotiations, enabling rapid responses to urgent international crises. Parliamentary diplomacy, while often slower due to legislative procedures and deliberations, provides greater flexibility through diverse stakeholder engagement and sustained dialogue over time. The contrast highlights summit diplomacy's efficacy in urgent scenarios versus parliamentary diplomacy's adaptability for long-term, multifaceted diplomatic efforts.
Impact on International Agreements
Summit diplomacy accelerates international agreements by gathering heads of state for direct, high-level negotiations that facilitate swift decision-making and tangible commitments. Parliamentary diplomacy enhances the legitimacy and sustainability of agreements by involving legislators who ensure democratic scrutiny and foster long-term cooperation through dialogue and consensus-building. Both forms impact international agreements by balancing immediacy and inclusiveness, shaping the durability and effectiveness of global cooperation.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Summit diplomacy, exemplified by the 1993 Oslo Accords between Israel and the PLO, achieved breakthrough peace negotiations through high-level face-to-face meetings, while the 2009 Copenhagen Climate Summit highlighted failures due to lack of consensus among heads of state. Parliamentary diplomacy proved effective in the European Union, where the European Parliament facilitated dialogue and ratification of trade agreements such as the EU-South Korea Free Trade Agreement, yet its influence was limited during the Brexit negotiations, reflecting challenges in parliamentary diplomacy's decision-making power. Both diplomatic approaches demonstrate that success depends on context, participant authority, and negotiation framework flexibility.
Challenges and Criticisms Faced by Both Methods
Summit diplomacy faces challenges such as limited time for in-depth negotiations and the risk of oversimplifying complex issues, which can lead to superficial agreements lacking detailed implementation plans. Parliamentary diplomacy encounters criticisms related to slower decision-making processes, diverse political interests causing fragmentation, and difficulties in achieving consensus among multiple representatives. Both methods struggle with balancing national interests and global cooperation while ensuring transparency and accountability in international relations.
Future Trends in Global Diplomacy
Summit diplomacy, characterized by high-level meetings between heads of state, will increasingly integrate advanced digital platforms to enable real-time decision-making and crisis management. Parliamentary diplomacy is expected to expand its role in fostering multilateral cooperation through enhanced inter-parliamentary networks and thematic caucuses addressing global challenges such as climate change and cyber security. Future trends highlight a hybrid approach where summit diplomacy sets strategic agendas while parliamentary diplomacy ensures legislative follow-through and public accountability.
Summit diplomacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com