Incremental budgeting involves adjusting the previous period's budget by a certain percentage, focusing on changes rather than starting from scratch. It is widely used for its simplicity and efficiency in organizations with stable operations, allowing quick budget preparation. Discover how incremental budgeting can streamline your financial planning in the detailed article ahead.
Table of Comparison
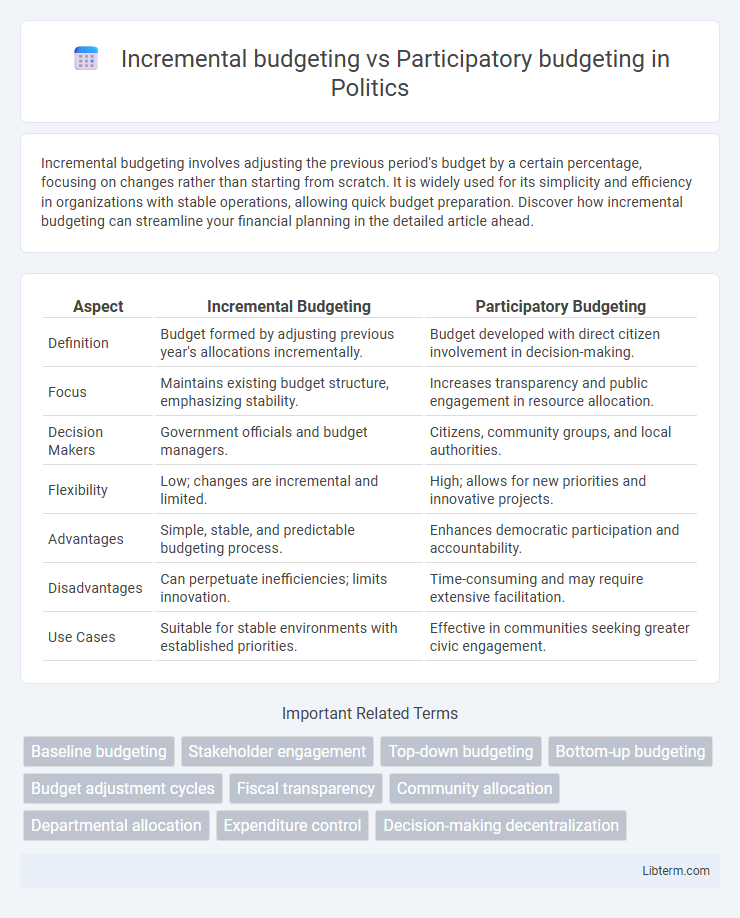
| Aspect | Incremental Budgeting | Participatory Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Budget formed by adjusting previous year's allocations incrementally. | Budget developed with direct citizen involvement in decision-making. |
| Focus | Maintains existing budget structure, emphasizing stability. | Increases transparency and public engagement in resource allocation. |
| Decision Makers | Government officials and budget managers. | Citizens, community groups, and local authorities. |
| Flexibility | Low; changes are incremental and limited. | High; allows for new priorities and innovative projects. |
| Advantages | Simple, stable, and predictable budgeting process. | Enhances democratic participation and accountability. |
| Disadvantages | Can perpetuate inefficiencies; limits innovation. | Time-consuming and may require extensive facilitation. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for stable environments with established priorities. | Effective in communities seeking greater civic engagement. |
Introduction to Incremental and Participatory Budgeting
Incremental budgeting allocates new budgets based on previous periods, adjusting for small changes in expenditures and revenues to maintain financial continuity. Participatory budgeting involves community members directly in decision-making, promoting transparency and aligning resource allocation with public priorities. Both methods offer distinct approaches to planning but vary in flexibility and stakeholder engagement.
Core Principles of Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting relies on the core principle of using the previous year's budget as a baseline and adjusting for incremental changes, such as inflation or new priorities, ensuring stability and predictability in financial planning. This method emphasizes continuity by allocating resources based on historical data, minimizing drastic shifts in funding allocations. Unlike participatory budgeting, incremental budgeting limits stakeholder engagement, focusing instead on administrative efficiency and incremental improvements.
Core Principles of Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting centers on community involvement, transparency, and democratic decision-making, allowing citizens to directly influence budget allocations and prioritize projects that address local needs. Unlike incremental budgeting, which adjusts previous budgets based on historical data and incremental changes, participatory budgeting fosters collaboration and accountability by engaging diverse stakeholders in the budgeting process. This approach enhances trust in governance, promotes social equity, and ensures that public funds are allocated more effectively according to collective priorities.
Key Differences Between Incremental and Participatory Budgeting
Incremental budgeting allocates resources based on previous budgets with slight adjustments, emphasizing stability and predictability, while participatory budgeting involves stakeholders or citizens directly in the decision-making process, promoting transparency and inclusiveness. Incremental budgeting often limits innovation due to its reliance on past allocations, whereas participatory budgeting fosters community engagement and prioritizes projects that reflect local needs and preferences. The key difference lies in incremental budgeting's top-down approach contrasted with participatory budgeting's bottom-up methodology that empowers public input and democratic governance.
Advantages of Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting simplifies the financial planning process by making adjustments based on previous budgets, minimizing complexity and saving time. This approach enhances stability and predictability in budget forecasts by focusing on incremental changes rather than complete overhauls. Incremental budgeting allows organizations to maintain control over expenditures while ensuring gradual improvements aligned with historical spending patterns.
Advantages of Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting enhances transparency by involving community members directly in allocation decisions, leading to increased trust and accountability in public spending. It fosters inclusivity and empowerment, allowing diverse voices to influence priorities and promoting equitable resource distribution based on actual community needs. This collaborative approach generates innovative solutions and strengthens civic engagement, ultimately improving the effectiveness and responsiveness of budget outcomes compared to traditional incremental budgeting methods.
Limitations of Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting often limits financial innovation by relying on previous budgets as a base, which can perpetuate inefficiencies and outdated allocations. This method typically overlooks the need for strategic resource reallocation and tends to reinforce organizational silos. In contrast, participatory budgeting engages stakeholders directly, enhancing transparency and aligning expenditures with community priorities.
Limitations of Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting faces limitations such as limited participant diversity, which may lead to unequal representation of community interests, and potential manipulation by dominant groups influencing decision outcomes. The process often requires significant time and resources, reducing its feasibility for larger or more complex municipal budgets. In contrast, incremental budgeting primarily focuses on historical budget adjustments, lacking the direct citizen engagement but offering a more streamlined and predictable approach to public financial planning.
Case Studies: Applications in the Public and Private Sectors
Incremental budgeting, commonly applied in the public sector, is exemplified by the U.S. federal government's method of adjusting previous year budgets with minor modifications, ensuring financial stability and predictability. Participatory budgeting, often utilized in municipalities like Porto Alegre, Brazil, empowers citizens to directly decide on budget allocations, enhancing transparency and local engagement in public projects. In the private sector, participatory budgeting is less prevalent but has been successfully integrated in some cooperatives and employee-owned companies to align budgeting with workforce priorities and improve organizational commitment.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Approach for Your Organization
Incremental budgeting emphasizes making small adjustments to the previous budget, ensuring stability and ease of forecasting, ideal for organizations with stable operations and predictable expenses. Participatory budgeting involves stakeholders at various levels, promoting transparency, engagement, and resource allocation aligned with community or employee priorities, suitable for organizations prioritizing collaboration and innovation. Choosing the right budgeting approach depends on your organization's culture, operational complexity, and strategic goals to balance efficiency with inclusive decision-making.
Incremental budgeting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com