Political lobbying influences legislation and policy-making by engaging directly with lawmakers and government officials to advocate for specific interests. Understanding how lobbying operates and its impact on democratic processes can help you navigate and critically assess political decisions. Explore the rest of the article to uncover the mechanisms and significance of political lobbying in shaping public policy.
Table of Comparison
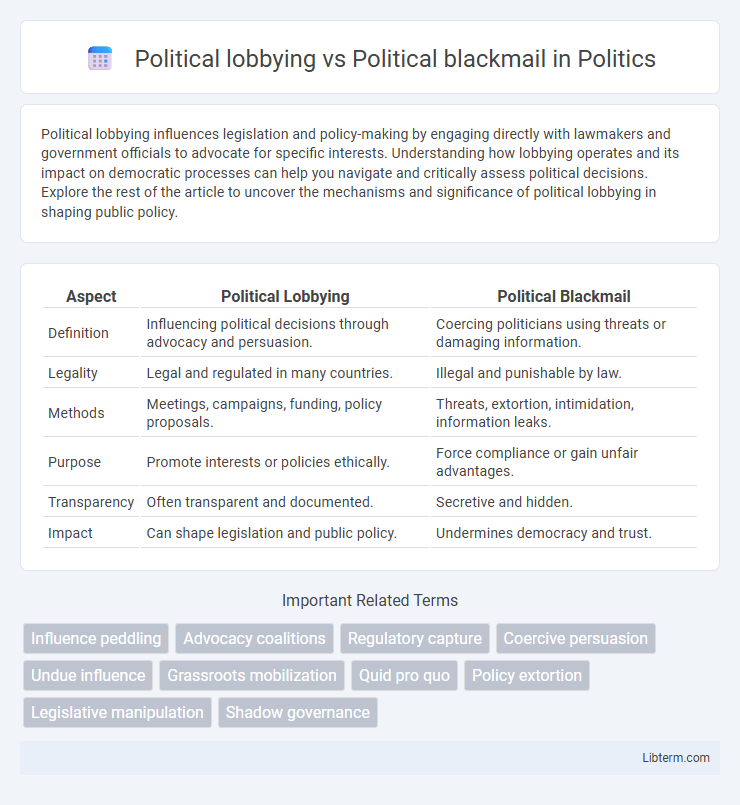
| Aspect | Political Lobbying | Political Blackmail |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Influencing political decisions through advocacy and persuasion. | Coercing politicians using threats or damaging information. |
| Legality | Legal and regulated in many countries. | Illegal and punishable by law. |
| Methods | Meetings, campaigns, funding, policy proposals. | Threats, extortion, intimidation, information leaks. |
| Purpose | Promote interests or policies ethically. | Force compliance or gain unfair advantages. |
| Transparency | Often transparent and documented. | Secretive and hidden. |
| Impact | Can shape legislation and public policy. | Undermines democracy and trust. |
Understanding Political Lobbying
Political lobbying involves organized efforts by interest groups or individuals to influence lawmakers and public policy through legal and transparent means, such as advocacy, research, and direct communication. It is a fundamental aspect of democratic governance that enables stakeholders to present their views and expertise to decision-makers. Understanding political lobbying requires recognizing its role in shaping legislation while ensuring ethical standards distinguish it sharply from political blackmail, which entails coercion or threats to manipulate political outcomes.
Defining Political Blackmail
Political blackmail involves coercing politicians or public officials by threatening to reveal damaging information or take harmful actions unless specific demands are met, contrasting with political lobbying, which seeks to influence decisions through persuasion and advocacy within legal and ethical boundaries. Unlike lobbying, political blackmail undermines democratic processes by leveraging fear, intimidation, or corruption to manipulate policy outcomes or gain illicit advantages. Defining political blackmail centers on its use of threats and unethical pressure tactics that compromise transparency and accountability in governance.
Key Differences Between Lobbying and Blackmail
Political lobbying involves legally advocating for policy changes by influencing legislators through information and persuasion, while political blackmail uses coercion or threats to manipulate political decisions. Lobbying relies on transparent communication and relationship-building with policymakers, whereas blackmail exploits confidential information or threats to force compliance. Key differences include the legality, ethical standards, and methods of influence, with lobbying operating within democratic norms and blackmail undermining trust and legal boundaries.
Legal Frameworks Surrounding Lobbying
Political lobbying operates within defined legal frameworks that regulate transparency, disclosure of activities, and ethical conduct to ensure accountability and prevent undue influence. These frameworks typically require lobbyists to register, report expenditures, and adhere to restrictions on gifts and campaign contributions, distinguishing lawful advocacy from coercive tactics. In contrast, political blackmail falls outside legal boundaries, involving threats or coercion that violate criminal laws and undermine democratic processes.
Legal Consequences of Political Blackmail
Political blackmail involves coercion or threats to influence political decisions, which constitutes criminal behavior subject to stringent legal consequences such as imprisonment, fines, and loss of political rights. Unlike legal political lobbying that seeks to persuade policymakers through lawful advocacy and transparency, blackmail undermines democratic processes and violates laws against extortion and corruption. Judicial systems worldwide treat political blackmail as a serious offense due to its potential to destabilize governance and erode public trust in political institutions.
Ethical Considerations in Political Influence
Political lobbying involves advocating for policy changes through transparent dialogue and lawful means, emphasizing accountability and respect for democratic processes. Political blackmail, by contrast, relies on coercion, threats, or manipulation to achieve political goals, undermining ethical standards and eroding public trust. Ethical considerations demand clear boundaries to distinguish legitimate lobbying efforts from corrupt practices, ensuring integrity in political influence.
Common Tactics Used in Political Lobbying
Political lobbying commonly employs tactics such as direct communication with lawmakers, campaign contributions, and orchestrating grassroots mobilization to influence policy decisions. Lobbyists often provide detailed research and expert testimony to shape legislation favorably for their clients or interest groups. These techniques aim to create a persuasive presence within the political system as distinct from political blackmail, which relies on coercion or threats.
Methods and Forms of Political Blackmail
Political blackmail employs coercive methods such as threats, intimidation, and extortion to manipulate political figures or sway decisions, often involving bribery, exposure of damaging information, or leveraging personal vulnerabilities. Unlike lobbying, which uses legal advocacy, political blackmail operates through clandestine tactics that undermine democratic processes by instilling fear or obligating compliance. Forms include financial blackmail, where funds are withheld or promised for political favors, and reputational blackmail, which exploits secrets or scandals to extract concessions.
Impact on Democracy and Governance
Political lobbying influences democracy by enabling interest groups to advocate for policies, but it risks disproportionate power for wealthy entities, potentially skewing governance priorities away from the public interest. Political blackmail undermines democratic processes by coercing officials through threats, eroding transparency and trust in governance. While lobbying operates within legal frameworks, political blackmail represents corruption that destabilizes institutional integrity and accountability.
Safeguarding Political Processes Against Abuse
Political lobbying involves legally influencing policymakers through transparent advocacy, whereas political blackmail exploits threats or coercion to manipulate decisions. Safeguarding political processes requires stringent regulations, disclosure requirements, and robust enforcement to distinguish legitimate lobbying from corrupt practices. Enhancing transparency and accountability mechanisms prevents abuse, ensuring political decisions reflect public interest rather than undue influence.
Political lobbying Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com