The conference committee plays a crucial role in organizing and managing successful events by coordinating logistics, selecting speakers, and overseeing schedules. Effective committees ensure seamless communication among participants, enhance networking opportunities, and maintain the event's overall quality. Explore the full article to discover how a strong conference committee can elevate your next event.
Table of Comparison
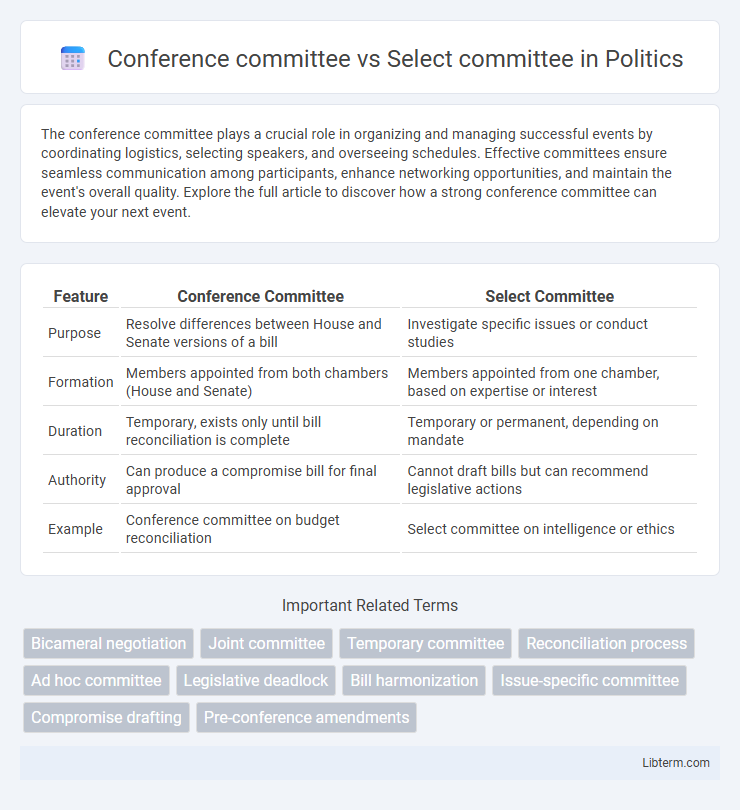
| Feature | Conference Committee | Select Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resolve differences between House and Senate versions of a bill | Investigate specific issues or conduct studies |
| Formation | Members appointed from both chambers (House and Senate) | Members appointed from one chamber, based on expertise or interest |
| Duration | Temporary, exists only until bill reconciliation is complete | Temporary or permanent, depending on mandate |
| Authority | Can produce a compromise bill for final approval | Cannot draft bills but can recommend legislative actions |
| Example | Conference committee on budget reconciliation | Select committee on intelligence or ethics |
Introduction to Congressional Committees
Conference committees resolve differences between House and Senate versions of a bill to produce a unified legislative text, playing a vital role in the final stages of lawmaking. Select committees are temporary panels established for specific investigations or issues, often addressing topics outside the jurisdiction of standing committees. Both types contribute to Congress's oversight and lawmaking functions by focusing on distinct legislative needs and processes.
Definition of Conference Committees
Conference committees are temporary joint committees formed by members of both the House and Senate to reconcile differences in legislation passed by each chamber. These committees work to produce a unified bill that both chambers can agree upon before final approval. Unlike select committees, which are created for specific investigations or issues and may be permanent or temporary, conference committees exist solely for resolving legislative discrepancies.
Definition of Select Committees
Select Committees are specialized legislative bodies established to investigate specific issues or conduct detailed studies that fall outside the scope of standing committees. Unlike Conference Committees, which reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill, Select Committees have a temporary or permanent mandate to address unique subjects, often providing in-depth oversight and policy recommendations. Their focused expertise enables legislatures to examine complex or emerging matters with greater precision and flexibility.
Composition and Membership
Conference committees consist of members from both the House and Senate, usually senior members from relevant standing committees, tasked with reconciling differences in legislation passed by both chambers. Select committees are typically temporary and composed of members appointed for a specific purpose, often drawn from one chamber, to investigate or address particular issues outside the jurisdiction of standing committees. The composition of conference committees is bipartisan and balanced, while select committees' membership varies widely based on their mandate and urgency.
Purpose and Functions
Conference committees reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill, ensuring a unified legislative text for final approval. Select committees conduct specialized investigations or address specific issues outside the jurisdiction of standing committees, providing focused oversight and expertise. Both play critical roles in shaping legislation, with conference committees finalizing laws and select committees guiding policy through detailed examination.
Creation and Duration
Conference committees are created jointly by both the House and Senate to reconcile disagreements on specific bills, typically forming after passage of differing versions to produce a final compromise. Their duration is temporary, lasting only as long as necessary to resolve the legislative differences, often concluding within days or weeks of formation. Select committees are established by either chamber for specialized, often investigative purposes and may exist for a fixed term or until their assigned task is complete, with durations varying from short-term inquiries to ongoing oversight functions.
Legislative Processes Involved
Conference committees reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill, ensuring a unified legislative text before final approval and enactment. Select committees conduct specialized investigations or studies to inform legislation but do not draft bills. Both play crucial roles in refining legislation, with conference committees finalizing compromise bills and select committees shaping policy through detailed analysis and recommendations.
Key Differences Between Conference and Select Committees
Conference committees reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill to produce a unified legislative text. Select committees are temporary panels established to investigate specific issues or conduct studies without crafting legislation. The key difference lies in their purpose: conference committees resolve legislative discrepancies, while select committees focus on specialized investigations or oversight.
Historical Examples and Case Studies
The Conference Committee, exemplified by the 1935 Social Security Act negotiations, serves to reconcile House and Senate bill versions before final passage, ensuring legislative consistency. Select Committees, such as the Senate Watergate Committee of 1973, are temporary bodies established to investigate specific issues or crises, providing detailed, focused oversight. Historical case studies highlight the Conference Committee's role in formal legislative harmonization, contrasted with Select Committees' investigative and special-purpose functions.
Conclusion: Importance in the Legislative Process
Conference committees reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill, ensuring a unified legislative text that can pass both chambers efficiently. Select committees conduct specialized investigations or studies, providing detailed expertise that shapes informed legislative decisions. Both committees play crucial roles in refining legislation, with conference committees finalizing laws and select committees influencing policy through focused analysis.
Conference committee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com