Enabling legislation grants specific authority to government agencies or officials to implement laws and regulations crucial for effective governance. This legal framework defines the scope and limits of power, ensuring accountability and clarity in administrative actions. Discover how enabling legislation shapes policy execution and affects your rights by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
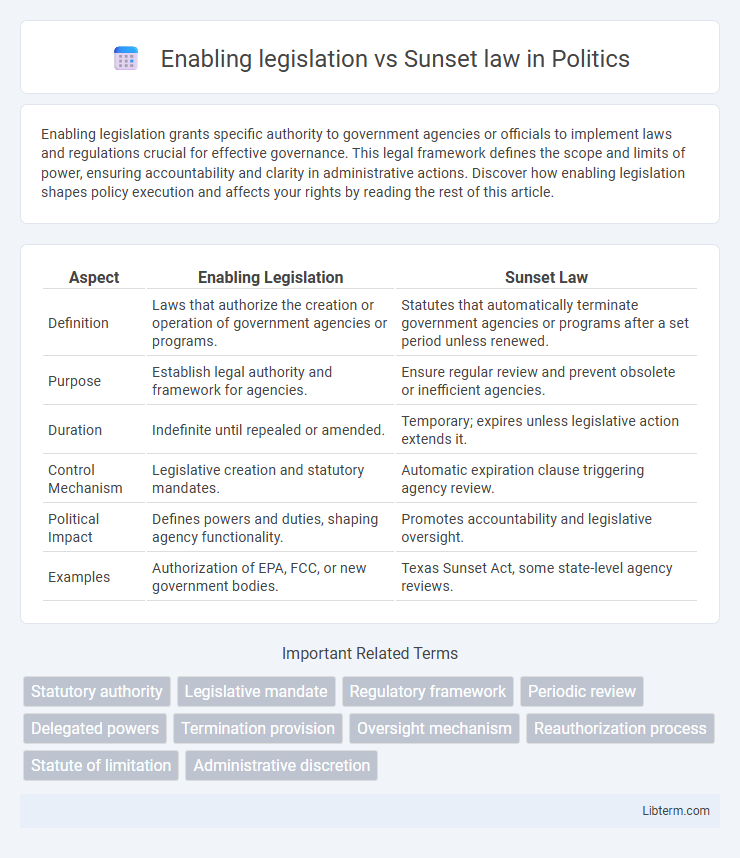
| Aspect | Enabling Legislation | Sunset Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laws that authorize the creation or operation of government agencies or programs. | Statutes that automatically terminate government agencies or programs after a set period unless renewed. |
| Purpose | Establish legal authority and framework for agencies. | Ensure regular review and prevent obsolete or inefficient agencies. |
| Duration | Indefinite until repealed or amended. | Temporary; expires unless legislative action extends it. |
| Control Mechanism | Legislative creation and statutory mandates. | Automatic expiration clause triggering agency review. |
| Political Impact | Defines powers and duties, shaping agency functionality. | Promotes accountability and legislative oversight. |
| Examples | Authorization of EPA, FCC, or new government bodies. | Texas Sunset Act, some state-level agency reviews. |
Introduction to Enabling Legislation and Sunset Laws
Enabling legislation provides the legal authority for government agencies or bodies to operate and implement specific policies, defining the scope, powers, and responsibilities necessary for their functions. Sunset laws mandate the automatic expiration or review of statutes, agencies, or programs after a predetermined period unless renewed by legislative action, ensuring accountability and preventing obsolete regulations. Both frameworks serve to regulate the lifecycle and oversight of government functions but focus differently on authorization and discontinuation.
Defining Enabling Legislation
Enabling legislation refers to statutes enacted by a legislative body that grant specific powers or authority to government agencies, officials, or entities, allowing them to implement and enforce laws within defined parameters. This type of legislation provides the legal framework necessary for administrative bodies to create regulations, execute policies, and carry out their designated functions effectively. Unlike sunset laws, which set expiration dates for statutes or agencies, enabling legislation primarily focuses on establishing and empowering governmental functions.
Understanding the Concept of Sunset Laws
Sunset laws mandate the automatic expiration of government agencies or programs after a specified period unless renewed by legislative action, ensuring regular review and accountability. Enabling legislation, in contrast, establishes the authority and framework for creating agencies or programs, providing the legal basis for their operation. Understanding sunset laws highlights their role in preventing outdated or unnecessary entities from continuing indefinitely, promoting efficient governance.
Key Differences Between Enabling Legislation and Sunset Laws
Enabling legislation establishes the legal authority for government agencies or programs to operate, defining their powers, functions, and structure. Sunset laws mandate the automatic termination or review of these agencies or programs after a specific period unless renewed by legislative action. The key difference lies in enabling legislation creating and empowering entities, while sunset laws impose expiration to ensure accountability and prevent outdated or unnecessary government functions.
Purpose and Objectives of Enabling Legislation
Enabling legislation establishes the legal authority for agencies or entities to operate, outlining their powers, duties, and scope of action to implement specific policies or programs effectively. Its purpose is to provide a structured framework that empowers organizations to create rules and enforce regulations aligned with legislative intent. In contrast, sunset laws aim to periodically review and determine whether these agencies should continue to exist, ensuring accountability and preventing outdated or unnecessary government functions.
Purpose and Objectives of Sunset Laws
Sunset laws are designed to systematically evaluate government agencies, programs, or regulations by setting predetermined expiration dates unless explicitly renewed, thereby promoting accountability and reducing inefficiency. Enabling legislation, in contrast, establishes and grants authority to these agencies or programs in the first place. The primary purpose of sunset laws is to ensure continual assessment and justify the ongoing existence of government functions, preventing outdated or ineffective operations from persisting indefinitely.
Impact on Governmental Agencies and Programs
Enabling legislation establishes the legal authority for governmental agencies and programs, defining their structure, functions, and powers, which provides stability and continuity in public administration. Sunset laws mandate automatic termination or periodic review of agencies and programs, ensuring accountability and preventing redundancy by requiring legislative approval to continue operations. The impact on government includes enhanced oversight, potential restructuring, and the promotion of efficiency through regular evaluation and elimination of obsolete entities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Enabling Legislation
Enabling legislation grants specific powers to government agencies or entities, allowing them to create regulations within a defined scope, which streamlines decision-making and policy implementation. Its advantages include providing clear authority and flexibility for agencies to address complex issues, while disadvantages involve the potential for overreach and lack of direct legislative oversight. Unlike sunset laws that impose automatic expiration dates on statutes, enabling legislation ensures ongoing operational authority without requiring periodic renewal.
Pros and Cons of Sunset Laws
Sunset laws automatically terminate government agencies or programs after a specific period unless renewed by legislation, promoting accountability and reducing wasteful spending but risking disruption if critical services face abrupt cutoffs. These laws encourage periodic review and evaluation of agency effectiveness, fostering transparency and efficient resource allocation. However, the rigid expiration dates may lead to rushed decision-making or loss of valuable institutional knowledge if extensions or renewals are not timely approved.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Enabling legislation grants agencies specific powers to create and enforce regulations, such as the Clean Air Act empowering the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to set emission standards. Sunset laws require periodic review and potential termination of agencies or regulations, exemplified by Texas' Sunset Act, which mandates the regular evaluation of state agencies to determine their effectiveness and necessity. Case studies reveal how enabling statutes drive regulatory frameworks while sunset provisions promote accountability and adaptability in government functions.
Enabling legislation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com