The ideological base forms the foundation of any political or social movement, shaping its values, goals, and strategies. Understanding this core helps you grasp how beliefs influence policies and actions within a group or society. Explore the rest of the article to discover how different ideological bases impact governance and social change.
Table of Comparison
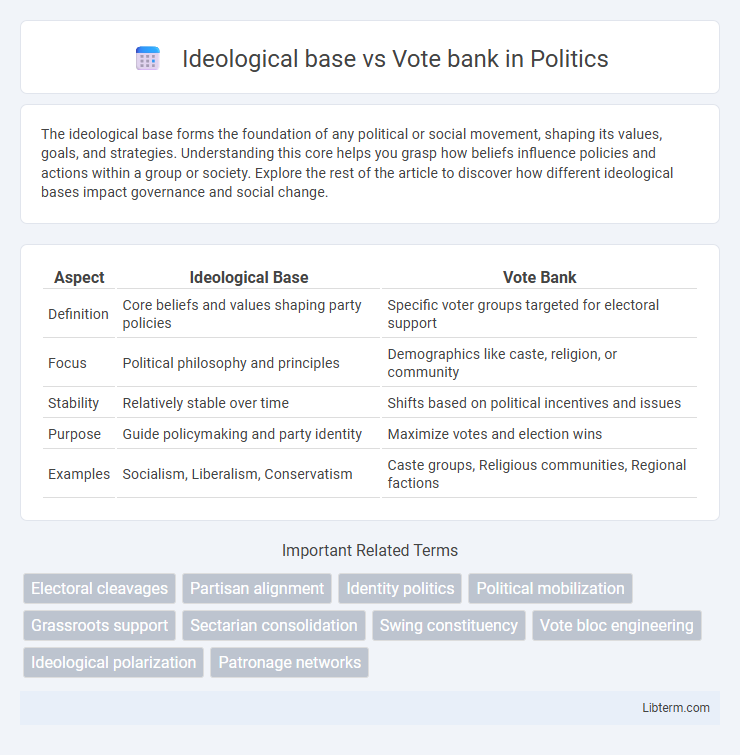
| Aspect | Ideological Base | Vote Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core beliefs and values shaping party policies | Specific voter groups targeted for electoral support |
| Focus | Political philosophy and principles | Demographics like caste, religion, or community |
| Stability | Relatively stable over time | Shifts based on political incentives and issues |
| Purpose | Guide policymaking and party identity | Maximize votes and election wins |
| Examples | Socialism, Liberalism, Conservatism | Caste groups, Religious communities, Regional factions |
Understanding the Ideological Base in Politics
The ideological base in politics refers to a core set of beliefs and principles that guide a political party's policies and actions, forming a coherent worldview that appeals to voters with shared values. Unlike a vote bank, which targets specific demographic groups for electoral support regardless of ideology, the ideological base fosters long-term loyalty through consistent and principled stances on social, economic, and cultural issues. Understanding this distinction helps clarify how parties build sustainable support beyond transactional vote-seeking, shaping stable political identities and issue-based engagement.
Defining the Concept of Vote Bank
A vote bank refers to a specific group of voters who consistently support a particular political party or candidate based on shared interests, identity, or communal affiliations rather than broad ideological alignment. Unlike an ideological base, which is driven by cohesive political beliefs and principles, a vote bank is anchored in social, religious, ethnic, or economic factors that ensure loyalty. This concept is crucial for understanding electoral strategies where politicians prioritize securing these reliable voter groups to maintain power.
Historical Evolution of Ideological Politics
The historical evolution of ideological politics traces how political parties initially formed around coherent ideologies reflecting class struggles and social reforms, such as Marxism or liberalism, gradually shifting in many democracies toward vote bank politics centered on identity groups and communal interests. Early democratic systems emphasized ideological platforms advocating economic policies and governance models, while later phases saw parties prioritize electoral gains through targeted appeals to caste, religion, or ethnic communities. This transformation impacted the nature of political representation, often diluting ideological consistency in favor of consolidating electoral support from specific social segments.
Vote Bank Politics: Roots and Growth
Vote bank politics originated as a strategy where political parties mobilize specific communities or social groups based on identity factors such as religion, caste, or ethnicity to secure electoral support. The growth of vote bank politics has been driven by the fragmentation of society and the emphasis on catering to narrow interests rather than broader ideological commitments. This phenomenon has contributed to political polarization, weakening policy coherence and democratic accountability by prioritizing group loyalty over national or ideological considerations.
Key Differences: Ideological Base vs Vote Bank
An ideological base consists of voters united by shared political beliefs and values, guiding consistent policy support, while a vote bank relies on securing electoral support from specific social groups through identity, caste, religion, or economic interests. Ideological bases tend to promote long-term party loyalty and policy-driven agendas, whereas vote banks often seek short-term electoral gains by catering to group-specific demands. The influence of an ideological base shapes party ideology and governance, contrasting with vote banks that prioritize electoral arithmetic over ideological coherence.
Impact on Policy-Making and Governance
An ideological base shapes consistent policy-making by aligning governance with core principles, ensuring long-term strategic goals and reforms. A vote bank prioritizes immediate electoral gains, often leading to populist measures that may compromise policy coherence and administrative efficiency. The dominance of vote bank politics can result in fragmented governance and short-term decision-making, whereas a strong ideological base fosters stable and principle-driven governance.
Voter Behavior: Loyalty or Pragmatism?
Voter behavior often oscillates between ideological base loyalty and pragmatic vote bank considerations, with electoral decisions influenced by core political beliefs or immediate material benefits. Ideological voters prioritize consistent alignment with party principles, reflecting deep-rooted values and long-term policy goals. Conversely, pragmatic voters shift support based on candidate performance, socio-economic incentives, and short-term gains, highlighting the complex dynamics shaping electoral outcomes.
Case Studies: Ideology vs Vote Bank in Practice
Case studies of Indian politics reveal how ideological commitment often clashes with the pragmatic pursuit of vote banks, as seen in the BJP's promotion of Hindutva ideology contrasted with its strategic outreach to OBCs and Dalits for electoral gains. The Congress party's historical reliance on a secular and inclusive ideology is frequently tested by its dependence on caste-based vote banks such as the Yadavs in Uttar Pradesh and Muslims nationwide. These examples demonstrate the tension between maintaining doctrinal purity and adapting to the demands of India's complex socio-political landscape to secure electoral success.
Challenges to Democratic Integrity
Ideological bases prioritize consistent policy values and principles, fostering informed voter engagement, while vote banks emphasize securing electoral support through caste, religion, or regional affiliations, risking identity politics. This practice challenges democratic integrity by promoting fragmentation and undermining merit-based leadership, leading to biased policymaking and reduced accountability. Persistent reliance on vote banks weakens the representational quality of democracy and exacerbates social divisions.
Future Trends: Shifting Political Dynamics
Future trends in political dynamics reveal a gradual shift from rigid ideological bases toward more fluid vote bank strategies driven by identity politics and issue-based mobilization. Political parties increasingly leverage data analytics and social media to target specific demographic groups, reflecting a move away from traditional ideology-centric approaches. This evolution indicates a nuanced electorate where emotional and material incentives often outweigh strict ideological commitments, reshaping campaign strategies and voter engagement patterns.
Ideological base Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com