Recall elections empower voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, ensuring accountability and responsiveness in government. This democratic tool varies by jurisdiction but typically requires a petition and a special vote to succeed. Explore how recall elections work and their impact on your community in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
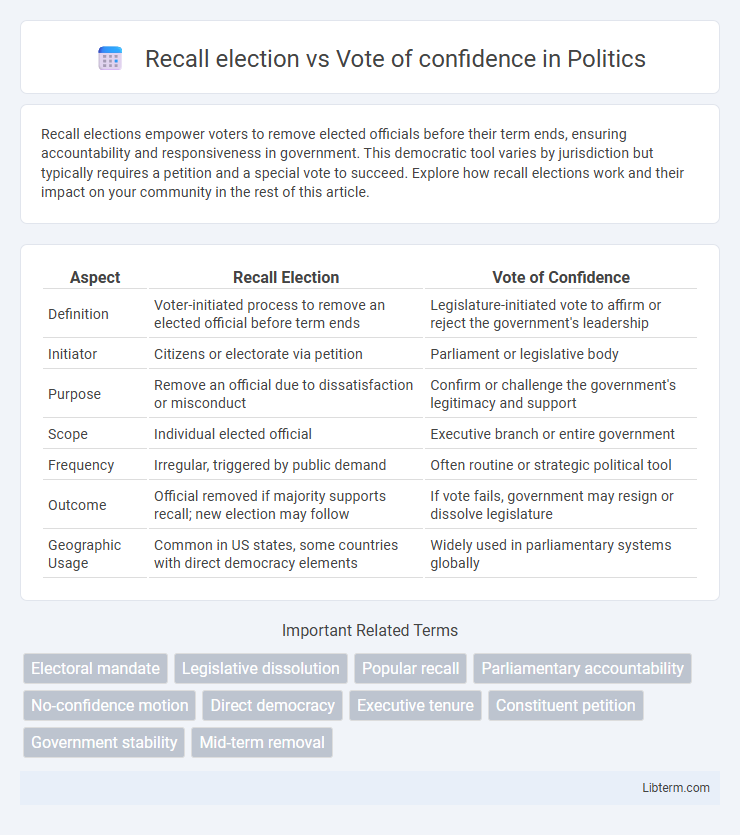
| Aspect | Recall Election | Vote of Confidence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voter-initiated process to remove an elected official before term ends | Legislature-initiated vote to affirm or reject the government's leadership |
| Initiator | Citizens or electorate via petition | Parliament or legislative body |
| Purpose | Remove an official due to dissatisfaction or misconduct | Confirm or challenge the government's legitimacy and support |
| Scope | Individual elected official | Executive branch or entire government |
| Frequency | Irregular, triggered by public demand | Often routine or strategic political tool |
| Outcome | Official removed if majority supports recall; new election may follow | If vote fails, government may resign or dissolve legislature |
| Geographic Usage | Common in US states, some countries with direct democracy elements | Widely used in parliamentary systems globally |
Understanding Recall Elections: Definition and Purpose
Recall elections enable voters to remove elected officials from office before their terms end, serving as a direct democratic mechanism for accountability. These elections are initiated through petitions or legislatures when officials are perceived to have failed in their duties or violated public trust. In contrast, a vote of confidence is typically a parliamentary procedure used to determine if a sitting government retains majority support, affecting its ability to govern rather than removing individual officials.
What is a Vote of Confidence? Key Concepts
A vote of confidence is a parliamentary procedure where legislators express their support or lack thereof for a government or a specific leader, typically the prime minister. This key mechanism ensures that the executive maintains the legislature's backing to govern effectively, often influencing the stability of the administration. Unlike a recall election, which allows voters to remove an elected official before the end of their term, a vote of confidence is conducted within the legislative body and reflects the political majority's approval.
Historical Origins of Recall Elections and Votes of Confidence
The historical origins of recall elections trace back to early 20th-century American progressive reforms designed to increase direct democracy and hold elected officials accountable between regular elections. Votes of confidence originated in the parliamentary systems of 19th-century Europe as a mechanism for the legislature to express support or withdraw support from the sitting government, thereby influencing its survival. Both mechanisms serve as tools for political accountability but emerged in distinct political contexts reflecting different approaches to democratic governance.
Legal Framework: Recall Elections vs Vote of Confidence
Recall elections and votes of confidence serve as mechanisms to assess the legitimacy and support of elected officials within democratic systems. Recall elections allow voters to remove an incumbent from office before the end of their term through a formal petition and subsequent vote, governed by specific legal statutes outlining qualifications, grounds, and procedural requirements. Votes of confidence are parliamentary tools, legally embedded in constitutional or legislative frameworks, enabling legislatures to express support or withdraw it from a government or leader, which may trigger resignation or new elections if the confidence is lost.
Procedure and Process Comparison
Recall elections and votes of confidence serve distinct democratic functions, with recall elections initiated by citizens seeking to remove an elected official before their term ends, requiring a petition process and subsequent public vote. Votes of confidence are parliamentary mechanisms initiated by the government or legislature to test whether the sitting administration retains majority support, typically involving a formal debate and a legislative vote. The recall process emphasizes direct voter participation and signature thresholds, while votes of confidence center on legislative procedures and majority rule within representative bodies.
Who Initiates: Citizens or Legislators?
Recall elections are initiated by citizens through a petition process that gathers a required number of signatures to remove an elected official before their term ends. Votes of confidence are initiated by legislators within a parliamentary system to confirm or withdraw support from the current government or leader. This fundamental difference highlights the direct democratic power wielded by citizens in recall elections versus the institutional control exercised by legislators in votes of confidence.
Impact on Political Stability and Governance
Recall elections disrupt political stability by enabling voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, often leading to governance uncertainties and potential policy reversals. Votes of confidence, typically initiated within legislative bodies, reinforce political legitimacy when passed, promoting stable governance by affirming support for the incumbent government or leader. Frequent recall elections can cause political fragmentation, while successful votes of confidence strengthen institutional continuity and coherent policy implementation.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Recall Elections
Recall elections allow voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, a democratic mechanism seen in countries like the United States and the Philippines. Prominent case studies include the 2003 California recall election that ousted Governor Gray Davis and the 2022 recall of Chilean senators, illustrating varying political contexts and legal frameworks. Unlike votes of confidence, which assess government legitimacy in parliamentary systems, recall elections empower citizens to directly challenge individual officeholders globally.
Vote of Confidence in Parliamentary Systems
A Vote of Confidence in parliamentary systems is a formal mechanism whereby the legislature expresses its support or lack thereof for the sitting government, directly impacting its ability to govern. Unlike a recall election, which allows voters to remove an elected official before the end of their term through a public vote, a Vote of Confidence occurs within the parliament and can trigger the government's resignation or a call for new elections if the vote fails. This procedure reinforces parliamentary accountability by ensuring that the executive maintains the legislature's approval to continue in office.
Pros and Cons: Recall Election vs Vote of Confidence
Recall elections empower citizens to remove elected officials before their term ends, enhancing direct democratic accountability but can lead to political instability and frequent costly elections. Votes of confidence serve as parliamentary tools to test government legitimacy, promoting governmental stability and continuity, yet may concentrate power within the legislative majority and reduce public participation. Both mechanisms balance accountability and governance risks, with recall elections prioritizing voter influence and votes of confidence emphasizing institutional checks.
Recall election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com