A Trojan horse is a type of malware that deceives users by masquerading as legitimate software, allowing cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to your system. It can steal sensitive information, install additional malicious programs, or create backdoors for remote control. Discover how to identify, prevent, and remove Trojan horses by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
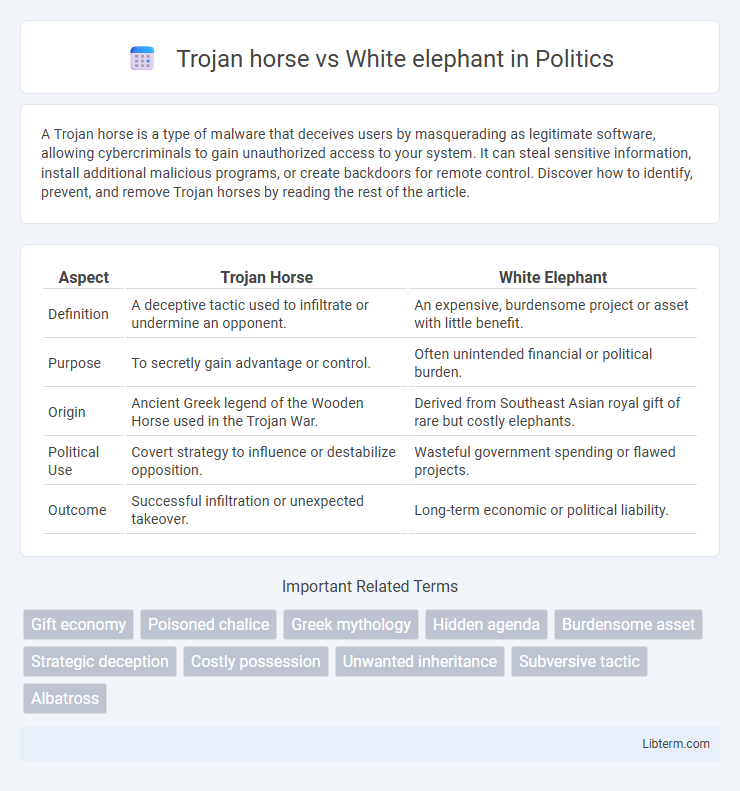
| Aspect | Trojan Horse | White Elephant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A deceptive tactic used to infiltrate or undermine an opponent. | An expensive, burdensome project or asset with little benefit. |
| Purpose | To secretly gain advantage or control. | Often unintended financial or political burden. |
| Origin | Ancient Greek legend of the Wooden Horse used in the Trojan War. | Derived from Southeast Asian royal gift of rare but costly elephants. |
| Political Use | Covert strategy to influence or destabilize opposition. | Wasteful government spending or flawed projects. |
| Outcome | Successful infiltration or unexpected takeover. | Long-term economic or political liability. |
Introduction: Understanding the Metaphors
The Trojan horse metaphor refers to a deceptive gift or strategy that hides harmful intentions within a seemingly beneficial offering, originating from the ancient Greek story of the Greeks infiltrating Troy. In contrast, a white elephant symbolizes a burdensome possession that is costly to maintain and offers little practical value, derived from the historical practice of Southeast Asian monarchs gifting rare albino elephants to impose financial strain. Understanding these metaphors reveals how language encapsulates complex concepts of hidden danger and costly burdens in cultural discourse.
Origins of Trojan Horse and White Elephant
The Trojan Horse originates from ancient Greek mythology, specifically during the Trojan War as described in Homer's epics and Virgil's Aeneid, where Greeks used a giant wooden horse to infiltrate and conquer the city of Troy. The White Elephant concept traces back to Southeast Asia, particularly Thailand and Burma, where rare albino elephants were considered sacred and burdensome royal gifts due to their upkeep costs and inability to be used for labor. Both terms have evolved metaphorically, with the Trojan Horse symbolizing deceptive tactics and the White Elephant representing costly possessions with little practical value.
Symbolic Meanings Explained
The Trojan Horse symbolizes deceptive danger hidden within something seemingly beneficial, representing betrayal and strategic cunning in historical and literary contexts. The White Elephant signifies burdensome gifts or possessions that are costly to maintain and difficult to dispose of, embodying unwanted responsibility and extravagance. Both symbols convey contrasting messages: the Trojan Horse warns of covert threats, while the White Elephant highlights the issue of impractical or excessive obligations.
Historical Instances in Context
The Trojan Horse symbolizes deceptive tactics dating back to ancient Greek mythology, where Greeks used a wooden horse to infiltrate and capture the city of Troy around 1200 BCE. In contrast, the White Elephant originates from Southeast Asian history, particularly in Thailand and Burma, where these rare albino elephants were considered sacred but often burdensome gifts that drained financial resources. Both terms illustrate historical instances of objects embodying hidden costs or strategic cunning within their respective cultural and temporal contexts.
Trojan Horse: Deception and Hidden Dangers
The Trojan Horse symbolizes deception through its guise as a gift that concealed hidden dangers, allowing enemies to infiltrate and cause destruction from within. This metaphor highlights the risks of trusting seemingly beneficial offers without thorough scrutiny, emphasizing vulnerability to covert threats. Understanding the Trojan Horse's legacy is crucial for recognizing and guarding against hidden dangers in cybersecurity and strategic decision-making.
White Elephant: Burdensome Gifts and Costs
White Elephants symbolize burdensome gifts that impose significant maintenance costs without practical benefits, often becoming financial and logistical liabilities. Unlike Trojan horses, which are deceptive traps designed to infiltrate, White Elephants highlight the ongoing expenses tied to unwanted possessions such as large estates or outdated technology. The concept underscores the economic strain and resource drain caused by accepting or maintaining such costly, impractical assets.
Comparing Strategic Implications
Trojan horse strategies exploit deception by embedding hidden threats within seemingly beneficial initiatives, enabling adversaries to infiltrate and undermine from within, while white elephant projects involve costly, non-productive investments that drain resources without delivering proportional value. The strategic implication of a Trojan horse lies in its capacity to manipulate trust and gain covert control, posing direct risks to security and operational integrity. White elephant projects, conversely, undermine organizational efficiency and financial stability by consuming capital and attention without advancing core objectives, leading to long-term strategic drag.
Modern Usage in Business and Politics
The Trojan horse in modern business and politics represents deceptive strategies that infiltrate organizations, often through disguised partnerships or misleading information, to gain competitive advantage or political influence. The white elephant symbolizes costly, burdensome projects or assets that drain resources without providing proportional value, commonly seen in large-scale government initiatives or corporate investments. Understanding these concepts aids leaders in identifying hidden threats and avoiding inefficient commitments in strategic decision-making.
Lessons Learned from Both Metaphors
The Trojan horse metaphor teaches the importance of vigilance against hidden threats and deceptive appearances in cybersecurity and strategic planning. The white elephant symbolizes the cost of maintaining burdensome assets that provide little value, emphasizing prudent resource management and critical evaluation before commitment. Together, these metaphors highlight the necessity of balancing caution with wisdom to avoid costly mistakes and vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metaphor
Selecting the appropriate metaphor between Trojan horse and white elephant depends on context and intended message. The Trojan horse symbolizes hidden dangers or deceit, often highlighting risks in seemingly beneficial situations. The white elephant represents costly burdens or impractical possessions, emphasizing wasted resources and maintenance challenges.
Trojan horse Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com