Halakhah, the collective body of Jewish religious laws derived from the Torah, Talmud, and rabbinic rulings, governs daily life, ethics, and religious practices for observant Jews. It provides detailed guidance on rituals, dietary laws, prayer, and interpersonal conduct, shaping the spiritual and communal identity of Jewish people. Discover how Halakhah influences various aspects of Jewish tradition by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
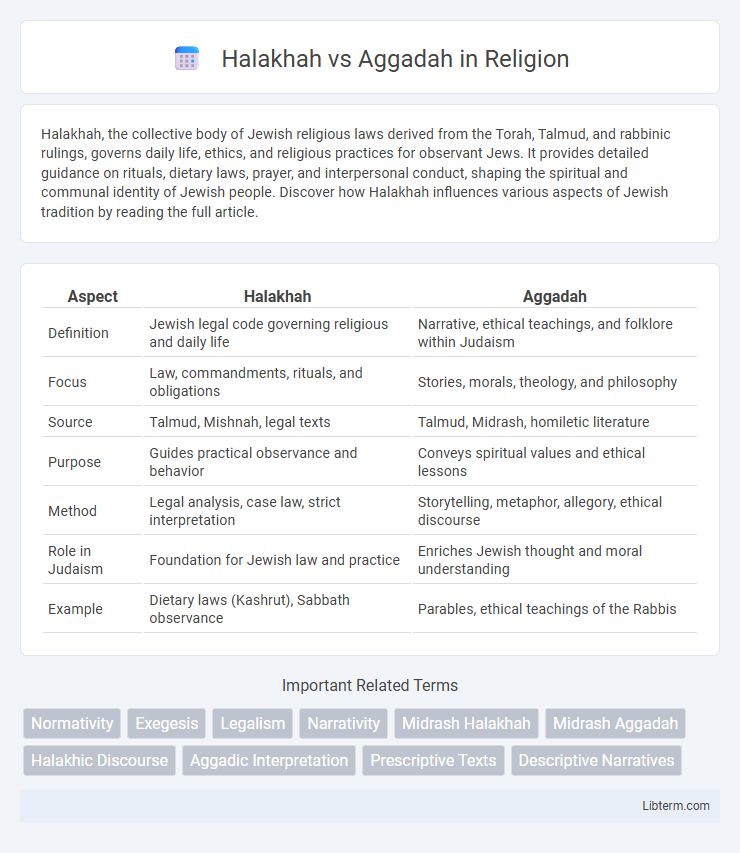
| Aspect | Halakhah | Aggadah |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jewish legal code governing religious and daily life | Narrative, ethical teachings, and folklore within Judaism |
| Focus | Law, commandments, rituals, and obligations | Stories, morals, theology, and philosophy |
| Source | Talmud, Mishnah, legal texts | Talmud, Midrash, homiletic literature |
| Purpose | Guides practical observance and behavior | Conveys spiritual values and ethical lessons |
| Method | Legal analysis, case law, strict interpretation | Storytelling, metaphor, allegory, ethical discourse |
| Role in Judaism | Foundation for Jewish law and practice | Enriches Jewish thought and moral understanding |
| Example | Dietary laws (Kashrut), Sabbath observance | Parables, ethical teachings of the Rabbis |
Introduction to Halakhah and Aggadah
Halakhah refers to the collective body of Jewish law derived from the Written and Oral Torah, outlining legal, ethical, and ritual obligations guiding daily life, while Aggadah encompasses the narrative, ethical teachings, and exegetical stories that provide moral and spiritual insight. Halakhah prioritizes legal norms and practical application, forming the foundation of Jewish practice, whereas Aggadah offers interpretive commentary that enriches understanding of scripture and tradition. Both components are integral to Rabbinic Judaism, balancing law and lore to shape Jewish identity and religious experience.
Defining Halakhah: Jewish Law
Halakhah, derived from the Hebrew root "halakh" meaning "to walk" or "to go," embodies the comprehensive Jewish legal system guiding religious, ethical, and social conduct. It includes commandments from the Torah, rabbinic enactments, and traditional interpretations, shaping daily life and communal norms. Halakhah contrasts with Aggadah, which encompasses narrative, folklore, and moral teachings without legal obligations.
Understanding Aggadah: Jewish Narrative
Aggadah encompasses the non-legalistic narratives, folklore, ethics, theology, and biblical exegesis found in rabbinic literature, providing rich insights into Jewish thought and spirituality beyond Halakhah's legal directives. These stories and teachings aim to inspire moral values, illustrate divine principles, and deepen the understanding of faith within the Jewish tradition. By exploring Aggadah, scholars and practitioners gain a nuanced appreciation of Jewish identity, history, and religious experience.
Historical Development of Halakhah and Aggadah
Halakhah and Aggadah emerged from the Jewish oral tradition, with Halakhah focusing on legal rulings and normative practices, while Aggadah encompasses narrative, ethics, and theology. Historically, Halakhah developed through the Mishnah and Talmud as a codified legal system guiding Jewish life, whereas Aggadah evolved as interpretive stories and moral lessons complementing the legal texts. The interplay between these two streams reflects the dynamic evolution of Rabbinic Judaism from the Second Temple period through the early medieval era.
Key Differences Between Halakhah and Aggadah
Halakhah consists of Jewish legal directives that regulate religious and ethical behavior, while Aggadah encompasses non-legalistic teachings, including stories, morals, and theological reflections. Halakhah provides precise rules derived from the Torah and Talmud to guide daily life and ritual practice, whereas Aggadah offers interpretative narratives aimed at inspiring faith and conveying cultural values. The primary distinction lies in Halakhah's binding authority in Jewish law contrasted with Aggadah's role in shaping communal identity and spiritual understanding.
Roles and Functions in Jewish Tradition
Halakhah serves as the legal framework guiding Jewish religious practices, ethical behavior, and daily life, ensuring the preservation and application of Jewish law. Aggadah encompasses the narrative, ethical teachings, and theological insights that enrich spiritual understanding and cultural identity within Judaism. Together, Halakhah and Aggadah balance practical observance with moral and philosophical reflection, shaping the comprehensive religious experience.
Interplay and Tensions: Halakhah vs Aggadah
Halakhah and Aggadah form two complementary yet sometimes tension-filled pillars of Jewish tradition, where Halakhah codifies legal norms governing daily life, while Aggadah offers rich narrative, ethical teachings, and spiritual insights. The interplay between these spheres reflects dynamic interpretative processes, as Halakhah's rigid jurisprudence often encounters Aggadah's expansive, allegorical dimensions, prompting ongoing debates about authority and meaning in Jewish law and lore. This tension underscores a holistic Jewish worldview that balances practical observance with moral imagination, ensuring law remains both grounded and inspired.
Examples from Rabbinic Literature
Halakhah, the legal aspect of Rabbinic literature, dictates practical laws such as Sabbath observance outlined in the Mishnah and Talmud, while Aggadah encompasses narrative and ethical teachings, exemplified by the parables in the Midrash that convey moral lessons. Halakhic texts include tractates like Berakhot, which govern prayer regulations, whereas Aggadic texts feature stories like Rabbi Akiva's discussions highlighting faith and spirituality. These two dimensions together shape Jewish tradition by balancing law with rich interpretive storytelling.
Modern Relevance and Interpretation
Halakhah and Aggadah offer distinct yet complementary frameworks within Jewish tradition, where Halakhah prescribes legal codes guiding ethical behavior, and Aggadah provides narrative, folklore, and ethical teachings enriching spiritual understanding. In modern interpretation, Halakhah adapts to contemporary issues such as bioethics, technology, and social justice, maintaining continuity with ancient laws while addressing evolving societal norms. Aggadah's value lies in its capacity to inspire and contextualize identity, offering metaphorical insights and moral lessons that resonate with modern existential questions and cross-cultural dialogue.
Conclusion: Harmony Within Diversity
Halakhah and Aggadah represent two complementary dimensions of Jewish tradition, with Halakhah focusing on legal rulings and practical observance, while Aggadah emphasizes ethical teachings, narratives, and spiritual insights. Their coexistence creates a dynamic balance, allowing Jewish law and lore to inform and enrich one another within a unified framework. This harmony within diversity reflects the multifaceted nature of Judaism, fostering a holistic approach to faith and practice.
Halakhah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com