Salvation represents the deliverance from sin and its consequences, often seen as a central concept in many religious beliefs. It offers hope, redemption, and a path to eternal peace, emphasizing spiritual renewal and moral transformation. Discover how understanding salvation can profoundly impact Your faith and life by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
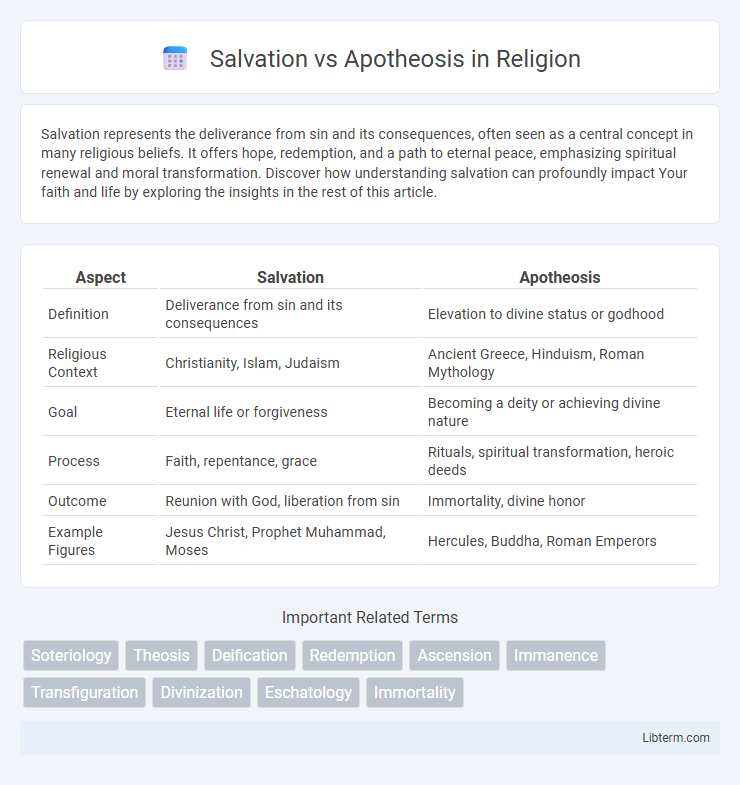
| Aspect | Salvation | Apotheosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliverance from sin and its consequences | Elevation to divine status or godhood |
| Religious Context | Christianity, Islam, Judaism | Ancient Greece, Hinduism, Roman Mythology |
| Goal | Eternal life or forgiveness | Becoming a deity or achieving divine nature |
| Process | Faith, repentance, grace | Rituals, spiritual transformation, heroic deeds |
| Outcome | Reunion with God, liberation from sin | Immortality, divine honor |
| Example Figures | Jesus Christ, Prophet Muhammad, Moses | Hercules, Buddha, Roman Emperors |
Understanding Salvation: Definition and Origins
Salvation refers to the deliverance from sin or its consequences, often emphasized in religious contexts such as Christianity, where it involves redemption through faith in Jesus Christ. Its origins trace back to ancient religious traditions that seek liberation from suffering or spiritual bondage, highlighting a path to eternal life or spiritual renewal. Understanding salvation entails exploring its theological definitions, historical interpretations, and its role as a foundational concept in various spiritual doctrines.
Apotheosis Explained: From Myth to Modernity
Apotheosis refers to the elevation of an individual to divine status, a concept rooted in ancient mythologies where heroes or rulers were deified after death or through extraordinary feats. In modernity, apotheosis transcends literal deification and often symbolizes ultimate achievement or glorification in culture, literature, and art. This transformation from myth to metaphor highlights humanity's persistent quest to embody perfection and transcend ordinary existence through symbolic or actual exaltation.
Historical Contexts: Salvation in World Religions
Salvation in world religions is often centered on the liberation from sin, suffering, or the cycle of rebirth, as seen in Christianity's emphasis on redemption through Jesus Christ, Hinduism's moksha, and Buddhism's nirvana. These diverse traditions share the goal of spiritual freedom but differ in methods and theological frameworks, with salvation typically involving divine grace, moral conduct, or enlightenment. Historically, salvation served as the foundation for ethical systems and communal identities, shaping cultural and religious narratives across civilizations.
Apotheosis in Ancient Cultures and Philosophies
Apotheosis, the elevation of a mortal to divine status, played a central role in ancient cultures such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome, often symbolizing ultimate spiritual fulfillment or heroic transcendence. In Greek philosophy, apotheosis involved the soul's ascent to the divine realm, reflecting ideals of virtue and enlightenment as seen in the works of Plato and Plotinus. Egyptian pharaohs and Roman emperors were frequently deified posthumously, reinforcing political power and cosmic order through ritualized worship and mythological narratives.
Core Differences Between Salvation and Apotheosis
Salvation primarily refers to the deliverance from sin and its consequences, often emphasizing redemption through a divine figure or grace, while apotheosis involves the elevation or deification of a person to a god-like status. Salvation is typically associated with spiritual rescue and eternal life in a transcendent realm, whereas apotheosis centers on transformation into a divine being or achieving immortality on a metaphysical plane. The core difference lies in salvation's focus on being saved from a fallen state versus apotheosis's emphasis on ascending to divine perfection or status.
Salvation Narratives: Themes of Redemption
Salvation narratives emphasize themes of redemption through sacrifice, forgiveness, and transformation, illustrating how individuals attain spiritual renewal and liberation from sin. Central to these stories is the concept of divine grace, which enables believers to overcome moral failings and achieve eternal life. The recurring motif of redemption underscores humanity's quest for reconciliation with the divine and restoration of spiritual harmony.
Apotheosis Narratives: Humans Becoming Divine
Apotheosis narratives depict humans transcending mortality to achieve divine status, often through heroic acts, spiritual enlightenment, or supernatural intervention. These stories emphasize transformation, immortality, and the attainment of god-like powers, reflecting cultural ideals of perfection and ultimate ascension. Iconic examples include the deification of figures such as Hercules in Greek mythology and the emperor Augustus in Roman history.
Intersection in Literature and Popular Culture
Salvation and apotheosis intersect in literature and popular culture through themes of transformation and transcendence, where characters achieve redemption or divine status. Works like Dante's *Divine Comedy* blend salvation's spiritual liberation with apotheosis's glorification, illustrating nuanced portrayals of human evolution. Popular media often depict protagonists undergoing both saving grace and godlike empowerment, highlighting humanity's complex quest for meaning and ultimate perfection.
Philosophical Implications of Both Concepts
Salvation and apotheosis represent distinct philosophical paradigms addressing human transcendence and ultimate purpose. Salvation typically involves liberation from sin or existential suffering through external divine intervention or grace, emphasizing moral redemption and spiritual renewal. Apotheosis, in contrast, connotes self-deification or the elevation of the mortal to divine status, highlighting human potential, self-realization, and the transformative power of individual agency within metaphysical frameworks.
Contemporary Perspectives: Relevance in Today’s World
Contemporary perspectives on salvation and apotheosis emphasize their relevance in the search for personal meaning and spiritual fulfillment amid rapid societal changes. Salvation often addresses the human desire for redemption and moral alignment within religious frameworks, while apotheosis symbolizes self-transcendence and the realization of one's highest potential beyond traditional spirituality. These concepts intersect in modern discourse on mental health, existential purpose, and transformative experiences, reflecting ongoing cultural shifts toward holistic well-being and self-actualization.
Salvation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com