Falun Gong is a spiritual practice combining meditation, gentle exercises, and moral philosophy centered on truthfulness, compassion, and tolerance. Originating in China in the early 1990s, it has gained a global following despite facing severe persecution and censorship from the Chinese government. Discover how Falun Gong's teachings and the ongoing challenges it faces impact practitioners worldwide by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
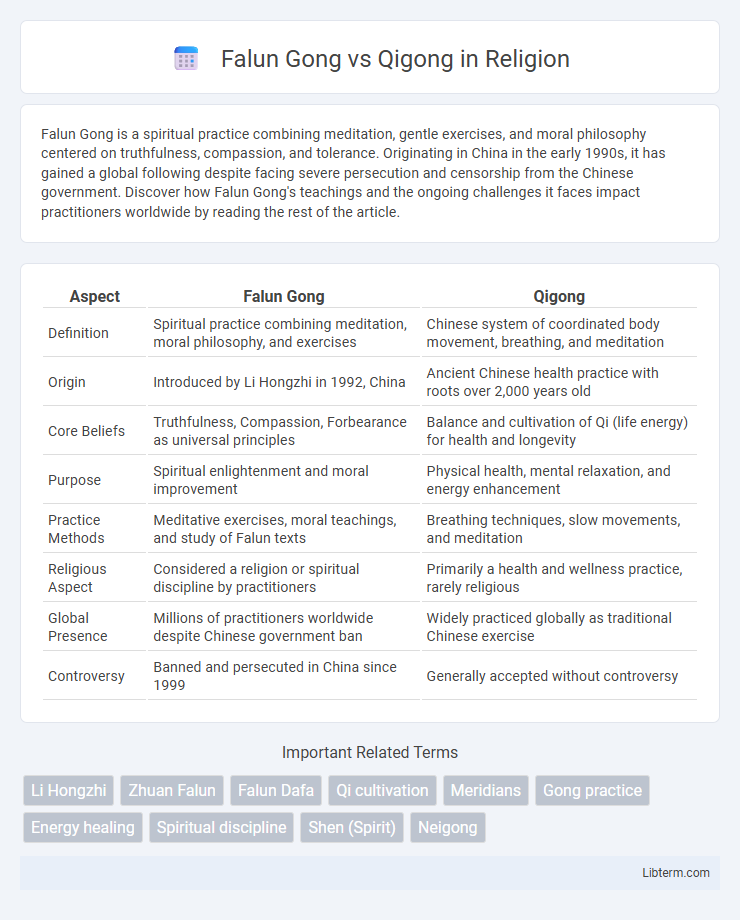
| Aspect | Falun Gong | Qigong |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual practice combining meditation, moral philosophy, and exercises | Chinese system of coordinated body movement, breathing, and meditation |
| Origin | Introduced by Li Hongzhi in 1992, China | Ancient Chinese health practice with roots over 2,000 years old |
| Core Beliefs | Truthfulness, Compassion, Forbearance as universal principles | Balance and cultivation of Qi (life energy) for health and longevity |
| Purpose | Spiritual enlightenment and moral improvement | Physical health, mental relaxation, and energy enhancement |
| Practice Methods | Meditative exercises, moral teachings, and study of Falun texts | Breathing techniques, slow movements, and meditation |
| Religious Aspect | Considered a religion or spiritual discipline by practitioners | Primarily a health and wellness practice, rarely religious |
| Global Presence | Millions of practitioners worldwide despite Chinese government ban | Widely practiced globally as traditional Chinese exercise |
| Controversy | Banned and persecuted in China since 1999 | Generally accepted without controversy |
Introduction to Falun Gong and Qigong
Falun Gong, also known as Falun Dafa, is a spiritual practice combining meditation, slow-moving exercises, and a moral philosophy rooted in the principles of truthfulness, compassion, and tolerance. Qigong is an ancient Chinese practice integrating physical postures, breathing techniques, and focused intention to cultivate and balance qi, or vital energy, for health and healing. While Falun Gong is a specific system with a strong emphasis on spiritual cultivation and ethical behavior, Qigong encompasses a broader range of practices aimed primarily at improving physical and mental well-being.
Origins and Historical Background
Falun Gong, introduced by Li Hongzhi in China in 1992, blends spiritual teachings with meditation and qigong exercises, emphasizing moral principles rooted in Buddhism and Taoism. Qigong, an ancient practice dating back over 4,000 years, centers on cultivating and balancing qi energy through physical movements, breathing techniques, and meditation, deeply embedded in traditional Chinese medicine and philosophy. While both share elements of energy cultivation, Falun Gong distinguishes itself with a unique spiritual framework and modern origins compared to the broad historical development of qigong.
Core Beliefs and Philosophies
Falun Gong emphasizes the principles of Truthfulness, Compassion, and Forbearance, focusing on spiritual cultivation and moral integrity to achieve enlightenment and improve health. Qigong generally centers on cultivating vital energy (qi) through physical exercises, breathing techniques, and meditation for health and wellness without a defined set of spiritual or moral doctrines. Falun Gong integrates a specific worldview with Buddhist and Taoist elements, while Qigong practices vary widely and typically do not include a unified philosophical framework.
Key Practices and Techniques
Falun Gong emphasizes meditation, Falun Gong exercises, and the cultivation of moral principles based on truthfulness, compassion, and tolerance, integrating spiritual beliefs with physical practice. Qigong encompasses a wide range of practices including breathing techniques, dynamic movements, and meditation aimed at cultivating and balancing qi (life energy) for health and vitality. Whereas Falun Gong is a specific spiritual discipline with a defined set of exercises and ethical teachings, Qigong represents a broader category of traditional Chinese energy practices used for healing and wellness.
Spiritual vs. Health-focused Approaches
Falun Gong emphasizes a spiritual cultivation centered on the principles of truthfulness, compassion, and forbearance, promoting moral and ethical self-improvement alongside meditation and exercises. Qigong primarily focuses on health enhancement and physical well-being through breath control, movement, and energy flow regulation, aiming to balance the body's qi for medical and fitness benefits. The spiritual dimension of Falun Gong distinguishes it from general Qigong practices that prioritize physical health outcomes without an overarching religious or philosophical doctrine.
Organizational Structure and Leadership
Falun Gong operates under a decentralized structure without formal leadership, relying on individual practice and grassroots dissemination, contrasting sharply with traditional Qigong organizations that often maintain hierarchical leadership and formal institutional frameworks. Falun Gong's global spread depends on practitioner networks and self-organized study groups, whereas Qigong schools are typically led by recognized masters or governing bodies that oversee training and certification. This fundamental difference shapes their respective mobilization strategies, with Falun Gong emphasizing spiritual self-cultivation outside formal institutions and Qigong emphasizing structured training within established organizations.
Public Perception and Media Coverage
Falun Gong's public perception is deeply polarized, with widespread media coverage highlighting its spiritual teachings contrasted by reports of controversy and government suppression, especially in China where it is banned. Qigong, seen as a traditional Chinese health practice, generally receives neutral or positive media attention focused on wellness and martial arts benefits. Media portrayal of Falun Gong emphasizes political conflict and human rights issues, whereas Qigong is primarily presented as a cultural and therapeutic discipline.
Government Relations and Controversies
Falun Gong, a spiritual practice combining meditation and moral philosophy, has faced severe government repression in China since its 1999 ban due to its rapid growth and perceived threat to the Communist Party's control, resulting in widespread human rights controversies and international criticism. In contrast, Qigong, a broader category of traditional Chinese energy exercises, generally maintains a more neutral relationship with the government, often being promoted as a health practice and cultural heritage. The Chinese government's crackdown on Falun Gong includes propaganda campaigns and alleged human rights abuses, distinguishing it sharply from the more apolitical and government-accepted status of mainstream Qigong groups.
Health Benefits and Scientific Studies
Falun Gong and Qigong both emphasize slow movements and meditation, promoting improved circulation, stress reduction, and enhanced mental clarity. Scientific studies on Qigong report benefits such as lowered blood pressure, increased immune function, and reduced anxiety, while research on Falun Gong, though more limited, suggests improvements in psychological well-being and physical endurance. Health benefits of both practices are linked to their holistic approach combining physical exercise, deep breathing, and mindfulness, contributing to overall wellness and chronic disease management.
Comparative Analysis: Falun Gong vs. Qigong
Falun Gong and Qigong both originate from traditional Chinese practices emphasizing energy cultivation and meditation, but Falun Gong incorporates a distinct moral philosophy centered on truthfulness, compassion, and forbearance, differentiating it from the broader Qigong systems that primarily focus on physical health and energy balance. Falun Gong's exercises combine gentle movements with these ethical principles, whereas Qigong encompasses diverse styles aimed at improving physical vitality, stress reduction, and spiritual growth without a unified doctrinal framework. The Chinese government's 1999 ban on Falun Gong due to its rapid growth and ideological influence starkly contrasts with the widespread state endorsement of various Qigong practices for health promotion.
Falun Gong Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com