Gnosticism emphasizes esoteric knowledge as the path to spiritual enlightenment and liberation from the material world's illusions. Rooted in ancient religious traditions, it contrasts the divine spark within humans against the flawed physical existence. Explore the profound beliefs and historical impact of Gnosticism in the detailed article ahead.
Table of Comparison
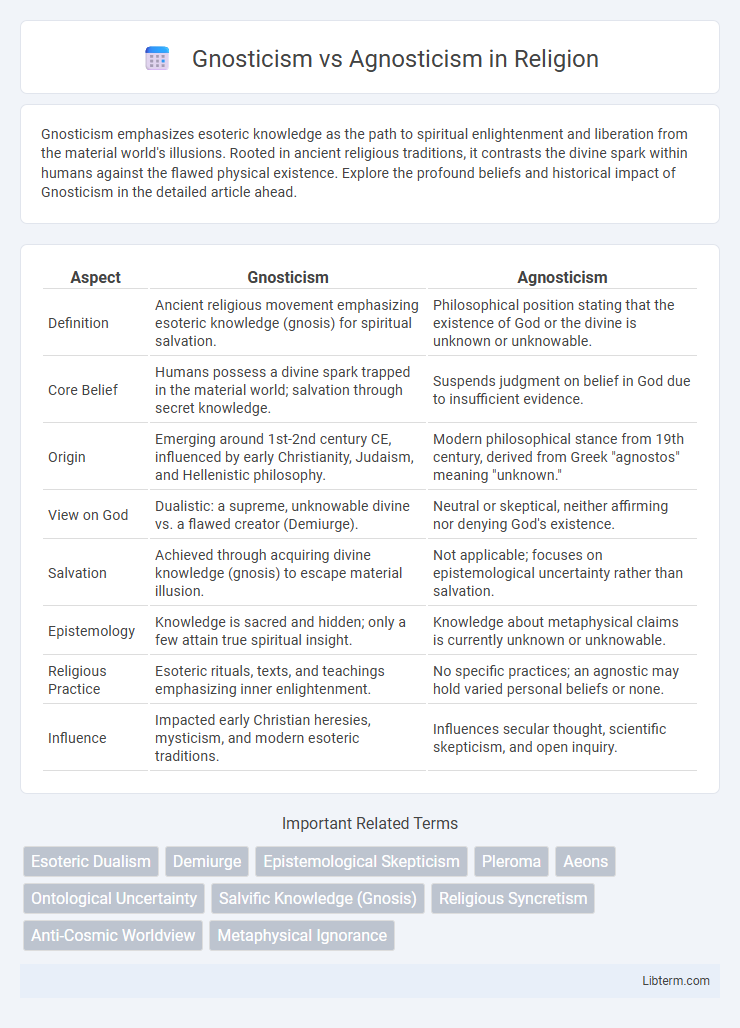
| Aspect | Gnosticism | Agnosticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ancient religious movement emphasizing esoteric knowledge (gnosis) for spiritual salvation. | Philosophical position stating that the existence of God or the divine is unknown or unknowable. |
| Core Belief | Humans possess a divine spark trapped in the material world; salvation through secret knowledge. | Suspends judgment on belief in God due to insufficient evidence. |
| Origin | Emerging around 1st-2nd century CE, influenced by early Christianity, Judaism, and Hellenistic philosophy. | Modern philosophical stance from 19th century, derived from Greek "agnostos" meaning "unknown." |
| View on God | Dualistic: a supreme, unknowable divine vs. a flawed creator (Demiurge). | Neutral or skeptical, neither affirming nor denying God's existence. |
| Salvation | Achieved through acquiring divine knowledge (gnosis) to escape material illusion. | Not applicable; focuses on epistemological uncertainty rather than salvation. |
| Epistemology | Knowledge is sacred and hidden; only a few attain true spiritual insight. | Knowledge about metaphysical claims is currently unknown or unknowable. |
| Religious Practice | Esoteric rituals, texts, and teachings emphasizing inner enlightenment. | No specific practices; an agnostic may hold varied personal beliefs or none. |
| Influence | Impacted early Christian heresies, mysticism, and modern esoteric traditions. | Influences secular thought, scientific skepticism, and open inquiry. |
Understanding Gnosticism: Core Beliefs
Gnosticism centers on esoteric knowledge (gnosis) as the path to spiritual enlightenment and salvation, emphasizing the dualism between the material world, often seen as flawed or evil, and the divine realm of light. Core beliefs include the existence of a divine spark within humans, trapped in the physical body, and the need to awaken this inner knowledge to transcend material existence. Gnostic texts frequently describe a demiurge as a lesser deity responsible for creating the material world, contrasting with the true, ineffable God beyond physical reality.
What Is Agnosticism? Defining the Perspective
Agnosticism is the philosophical position asserting that the existence or nonexistence of deities is unknown or unknowable, emphasizing intellectual humility regarding spiritual knowledge. It neither affirms belief in God nor denies it, instead maintaining that human evidence and reasoning are insufficient to reach a definitive conclusion. This perspective contrasts with Gnosticism, which claims esoteric knowledge of divine truths, positioning agnosticism as a commitment to doubt and open inquiry about metaphysical claims.
Historical Origins of Gnosticism
Gnosticism originated in the early centuries of the Common Era, emerging as a diverse set of religious movements in the Mediterranean region, particularly within the context of Hellenistic Judaism and early Christianity. It emphasized esoteric knowledge (gnosis) as the path to spiritual salvation, contrasting with orthodox Christian teachings. Unlike agnosticism, which centers on the epistemological stance regarding the unknowability of divine existence, Gnosticism presents a defined cosmology and mythology explaining the material world's origin and the soul's divine spark.
The Evolution of Agnosticism Through Time
Agnosticism has evolved significantly since its introduction by Thomas Huxley in the 19th century, shifting from a strict stance of withholding belief about the existence of deities to encompassing a broader philosophical inquiry into knowledge and certainty. Unlike Gnosticism, which claims special spiritual knowledge or gnosis about divine truths, agnosticism emphasizes skepticism and the limits of human understanding regarding metaphysical claims. Over time, agnosticism has diversified into various forms, including strong agnosticism, which asserts that knowledge of the divine is inherently unknowable, and weak agnosticism, which maintains that such knowledge is currently unknown but not necessarily unknowable.
Key Differences Between Gnosticism and Agnosticism
Gnosticism centers on the belief that spiritual knowledge (gnosis) is essential for salvation, emphasizing the existence of a divine realm beyond material reality. Agnosticism maintains a position of uncertainty or skepticism regarding the existence of deities, asserting that such knowledge is inherently unknowable or currently unknown. The key difference lies in Gnosticism's claim to esoteric knowledge about the divine, while Agnosticism refrains from making definitive claims about spiritual truths.
Spiritual Knowledge vs. Skeptical Inquiry
Gnosticism centers on obtaining direct spiritual knowledge (gnosis) through mystical experiences and inner revelation, asserting that true understanding of divine realities transcends empirical evidence. Agnosticism emphasizes skeptical inquiry and the suspension of judgment regarding metaphysical claims, maintaining that definitive knowledge of spiritual or divine matters is inherently unknowable. The fundamental distinction lies in Gnosticism's confidence in esoteric spiritual insight versus Agnosticism's commitment to intellectual humility and uncertainty.
Major Texts and Influential Figures
Gnosticism is characterized by sacred texts like the Nag Hammadi library, including the Gospel of Thomas and the Apocryphon of John, and influential figures such as Valentinus and Basilides, who emphasized esoteric knowledge for spiritual awakening. Agnosticism lacks canonical texts but is rooted in philosophical inquiry with prominent figures like Thomas Huxley, who coined the term, advocating for the suspension of belief due to insufficient evidence regarding the existence of deities. The contrast highlights Gnosticism's mystical scripture-based tradition versus Agnosticism's empirical skepticism and critique of dogma.
Gnosticism and Agnosticism in Modern Thought
Gnosticism in modern thought emphasizes esoteric knowledge and spiritual insight as the path to understanding existence, influencing contemporary metaphysical and philosophical discussions. Agnosticism focuses on the inherent uncertainty of knowledge, particularly regarding the existence of deities, shaping scientific skepticism and secular humanism. The contrast highlights Gnosticism's pursuit of hidden truths versus Agnosticism's acceptance of epistemological limits.
Common Misconceptions and Myths
Gnosticism is a religious philosophy emphasizing esoteric knowledge (gnosis) for spiritual enlightenment, while agnosticism is an epistemological stance that asserts the unknowability of gods or metaphysical truths. A common misconception is that gnostics deny the existence of God, whereas they actually claim special knowledge of the divine, contrasting with agnostics who suspend belief due to insufficient evidence. Another myth conflates agnosticism with atheism; agnostics neither affirm nor deny deities but maintain a position of doubt or uncertainty.
Which Path Resonates? Choosing Your Own Perspective
Gnosticism emphasizes the pursuit of esoteric knowledge to achieve spiritual enlightenment and understanding of divine mysteries, positioning knowledge as the path to salvation. Agnosticism adopts a stance of uncertainty regarding the existence of deities, emphasizing skepticism and the limitations of human knowledge rather than asserting definitive beliefs. Choosing between Gnosticism and Agnosticism depends on whether one resonates more with the quest for hidden spiritual truths or the acceptance of uncertainty and critical inquiry.
Gnosticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com