Hadiths are sayings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad that provide essential guidance for Islamic beliefs and practices. Understanding Hadith helps in interpreting the Quran and applying Islamic principles in daily life. Explore the detailed insights in the rest of this article to deepen your knowledge of Hadith and its significance.
Table of Comparison
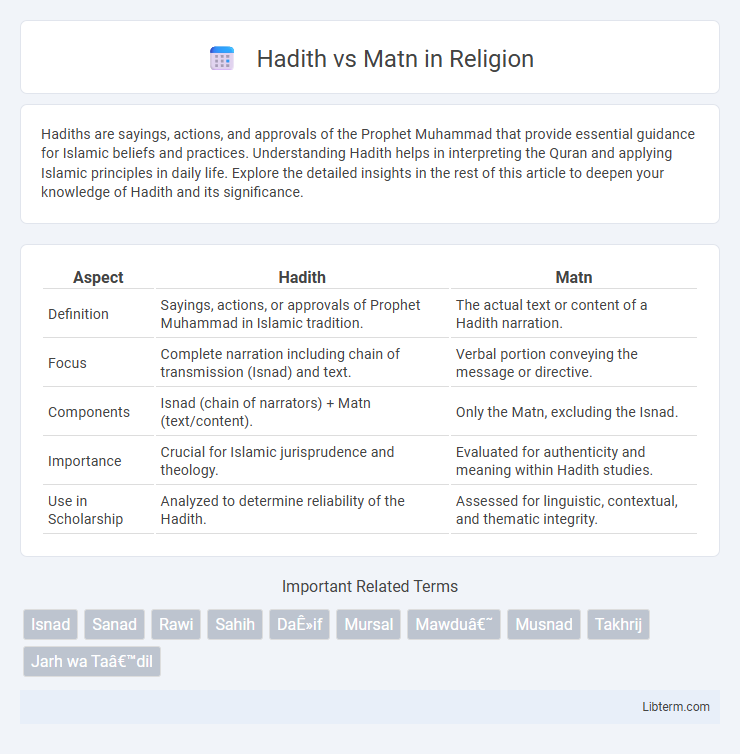
| Aspect | Hadith | Matn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sayings, actions, or approvals of Prophet Muhammad in Islamic tradition. | The actual text or content of a Hadith narration. |
| Focus | Complete narration including chain of transmission (Isnad) and text. | Verbal portion conveying the message or directive. |
| Components | Isnad (chain of narrators) + Matn (text/content). | Only the Matn, excluding the Isnad. |
| Importance | Crucial for Islamic jurisprudence and theology. | Evaluated for authenticity and meaning within Hadith studies. |
| Use in Scholarship | Analyzed to determine reliability of the Hadith. | Assessed for linguistic, contextual, and thematic integrity. |
Introduction to Hadith and Matn
Hadith refers to the recorded sayings, actions, and approvals of Prophet Muhammad, serving as a primary source for Islamic teachings alongside the Quran. Matn is the textual content or the actual wording of the Hadith, which must be analyzed for authenticity, context, and meaning. Understanding the distinction between Hadith and Matn is essential for accurate interpretation and application of Islamic jurisprudence.
Defining Hadith: Structure and Components
Hadith consists of two primary components: the Isnad (chain of narration) and the Matn (text or content). The Isnad ensures the authenticity of the Hadith by tracing the transmission through reliable narrators, while the Matn conveys the actual message or teaching attributed to the Prophet Muhammad. Understanding both the Isnad and Matn is crucial for the classification and validation of Hadith in Islamic scholarship.
Understanding Matn: The Core Text
The Matn represents the core text of a Hadith, containing the actual sayings, actions, or approvals of the Prophet Muhammad, making it essential for Islamic jurisprudence and theology. Understanding the Matn involves analyzing its language, context, and meaning, distinguishing it from the Isnad, which is the chain of narrators that authenticates the Hadith. Scholars prioritize Matn examination to extract legal rulings and spiritual guidance, ensuring correct application and interpretation within Islamic tradition.
Difference Between Hadith and Matn
Hadith refers to the entire recorded tradition of the sayings, actions, and approvals of Prophet Muhammad, encompassing both the chain of narrators (isnad) and the content (matn). Matn specifically denotes the actual text or content of the hadith, detailing what was said or done by the Prophet. The key difference is that hadith includes the full transmission framework ensuring authenticity, while matn focuses solely on the textual message conveyed.
Role of Isnad in Hadith Authentication
Isnad plays a critical role in Hadith authentication by providing a chain of transmission that verifies the reliability and credibility of the narrator sequence. Scholars meticulously analyze each link in the Isnad to ensure the integrity of the Hadith, distinguishing authentic reports from fabricated or weak ones. The strength of the Isnad directly impacts the acceptance of the Matn, or the content of the Hadith, within Islamic jurisprudence and theology.
Criteria for Assessing Matn Authenticity
The criteria for assessing Matn authenticity focus on analyzing the text's consistency with the established principles of the Qur'an, Shar'iah, and other verified Hadiths. Experts evaluate the Matn's language, coherence, and absence of contradictions or anomalies to ensure it reflects the Prophet Muhammad's authentic words and teachings. Rigorous scrutiny also involves examining the Matn's compatibility with known historical and linguistic contexts to identify potential fabrications or alterations.
Common Errors in Evaluating Hadith and Matn
Common errors in evaluating Hadith and Matn include neglecting the context of the narration and misunderstanding the linguistic nuances of classical Arabic, which leads to misinterpretation. Analysts often overlook the authenticity chain (Isnad) while placing excessive emphasis solely on the text (Matn), resulting in flawed conclusions about the Hadith's validity. Failure to cross-reference with established scholarly commentaries frequently causes overlooking weak or fabricated narrations disguised as genuine Hadith.
Influence of Matn Analysis in Islamic Scholarship
Matn analysis plays a crucial role in Islamic scholarship by providing a detailed examination of the textual content of hadiths to ensure authenticity and prevent misinterpretations. Scholars use matn criticism to evaluate linguistic coherence, contextual relevance, and consistency with established Islamic principles, which strengthens the reliability of hadith collections. This rigorous scrutiny influences jurisprudential rulings and theological discussions by establishing a clear framework for verifying prophetic traditions.
Prominent Scholars on Hadith vs. Matn Evaluation
Prominent scholars such as Imam Bukhari and Imam Muslim emphasized rigorous evaluation of Hadith authenticity through Isnad (chain of narration) and Matn (text) scrutiny to ensure reliability. Ibn Hajar al-Asqalani contributed extensive commentary on Hadith texts, analyzing Matn for consistency with established Islamic principles and historical context. Contemporary experts like Shaykh al-Albani expanded the science of Hadith criticism by systematically verifying Matn integrity against linguistic, theological, and contextual benchmarks.
Conclusion: The Importance of Distinguishing Hadith and Matn
Understanding the distinction between Hadith and Matn is crucial for accurate Islamic scholarship and jurisprudence, as Hadith encompasses the entire prophetic tradition including isnad (chain of transmission), while Matn specifically refers to the text of the narration itself. Properly distinguishing them helps ensure authenticity verification and guards against misinterpretation or misuse of prophetic teachings. This differentiation supports more precise application of Shariah and preserves the integrity of Islamic knowledge transmission.
Hadith Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com