Gnosticism explores the idea that spiritual knowledge, or gnosis, is the key to understanding the divine and achieving enlightenment beyond the material world. Many Gnostic texts emphasize the dualism between the physical realm, often seen as flawed, and the spiritual realm, highlighting a journey toward inner truth and self-discovery. Dive deeper into this fascinating belief system to uncover how Gnosticism can influence your perspective on spirituality and existence.
Table of Comparison
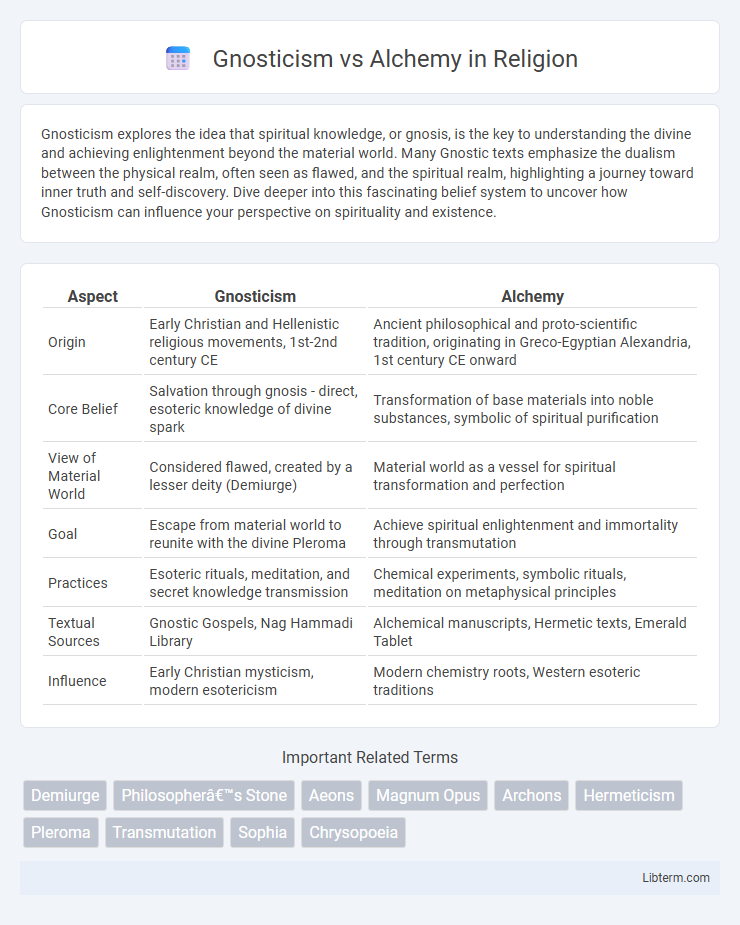
| Aspect | Gnosticism | Alchemy |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Early Christian and Hellenistic religious movements, 1st-2nd century CE | Ancient philosophical and proto-scientific tradition, originating in Greco-Egyptian Alexandria, 1st century CE onward |
| Core Belief | Salvation through gnosis - direct, esoteric knowledge of divine spark | Transformation of base materials into noble substances, symbolic of spiritual purification |
| View of Material World | Considered flawed, created by a lesser deity (Demiurge) | Material world as a vessel for spiritual transformation and perfection |
| Goal | Escape from material world to reunite with the divine Pleroma | Achieve spiritual enlightenment and immortality through transmutation |
| Practices | Esoteric rituals, meditation, and secret knowledge transmission | Chemical experiments, symbolic rituals, meditation on metaphysical principles |
| Textual Sources | Gnostic Gospels, Nag Hammadi Library | Alchemical manuscripts, Hermetic texts, Emerald Tablet |
| Influence | Early Christian mysticism, modern esotericism | Modern chemistry roots, Western esoteric traditions |
Introduction to Gnosticism and Alchemy
Gnosticism is an ancient spiritual movement emphasizing esoteric knowledge (gnosis) as the path to divine enlightenment and salvation. Alchemy, rooted in Hellenistic and medieval traditions, combines mystical philosophy and proto-scientific experimentation aimed at transforming base materials into noble substances and achieving spiritual transmutation. Both systems share a symbolic language reflecting inner transformation but diverge in methods and metaphysical goals.
Historical Origins and Development
Gnosticism emerged in the early Christian era, around the 1st and 2nd centuries CE, emphasizing esoteric knowledge (gnosis) for spiritual salvation and developing distinct cosmologies and mythologies. Alchemy began as a philosophical and proto-scientific tradition in Hellenistic Egypt during the 3rd century BCE, blending Greek, Egyptian, and later Islamic influences, focusing on the transformation of matter and spiritual purification. Both systems evolved through the Middle Ages, with Gnosticism influencing mystical Christian sects and Alchemy merging with medieval science and mysticism, paving the way for modern chemistry and esoteric thought.
Core Beliefs and Philosophies
Gnosticism centers on the belief that salvation comes through secret knowledge (gnosis) revealing the divine spark within humans trapped in a flawed material world created by a lesser deity. Alchemy emphasizes the transformation of base materials into noble substances, symbolizing spiritual purification and the pursuit of enlightenment through mystical and scientific processes. Both systems view the material realm as imperfect, but Gnosticism prioritizes inward mystical knowledge for liberation, whereas alchemy blends metaphysical insight with practical experimentation for spiritual and physical transmutation.
Spiritual Practices and Rituals
Gnosticism centers on spiritual practices involving secret knowledge (gnosis) to achieve divine enlightenment and liberation from material existence, emphasizing inner revelation through meditation and mystical rituals. Alchemy combines spiritual transformation with physical processes, using symbolic rituals and the transmutation of substances as metaphors for personal purification and the attainment of spiritual perfection. Both traditions utilize esoteric rituals to elevate the soul, but Gnosticism focuses on awakening divine knowledge, whereas alchemy encodes spiritual ascent within the symbolism of material transformation.
The Concept of Knowledge and Enlightenment
Gnosticism and alchemy both emphasize the pursuit of knowledge and enlightenment but differ fundamentally in their approaches and goals. Gnosticism centers on esoteric spiritual knowledge (gnosis) that reveals the divine spark within and facilitates liberation from material illusions. Alchemy focuses on the transformation of both matter and the self, using symbolic processes to achieve spiritual purification and the philosopher's stone, a metaphor for ultimate enlightenment and immortality.
Symbols and Sacred Texts
Gnosticism employs symbols like the Pleroma, Aeons, and the Demiurge to convey complex cosmological ideas found in sacred texts such as the Nag Hammadi library, highlighting the dualism between spiritual knowledge and material ignorance. Alchemy utilizes symbols including the ouroboros, philosopher's stone, and elements like mercury and sulfur, which are detailed in manuscripts like the Emerald Tablet and works by Paracelsus, focusing on transformation and the unity of matter and spirit. Both systems use esoteric symbolism and cryptic writings to encode spiritual truths, but Gnosticism emphasizes gnosis as liberation from the material world, while alchemy centers on physical and spiritual transmutation.
Views on the Material World
Gnosticism views the material world as a flawed, often malevolent creation trapping the divine spark within physical bodies, emphasizing spiritual liberation through knowledge (gnosis). Alchemy treats the material world as a transformative substrate where physical and spiritual purification converge, aiming to transmute base materials into noble substances like gold, symbolizing inner enlightenment. Both systems perceive the material realm as imperfect but differ in their approach: Gnosticism advocates transcendence, while Alchemy seeks transformation within it.
Transformation and Salvation: Contrasting Goals
Gnosticism centers on spiritual transformation through self-knowledge and awakening to attain salvation by escaping the material world's illusions. Alchemy emphasizes physical and symbolic transformation, aiming to purify and perfect matter, often represented by the quest to create the philosopher's stone. Both pursue transformation, yet Gnosticism targets liberation of the soul, while alchemy seeks material and spiritual harmony.
Influence on Modern Esoteric Traditions
Gnosticism and alchemy profoundly shaped modern esoteric traditions by embedding themes of spiritual transformation and hidden knowledge. Gnosticism's emphasis on divine enlightenment and dualistic cosmology influenced occult philosophies and mystical practices, while alchemy's symbolic language of transmutation informed ceremonial magic and psychological alchemy in Jungian thought. These ancient systems collectively inspired contemporary movements such as Theosophy, Hermeticism, and New Age spirituality, integrating metaphysical concepts with personal spiritual development.
Key Figures in Gnosticism and Alchemy
Key figures in Gnosticism include Valentinus, Basilides, and Marcion, who shaped early Christian mystical thought through their teachings on divine knowledge and salvation. In Alchemy, prominent figures such as Hermes Trismegistus, Paracelsus, and Isaac Newton advanced the transformation of matter and the quest for the philosopher's stone, blending spiritual and scientific inquiry. These individuals represent the core intellectual forces driving the esoteric traditions of Gnosticism and Alchemy, each contributing unique methodologies to understanding spiritual transcendence and material transformation.
Gnosticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com