Liberal Protestantism emphasizes individual freedom of belief and the use of reason in interpreting Christian faith, often embracing modern scholarship and social justice issues. It tends to focus on ethical living and societal progress rather than strict adherence to traditional dogma. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Liberal Protestantism shapes contemporary religious practice and thought.
Table of Comparison
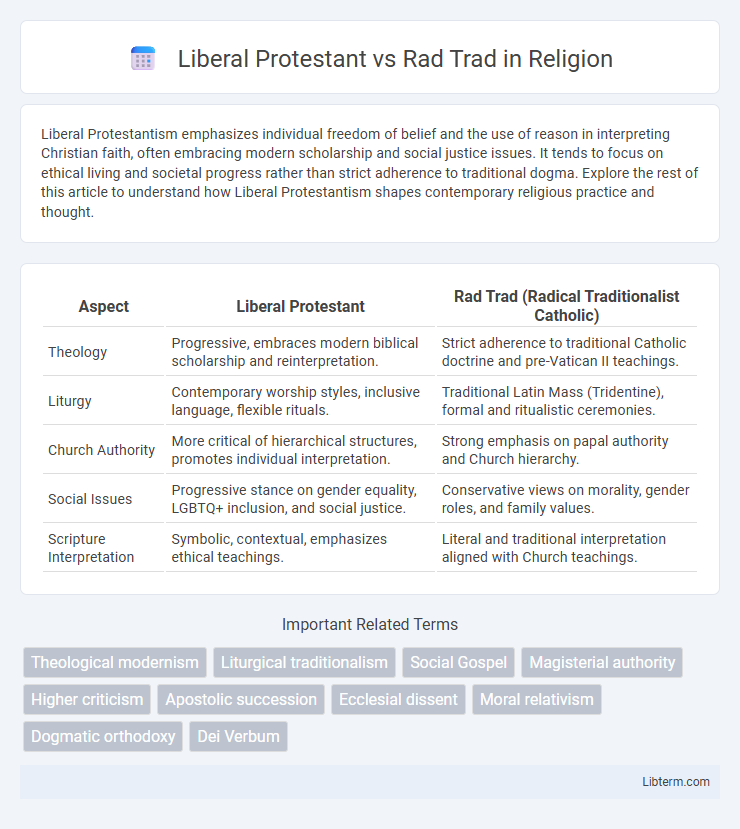
| Aspect | Liberal Protestant | Rad Trad (Radical Traditionalist Catholic) |
|---|---|---|
| Theology | Progressive, embraces modern biblical scholarship and reinterpretation. | Strict adherence to traditional Catholic doctrine and pre-Vatican II teachings. |
| Liturgy | Contemporary worship styles, inclusive language, flexible rituals. | Traditional Latin Mass (Tridentine), formal and ritualistic ceremonies. |
| Church Authority | More critical of hierarchical structures, promotes individual interpretation. | Strong emphasis on papal authority and Church hierarchy. |
| Social Issues | Progressive stance on gender equality, LGBTQ+ inclusion, and social justice. | Conservative views on morality, gender roles, and family values. |
| Scripture Interpretation | Symbolic, contextual, emphasizes ethical teachings. | Literal and traditional interpretation aligned with Church teachings. |
Understanding Liberal Protestantism: Core Beliefs and Practices
Liberal Protestantism emphasizes individual interpretation of scripture, social justice, and the integration of modern science with faith, promoting inclusivity and progressive theology. It often embraces a metaphorical understanding of biblical texts and advocates for social reforms aligned with Christian ethics. Worship practices in Liberal Protestant communities tend to be flexible, focusing on personal experience and contemporary relevance.
Radical Traditionalism (Rad Trad): Definition and Historical Roots
Radical Traditionalism (Rad Trad) is a conservative theological movement within Catholicism emphasizing strict adherence to pre-Vatican II liturgy and doctrines, rejecting modernist influences such as the Second Vatican Council reforms. Rooted in early 20th-century Catholic Traditionalism and mainstream opposition to modernist theology, Radical Traditionalism emerged prominently in response to perceived secularization and doctrinal dilution. Key figures include Archbishop Marcel Lefebvre and groups like the Society of St. Pius X, advocating for the Latin Mass and traditional Catholic teachings as a means to preserve authentic faith and ecclesiastical continuity.
Theology: Comparing Views on Scripture and Authority
Liberal Protestant theology interprets Scripture through a historical-critical lens, emphasizing human reason and experience as sources of authority alongside the Bible. In contrast, Rad Trad (Radical Traditionalist) theology holds a strict literal interpretation of Scripture and upholds the Magisterium and Church tradition as infallible authorities. These differing views create fundamental divides in doctrine, worship, and moral teachings between the two.
Worship Styles: Contemporary Adaptations vs. Ancient Rituals
Liberal Protestant worship styles typically feature contemporary adaptations, including modern music, informal liturgies, and inclusive language to foster personal engagement and cultural relevance. In contrast, Radical Traditionalist (Rad Trad) worship emphasizes ancient rituals, preserving Latin Mass, Gregorian chant, and solemn ceremonies that reflect historical continuity and doctrinal orthodoxy. These divergent approaches highlight the theological priorities of each tradition, with Liberal Protestantism valuing innovation and accessibility, while Rad Trad upholds tradition and ritual solemnity.
Social Issues: Progressive Activism vs. Conservative Values
Liberal Protestantism champions progressive activism by supporting social justice causes such as LGBTQ+ rights, racial equality, and gender inclusivity, reflecting an adaptive interpretation of scripture aligned with modern social ethics. In contrast, Radical Traditionalism upholds conservative values emphasizing strict adherence to traditional doctrines, opposing changes to established moral teachings on issues like marriage, sexuality, and family structure. These divergent approaches to social issues highlight a broader clash between evolving cultural norms and preservation of historical religious beliefs within Christian communities.
Gender Roles and Ordination: Diverging Perspectives
Liberal Protestant denominations advocate for gender equality in church leadership, supporting the ordination of women and embracing diverse gender identities within clergy roles. In contrast, Radical Traditionalist (Rad Trad) groups uphold strict gender roles based on traditional interpretations of scripture, generally restricting ordination to men and opposing female clergy. These diverging perspectives highlight fundamental theological differences regarding gender roles and ecclesiastical authority between modern liberal theology and conservative traditionalism.
Approach to Ecumenism and Interfaith Dialogue
Liberal Protestantism embraces ecumenism and interfaith dialogue by promoting theological openness, inclusivity, and mutual understanding across diverse religious traditions. It actively seeks common ground and cooperative efforts to address global social issues, fostering respectful engagement without strict doctrinal boundaries. In contrast, Radical Traditionalism maintains a rigid stance rooted in doctrinal purity, often rejecting ecumenical initiatives and interfaith conversations to preserve perceived authentic religious identity and orthodoxy.
Church Governance: Hierarchy vs. Congregational Model
Liberal Protestant churches typically adopt a congregational model of church governance, emphasizing local autonomy where individual congregations make decisions independently without a centralized authority. In contrast, Radical Traditionalist (Rad Trad) Catholic communities uphold a strict hierarchical structure, with authority flowing from the pope and bishops down to the parish level, reinforcing adherence to established doctrine and liturgical practices. This fundamental difference shapes worship styles, doctrinal enforcement, and community leadership within these religious traditions.
Impact on Community Life and Membership Trends
Liberal Protestant churches typically promote inclusive community engagement and progressive social values, attracting diverse and often younger members, which fosters dynamic community life but sometimes leads to fluctuating membership. In contrast, Traditionalist (Rad Trad) Catholic communities emphasize strict adherence to historic doctrines and liturgical practices, creating tight-knit groups with stable but aging memberships. These differing approaches significantly influence participation rates and the long-term sustainability of their respective religious communities.
Future Trajectories: Challenges and Opportunities
Liberal Protestantism faces challenges such as declining membership and doctrinal diversity but opportunities lie in embracing social justice initiatives and interfaith dialogue to remain relevant. Traditionalist Catholicism (Rad Trad) encounters obstacles including cultural marginalization and internal divisions, while prospects emerge through reaffirming liturgical heritage and expanding global networks. Both trajectories require strategic engagement with modern societal values and digital platforms to foster growth and influence.
Liberal Protestant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com