Matriarchate refers to a social system where women, particularly mothers, hold primary power and authority over political leadership, moral authority, and property control. This ancient structure contrasts with patriarchal societies and can influence family dynamics, inheritance, and community roles. Discover more about how matriarchate shapes cultures throughout history in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
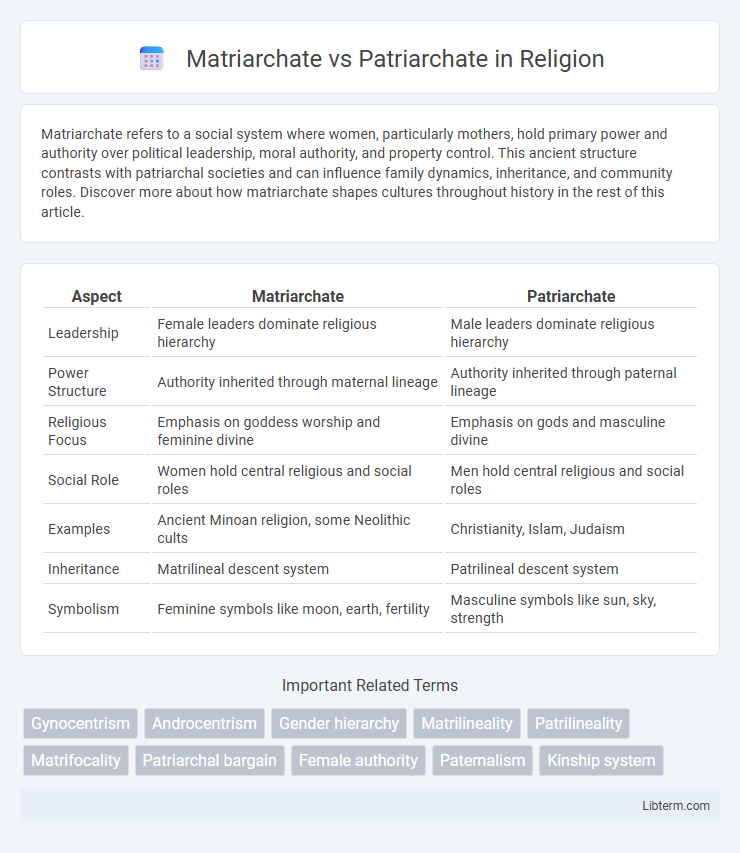
| Aspect | Matriarchate | Patriarchate |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership | Female leaders dominate religious hierarchy | Male leaders dominate religious hierarchy |
| Power Structure | Authority inherited through maternal lineage | Authority inherited through paternal lineage |
| Religious Focus | Emphasis on goddess worship and feminine divine | Emphasis on gods and masculine divine |
| Social Role | Women hold central religious and social roles | Men hold central religious and social roles |
| Examples | Ancient Minoan religion, some Neolithic cults | Christianity, Islam, Judaism |
| Inheritance | Matrilineal descent system | Patrilineal descent system |
| Symbolism | Feminine symbols like moon, earth, fertility | Masculine symbols like sun, sky, strength |
Defining Matriarchate and Patriarchate
Matriarchate refers to a social system or structure where women, especially mothers, hold primary power positions in roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property. Patriarchate denotes a societal organization in which men, particularly fathers or elder males, dominate in authority, decision-making, and lineage inheritance. These contrasting systems shape the distribution of power and influence within families and communities, reflecting deep-rooted cultural values and historical contexts.
Historical Development of Matriarchal Societies
Matriarchal societies historically emerged in various regions as social systems where lineage and inheritance were traced through the female line, emphasizing women's central roles in leadership, spirituality, and property control. Archaeological evidence and anthropological studies reveal that early human communities in parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas practiced matrilineality, often aligning with agrarian lifestyles that valued women's roles in cultivation and social cohesion. Contrasting with patriarchal systems that later became predominant through conquests and state formations, matriarchal societies highlight diverse models of social organization and challenge assumptions about gender roles in historical power structures.
Evolution of Patriarchal Systems
Patriarchal systems evolved from early human societies where male dominance was linked to physical strength and control over resources, solidifying power structures centered around male lineage and authority. Over time, patriarchal norms were reinforced through legal, religious, and cultural institutions, embedding male supremacy in governance, property rights, and social roles. This evolution contrasts with matriarchal systems, which emphasize female leadership and kinship through maternal descent, but remain less prevalent historically in shaping major societal frameworks.
Key Differences Between Matriarchy and Patriarchy
Matriarchy centers on female leadership and inheritance, where women hold primary power in social, political, and economic spheres, contrasting with patriarchy's dominance of males in those roles. In a matriarchal system, lineage and property are often traced through the mother's side, whereas patriarchal societies follow paternal lineage and male authority. Social norms and cultural values in matriarchies prioritize communal care and egalitarian roles, differing significantly from patriarchal structures that emphasize hierarchical roles and male dominance.
Social Organization and Power Structures
Matriarchate social organization centers on female leadership, where lineage and inheritance pass through the mother's line, emphasizing communal decision-making and cooperative power distribution among women. Patriarchate power structures typically prioritize male authority, with social roles and inheritance determined by patrilineal descent, reinforcing hierarchical systems controlled by men. These divergent frameworks shape societal norms, governance, and resource control, influencing gender roles and family dynamics across cultures.
Gender Roles and Family Dynamics
Matriarchate societies center authority and lineage through female figures, emphasizing communal child-rearing and cooperative decision-making within family units. Patriarchate systems prioritize male dominance in social roles, inheritance, and leadership, often enforcing hierarchical family dynamics with clear gender divisions. Gender roles in matriarchal cultures are more fluid and equitable, contrasting with patriarchal structures that reinforce traditional masculinity and female subordination.
Economic Impact of Matriarchal vs Patriarchal Systems
Matriarchal systems often emphasize communal resource sharing and cooperative economic activities, leading to more equitable wealth distribution and sustainable local economies. In contrast, patriarchal systems typically concentrate wealth and economic power within male-dominated hierarchies, which can result in pronounced income inequality and resource monopolization. Studies show matriarchal communities frequently invest in social welfare and environmental stewardship, enhancing long-term economic resilience.
Cultural Expressions and Traditions
Matriarchate systems emphasize cultural expressions and traditions centered around female leadership, with rituals, storytelling, and art often celebrating women's roles in community and ancestry. Patriarchate traditions typically highlight male authority, with cultural narratives and ceremonies reinforcing male dominance and lineage through paternal descent. These differing social frameworks influence gender roles, spiritual beliefs, and the transmission of cultural heritage in distinct ways across societies.
Influence on Modern Societies
Matriarchate and patriarchate systems shape gender roles, power distribution, and cultural norms in modern societies, influencing leadership dynamics and social structures. Patriarchal societies often emphasize male dominance in political, economic, and familial spheres, affecting gender equality and women's rights movements globally. Matriarchal influences promote cooperative governance and egalitarian values, contributing to alternative social models and challenging traditional power hierarchies.
Future Outlook: Shifting Gender Paradigms
Increasing global advocacy for gender equality and women's leadership is catalyzing a reevaluation of patriarchal structures, with some societies exploring matriarchal principles for more inclusive governance. Emerging research in sociology and anthropology highlights the benefits of matriarchate-inspired decision-making, promoting communal well-being and environmental stewardship. Technological advancements in education and communication empower marginalized voices, accelerating the shift towards balanced gender paradigms in future social frameworks.
Matriarchate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com