Imams serve as spiritual leaders in the Muslim community, guiding prayers, interpreting Islamic teachings, and offering moral support. Their role extends beyond religious duties, often involving educational and social responsibilities that strengthen communal bonds. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your connection with an Imam can enrich your spiritual journey.
Table of Comparison
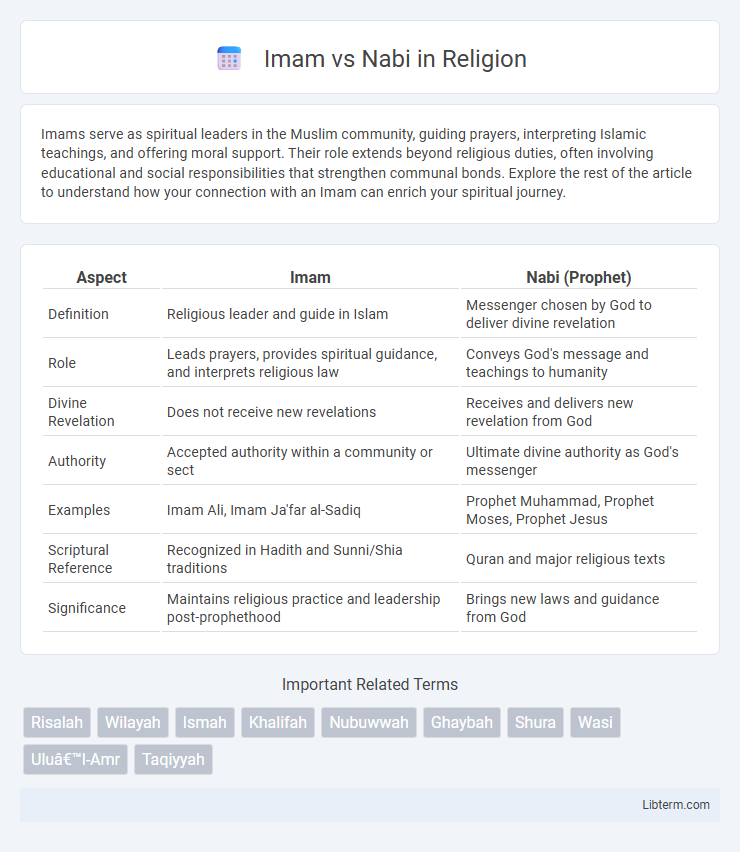
| Aspect | Imam | Nabi (Prophet) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Religious leader and guide in Islam | Messenger chosen by God to deliver divine revelation |
| Role | Leads prayers, provides spiritual guidance, and interprets religious law | Conveys God's message and teachings to humanity |
| Divine Revelation | Does not receive new revelations | Receives and delivers new revelation from God |
| Authority | Accepted authority within a community or sect | Ultimate divine authority as God's messenger |
| Examples | Imam Ali, Imam Ja'far al-Sadiq | Prophet Muhammad, Prophet Moses, Prophet Jesus |
| Scriptural Reference | Recognized in Hadith and Sunni/Shia traditions | Quran and major religious texts |
| Significance | Maintains religious practice and leadership post-prophethood | Brings new laws and guidance from God |
Definition of Imam and Nabi
An Imam in Islamic tradition is a religious leader or guide who leads prayers, provides spiritual guidance, and interprets Islamic law, particularly recognized in Shia Islam as a divinely appointed successor of the Prophet Muhammad. A Nabi, meaning prophet, is a messenger chosen by Allah to deliver divine revelations and guide humanity, with Prophet Muhammad being the final Nabi in Islam. The key distinction lies in the Nabi's role as the conveyor of new divine law and messages, whereas the Imam upholds and interprets existing teachings.
Linguistic Origins of Imam and Nabi
The term "Imam" originates from the Arabic root "`amma," meaning to lead or to guide, emphasizing a role of leadership in prayer and community. "Nabi" derives from the Arabic root "n-b-a," meaning to announce or to bring news, signifying one who receives and conveys divine revelation. Linguistically, "Imam" highlights guidance and leadership, whereas "Nabi" centers on prophecy and communication of God's message.
Roles and Responsibilities: Imam vs. Nabi
An Imam serves as a religious leader and guide for a community, leading prayers, delivering sermons, and providing spiritual support, whereas a Nabi (Prophet) is divinely chosen to deliver God's revelations and establish foundational religious laws. The Imam's role is primarily centered on maintaining religious practices and community cohesion, while the Nabi's responsibilities include conveying new divine messages and guiding humanity on a prophetic mission. Unlike Imams, who follow established scripture, a Nabi holds the authority to receive and communicate divine commandments directly from God.
Divine Appointment: Imam and Nabi in Revelation
A Nabi, or prophet, receives direct revelation from Allah to convey divine guidance and law, marking a foundational role in Islam's spiritual framework. An Imam, especially in Shia Islam, is divinely appointed to lead and interpret this revelation, ensuring its correct application and preserving the prophetic legacy. While the Nabi brings new divine messages, the Imam sustains and exemplifies their implementation within the community.
Historical Examples of Imams and Prophets
Imams and Prophets hold distinct roles in Islamic history, with Prophets like Prophet Muhammad and Prophet Isa (Jesus) delivering divine revelations and establishing religious laws, whereas Imams such as Imam Ali and Imam Hussain provided spiritual leadership, guidance, and interpretation of these teachings. Historical examples include Prophet Muhammad, who founded Islam and received the Quran, and Imam Ali, recognized for his wisdom and justice during the early Islamic caliphate. Imams, particularly in Shia Islam, serve as hereditary leaders and protectors of the Prophet's legacy, exemplified by figures like Imam Jafar al-Sadiq, who contributed significantly to Islamic theology and jurisprudence.
Authority in Religious Leadership
Imams hold significant authority as religious leaders in Islam, particularly within Shia tradition, where they are considered divinely appointed guides with spiritual and temporal leadership roles. In contrast, a Nabi (Prophet) receives direct revelation from God and serves as a messenger to convey divine guidance to humanity, establishing foundational religious principles. The authority of an Imam is thus rooted in interpreting and preserving the teachings of a Nabi, while a Nabi's authority originates from the direct reception of divine revelation.
Distinction in Islamic Theology
In Islamic theology, a Nabi (Prophet) is a messenger chosen by Allah to receive and convey divine revelations, establishing new laws or reinforcing existing ones, while an Imam is primarily a spiritual and community leader who guides followers in interpreting and practicing Islamic teachings without necessarily bringing new revelation. Nabis possess the unique authority to introduce Shariah, whereas Imams serve as custodians of religious knowledge and provide leadership within the Muslim Ummah based on the Quran and Hadith. This distinction underscores the prophetic role in foundational religious change contrasted with the ongoing leadership and guidance role of Imams within Islam.
Role in Guiding the Community
Imams serve as spiritual leaders and interpreters of Islamic law, guiding the community through religious teachings, rituals, and daily practices, while Nabis (Prophets) are divinely chosen messengers who deliver God's revelations and establish foundational religious principles. Imams uphold and transmit the prophetic message by providing ongoing moral and legal guidance, ensuring the community's adherence to Islamic doctrine. The role of a Nabi is unique and absolute, as they receive direct communication from God, whereas Imams derive authority through religious scholarship and communal leadership within the established framework.
Significance in Different Islamic Sects
Imams hold a central role in Shia Islam as divinely appointed leaders and spiritual guides, whereas in Sunni Islam, a Nabi (Prophet) is a messenger chosen by Allah to deliver His revelations. The Shia sect, particularly the Twelvers, regards the Twelve Imams as infallible and essential for interpreting Islamic law and theology, while Sunnis emphasize the finality of Prophet Muhammad as the last Nabi without infallible successors. This distinction underscores the theological divide, where Imams in Shia belief serve both spiritual and political leadership roles, contrasting with the Sunni focus on prophetic guidance and community consensus.
Contemporary Relevance of Imam and Nabi
Imams serve as spiritual guides and community leaders, providing contemporary Muslims with religious interpretation and guidance rooted in Islamic jurisprudence and ethics. Prophets, or Nabis, hold a unique status as recipients of divine revelation, establishing the foundational principles of Islamic faith that continue to shape moral and legal frameworks today. Understanding the distinct roles of Imams and Nabis is essential for appreciating ongoing religious authority and communal leadership in modern Islamic societies.
Imam Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com