Hermeticism is an ancient spiritual tradition that explores the connection between the divine, the cosmos, and human consciousness through esoteric teachings and symbolic texts. Rooted in the writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, it emphasizes concepts like alchemy, astrology, and theurgy to achieve spiritual transformation and inner wisdom. Discover how Hermeticism can deepen Your understanding of hidden knowledge by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
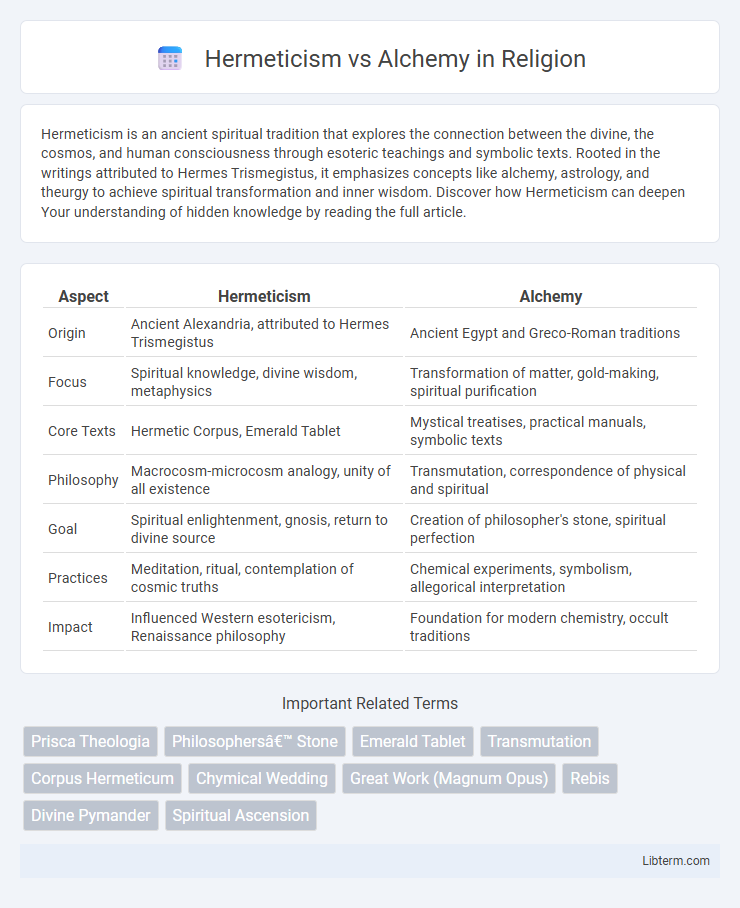
| Aspect | Hermeticism | Alchemy |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Alexandria, attributed to Hermes Trismegistus | Ancient Egypt and Greco-Roman traditions |
| Focus | Spiritual knowledge, divine wisdom, metaphysics | Transformation of matter, gold-making, spiritual purification |
| Core Texts | Hermetic Corpus, Emerald Tablet | Mystical treatises, practical manuals, symbolic texts |
| Philosophy | Macrocosm-microcosm analogy, unity of all existence | Transmutation, correspondence of physical and spiritual |
| Goal | Spiritual enlightenment, gnosis, return to divine source | Creation of philosopher's stone, spiritual perfection |
| Practices | Meditation, ritual, contemplation of cosmic truths | Chemical experiments, symbolism, allegorical interpretation |
| Impact | Influenced Western esotericism, Renaissance philosophy | Foundation for modern chemistry, occult traditions |
Origins and Historical Context of Hermeticism and Alchemy
Hermeticism originated in late antiquity, rooted in the purported teachings of Hermes Trismegistus, blending Greek, Egyptian, and Christian elements into a philosophical and spiritual tradition emphasizing cosmic unity and divine knowledge. Alchemy emerged in the Hellenistic period, influenced by Hermetic principles, combining practical metallurgy and proto-chemistry with spiritual transformation concepts, aimed at transmuting base metals into gold and achieving the philosopher's stone. Both traditions evolved through medieval and Renaissance Europe, intertwining but maintaining distinct focuses: Hermeticism on esoteric wisdom and cosmology, Alchemy on physical and metaphysical transformation.
Core Philosophical Principles of Hermeticism
Hermeticism centers on the core philosophical principles of divine unity, the correspondence between the macrocosm and microcosm, and the pursuit of spiritual transformation through gnosis. It emphasizes the belief that all things are interconnected, expressed in the axiom "As above, so below," symbolizing the reflection of the universe within the individual. Hermetic teachings advocate for the harmonization of spirit and matter, aiming to achieve enlightenment and mastery over natural forces.
Alchemical Traditions and Practices Explained
Alchemical traditions center on the transformative process of turning base metals into noble ones, symbolizing spiritual purification and enlightenment. Practices involve intricate laboratory work combined with symbolic rituals that represent inner psychological and mystical changes. Hermeticism provides the philosophical and metaphysical framework underpinning alchemy, emphasizing the unity of the cosmos and the concept of "as above, so below.
Key Texts: The Hermetic Corpus vs Alchemical Manuscripts
The Hermetic Corpus, a collection of Greek and Latin texts attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, forms the foundational literature of Hermeticism, exploring divine knowledge, cosmology, and spiritual transformation. In contrast, alchemical manuscripts such as the Rosarium Philosophorum and the Emerald Tablet emphasize practical experimentation with matter, detailing processes like transmutation and the creation of the Philosopher's Stone. While both bodies of work share symbolic language and themes of transformation, the Hermetic Corpus leans toward metaphysical wisdom, whereas alchemical texts focus on proto-scientific techniques and material change.
Similarities Between Hermeticism and Alchemy
Hermeticism and alchemy both emphasize the transformation of the self and the material world through esoteric knowledge and spiritual practice. Each tradition draws on ancient symbolism, particularly the concept of the unity between the macrocosm and microcosm, reflecting a belief in the interconnectedness of all existence. Both systems employ mystical texts, such as the Hermetic Corpus and alchemical manuscripts, to guide initiates toward enlightenment and the pursuit of the philosopher's stone or ultimate wisdom.
Major Differences in Worldview and Goals
Hermeticism centers on spiritual enlightenment and the pursuit of divine knowledge through esoteric wisdom, emphasizing the unity of the cosmos and the soul's connection to the divine. Alchemy primarily focuses on the transformation of matter, aiming to transmute base metals into gold and discover the elixir of life, symbolizing physical and spiritual purification. While Hermeticism seeks metaphysical understanding and cosmic harmony, Alchemy combines practical experimentation with mystical symbolism aimed at both material and spiritual transformation.
Influential Figures in Hermeticism and Alchemy
Hermeticism is deeply influenced by figures like Hermes Trismegistus, whose writings shaped spiritual and philosophical traditions emphasizing divine wisdom and cosmic unity. Alchemy features pivotal figures such as Paracelsus and Nicolas Flamel, known for advancing proto-chemical knowledge and mystical interpretations of transformation and the philosopher's stone. Both traditions intertwine esoteric symbolism but differ in their primary focus: Hermeticism on metaphysical teachings and Alchemy on material transmutation.
Spiritual Versus Material Transformation
Hermeticism emphasizes spiritual transformation through the pursuit of divine knowledge and inner enlightenment, aiming to transcend physical limitations and achieve unity with the cosmos. Alchemy primarily focuses on material transformation, seeking to transmute base metals into noble ones like gold while simultaneously symbolizing the purification and perfection of the soul. Both traditions intertwine these processes, but Hermeticism prioritizes metaphysical ascension, whereas alchemy grounds transformation in tangible, physical practices.
Impact on Western Esotericism and Occultism
Hermeticism and Alchemy profoundly shaped Western esotericism and occultism by providing foundational philosophical frameworks and symbolic systems. Hermeticism's emphasis on divine knowledge and cosmic correspondences influenced mystical traditions, while alchemy contributed transformative metaphors for spiritual and material transmutation. Together, these disciplines enriched occult practices, inspiring rituals, symbolism, and the quest for hidden wisdom.
Modern Interpretations and Legacy
Modern interpretations of Hermeticism emphasize its philosophical and spiritual principles, influencing contemporary esotericism, psychology, and new age movements through concepts like the unity of mind and cosmos. Alchemy today is often viewed symbolically, representing personal transformation and psychological development rather than literal transmutation of metals. Both traditions have left a lasting legacy by inspiring modern spiritual practices, scientific exploration of consciousness, and artistic expressions in literature and visual arts.
Hermeticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com