Salvation represents the deliverance from sin and its consequences, often seen as the pathway to eternal life and spiritual freedom. Many religious traditions emphasize the importance of faith, repentance, and grace in attaining salvation. Discover how the concept of salvation can transform your understanding of faith and purpose by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
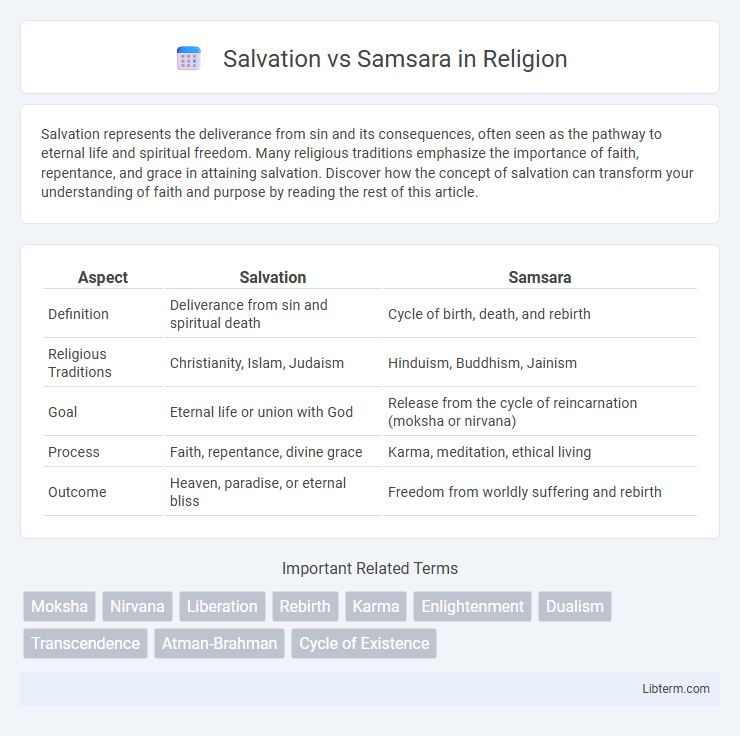
| Aspect | Salvation | Samsara |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliverance from sin and spiritual death | Cycle of birth, death, and rebirth |
| Religious Traditions | Christianity, Islam, Judaism | Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism |
| Goal | Eternal life or union with God | Release from the cycle of reincarnation (moksha or nirvana) |
| Process | Faith, repentance, divine grace | Karma, meditation, ethical living |
| Outcome | Heaven, paradise, or eternal bliss | Freedom from worldly suffering and rebirth |
Understanding Salvation and Samsara: Core Definitions
Salvation refers to the liberation from suffering and the cycle of rebirth, often achieved through spiritual realization or divine grace in religious traditions like Christianity and Buddhism. Samsara is the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth characterized by suffering and desire, central to Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Understanding these core definitions highlights the contrast between the eternal bondage of Samsara and the ultimate freedom offered by Salvation.
Historical Origins: Salvation in Western Religions vs Samsara in Eastern Traditions
Salvation in Western religions such as Christianity and Judaism originates from ancient theological frameworks emphasizing divine intervention and moral redemption to overcome sin and attain eternal life. Samsara in Eastern traditions like Hinduism and Buddhism emerges from Vedic and Upanishadic texts, describing a cyclic process of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma and spiritual ignorance. These historical origins reflect contrasting metaphysical understandings: linear salvation versus cyclical liberation.
The Cycle of Rebirth: Exploring Samsara
Samsara represents the endless cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, driven by karma and desire, trapping beings in suffering and ignorance. Salvation in spiritual traditions such as Hinduism and Buddhism involves breaking free from Samsara by attaining moksha or nirvana, states of liberation and eternal peace. Understanding the Cycle of Rebirth highlights the importance of ethical living, meditation, and self-realization to transcend Samsara's perpetual bondage.
The Path to Liberation: Salvation Explained
Salvation represents the ultimate freedom from sin and spiritual bondage, achieved through faith, repentance, and divine grace in many religious traditions. It involves a transformative process where the soul attains eternal peace and unity with the divine, breaking free from the cycle of worldly suffering. This path to liberation emphasizes redemption, moral purification, and divine forgiveness as the means to eternal salvation.
Goal of Existence: Escaping Samsara vs Attaining Salvation
The goal of escaping samsara centers on liberation from the endless cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, achieving moksha or nirvana, which represents freedom from suffering and worldly attachments. In contrast, attaining salvation often refers to being saved or redeemed by a divine power, such as God, resulting in eternal life or union with the divine. Both concepts emphasize transcendence, but samsara escape focuses on self-realization and enlightenment, while salvation typically involves faith and grace.
Role of Karma and Grace in Salvation and Samsara
Karma plays a crucial role in both salvation and samsara, as it dictates the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth based on one's actions, influencing spiritual progress or entrapment in samsara. Grace, particularly in many religious traditions, is seen as the divine intervention or unearned favor that can override negative karma, enabling individuals to attain salvation or liberation. The dynamic interplay between karma and grace shapes the path toward spiritual freedom, where accumulated deeds and divine compassion together determine ultimate redemption or continued existence within samsara.
Practices and Rituals: Approaches to Liberation
Salvation in Christianity emphasizes faith, prayer, and sacraments such as baptism and communion to achieve eternal life with God, while Samsara in Hinduism and Buddhism centers on karma, meditation, and rituals like puja or chanting to escape the cycle of rebirth. Christian practices involve confession and adherence to scripture to receive divine grace, whereas Samsara liberation requires self-realization through mindfulness, ethical living, and spiritual disciplines. Both paths prescribe disciplined rituals and ethical conduct as essential approaches to ultimate liberation or salvation.
Philosophical Contrasts: Dualism vs Non-dualism
Salvation in many Western traditions often embraces dualism, emphasizing the separation between soul and body, good and evil, or God and humanity, aiming for liberation from sin and union with a transcendent deity. Samsara in Hinduism and Buddhism is grounded in non-dualism, where the self and the cosmos are interconnected, and liberation involves realizing the unity of all existence beyond illusion. This philosophical contrast shapes divergent spiritual goals: salvation seeks transcendence of the material world, while samsara focuses on awakening to the inherent oneness within it.
Modern Interpretations of Salvation and Samsara
Modern interpretations of salvation often emphasize personal transformation and psychological liberation, viewing it as overcoming suffering through inner awakening rather than solely spiritual redemption. Samsara is increasingly understood as the perpetual cycle of stress and dissatisfaction generated by attachment, which mindfulness and meditation seek to transcend. Contemporary perspectives blend traditional religious concepts with secular practices, highlighting the universal human quest for meaning and freedom from existential suffering.
Salvation vs Samsara: Implications for Human Experience
Salvation, representing liberation from suffering and union with the divine, contrasts with Samsara, the endless cycle of birth, death, and rebirth rooted in desire and ignorance. This dichotomy profoundly impacts human experience by framing existence either as a transient, suffering-bound journey or a path toward ultimate freedom and spiritual fulfillment. Understanding this distinction influences ethical decisions, emotional resilience, and the pursuit of meaning across various religious and philosophical traditions.
Salvation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com