Hatha yoga focuses on physical postures and breathing techniques to balance your body and mind, promoting overall health and relaxation. This practice helps improve flexibility, strength, and mental clarity through mindful movements and controlled breaths. Discover how incorporating Hatha yoga into your routine can transform your well-being by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
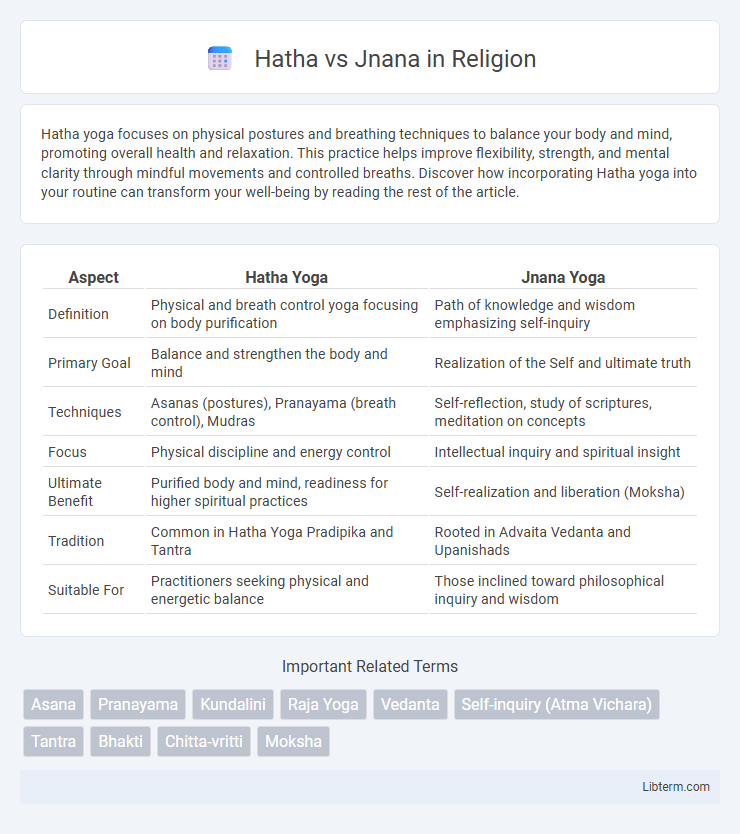
| Aspect | Hatha Yoga | Jnana Yoga |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical and breath control yoga focusing on body purification | Path of knowledge and wisdom emphasizing self-inquiry |
| Primary Goal | Balance and strengthen the body and mind | Realization of the Self and ultimate truth |
| Techniques | Asanas (postures), Pranayama (breath control), Mudras | Self-reflection, study of scriptures, meditation on concepts |
| Focus | Physical discipline and energy control | Intellectual inquiry and spiritual insight |
| Ultimate Benefit | Purified body and mind, readiness for higher spiritual practices | Self-realization and liberation (Moksha) |
| Tradition | Common in Hatha Yoga Pradipika and Tantra | Rooted in Advaita Vedanta and Upanishads |
| Suitable For | Practitioners seeking physical and energetic balance | Those inclined toward philosophical inquiry and wisdom |
Introduction to Hatha and Jnana Yoga
Hatha Yoga emphasizes physical postures (asanas), breath control (pranayama), and meditation to balance the body and mind, fostering physical strength and mental clarity. Jnana Yoga centers on the pursuit of spiritual knowledge and self-inquiry, aiming to transcend ignorance through philosophical study and meditation on the nature of the self. Both paths offer distinct approaches to self-realization, with Hatha Yoga focusing on physical discipline and Jnana Yoga on intellectual discernment.
Defining Hatha Yoga: Focus and Practice
Hatha Yoga emphasizes physical postures (asanas), breath control (pranayama), and purification techniques to prepare the body and mind for meditation. Its practice aims to balance the energies within the body, promote strength, flexibility, and mental clarity through tangible, physical discipline. This contrasts with Jnana Yoga's philosophical approach centered on self-inquiry and the pursuit of knowledge (jnana) to realize the true nature of the self.
Understanding Jnana Yoga: The Path of Knowledge
Jnana Yoga, known as the path of knowledge, emphasizes self-inquiry and meditation to realize the true nature of the self beyond physical existence. Unlike Hatha Yoga, which focuses on physical postures and breath control to prepare the body, Jnana Yoga cultivates wisdom through study of scriptures and introspective contemplation. This philosophical approach aims to dissolve ignorance (avidya) and attain liberation (moksha) by discerning the eternal self (Atman) from the temporary body and mind.
Philosophical Foundations: Body vs. Mind
Hatha Yoga emphasizes the mastery and purification of the physical body through postures (asanas) and breath control (pranayama), viewing the body as a vessel for spiritual awakening. Jnana Yoga centers on the intellect and mind, employing self-inquiry and discernment (viveka) to realize the ultimate truth and dissolve the ego's illusions. Both paths seek liberation (moksha) but diverge by prioritizing physical discipline versus mental introspection as the means to transcendence.
Core Techniques: Postures vs. Inquiry
Hatha yoga emphasizes physical postures (asanas) and breath control (pranayama) to prepare the body and mind for meditation, promoting physical strength and flexibility. Jnana yoga centers on self-inquiry (atma vichara) and contemplation to realize the nature of the self through knowledge and wisdom. The core technique in Hatha yoga is disciplined bodily practice, while Jnana yoga relies on deep philosophical questioning and discernment to attain spiritual enlightenment.
Goals and Outcomes of Each Path
Hatha Yoga primarily aims to prepare the body and mind through physical postures, breath control, and purification techniques, leading to enhanced physical health and mental clarity. Jnana Yoga, centered on wisdom and self-inquiry, seeks to transcend ignorance by realizing the true self and attaining spiritual liberation (moksha). The outcome of Hatha Yoga is often greater bodily control and mental focus, while Jnana Yoga results in profound self-awareness and ultimate freedom from the cycle of birth and rebirth.
Who Should Choose Hatha Yoga?
Hatha Yoga is ideal for beginners and individuals seeking a balanced physical and mental practice, as it emphasizes basic postures and breath control to build strength and flexibility. Those recovering from stress, stiffness, or sedentary lifestyles benefit from Hatha's gentle pace and focus on mindfulness, making it accessible for all ages and fitness levels. Practitioners aiming to improve body awareness before exploring more intense or philosophical approaches like Jnana Yoga should prioritize Hatha Yoga for foundational development.
Who Should Pursue Jnana Yoga?
Jnana Yoga is best suited for individuals with a strong intellectual curiosity and a desire for self-inquiry and philosophical understanding. Those who seek to realize the nature of the self through meditation, study of scriptures, and deep contemplation benefit greatly from this path. It appeals to thinkers and seekers inclined towards mental discipline rather than physical postures or rituals characteristic of Hatha Yoga.
Integrating Hatha and Jnana Yoga
Integrating Hatha and Jnana Yoga cultivates a balanced approach by combining physical discipline with intellectual inquiry, enhancing both body and mind. Hatha Yoga's emphasis on asanas and pranayama prepares the body for prolonged meditation, while Jnana Yoga encourages self-inquiry and realization of the true self through study and contemplation. Together, they create a holistic spiritual practice that fosters physical vitality and profound wisdom for deeper self-awareness.
Choosing the Right Yoga Path for You
Choosing the right yoga path depends on your personal goals and temperament, with Hatha Yoga emphasizing physical postures and breath control to prepare the body, while Jnana Yoga focuses on intellectual inquiry and self-realization through study and meditation. Hatha is ideal for those seeking balance and physical wellness, whereas Jnana suits individuals drawn to philosophical exploration and mental clarity. Understanding your priorities helps align practice with your spiritual or health objectives for deeper fulfillment.
Hatha Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com