Grace embodies elegance, kindness, and a sense of refined beauty that influences personal interactions and artistic expression. Cultivating grace enhances your social presence and fosters positive connections in both personal and professional settings. Explore the rest of the article to discover how grace can transform your daily life and relationships.
Table of Comparison
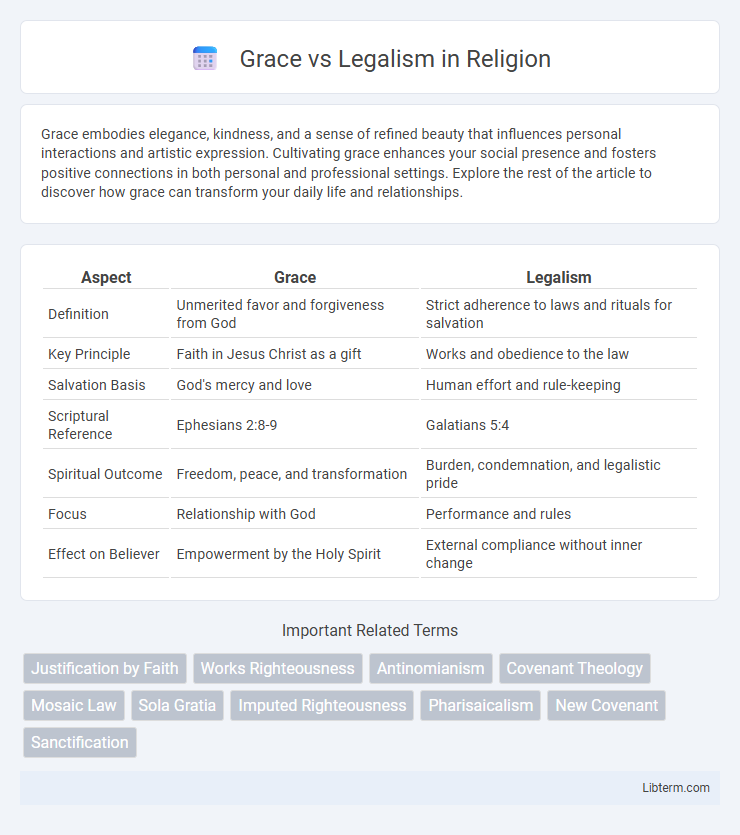
| Aspect | Grace | Legalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unmerited favor and forgiveness from God | Strict adherence to laws and rituals for salvation |
| Key Principle | Faith in Jesus Christ as a gift | Works and obedience to the law |
| Salvation Basis | God's mercy and love | Human effort and rule-keeping |
| Scriptural Reference | Ephesians 2:8-9 | Galatians 5:4 |
| Spiritual Outcome | Freedom, peace, and transformation | Burden, condemnation, and legalistic pride |
| Focus | Relationship with God | Performance and rules |
| Effect on Believer | Empowerment by the Holy Spirit | External compliance without inner change |
Understanding Grace: A Biblical Perspective
Grace, from a biblical perspective, is the unmerited favor and love bestowed by God upon humanity through Jesus Christ, contrasting sharply with legalism, which emphasizes strict adherence to the law for salvation. Ephesians 2:8-9 highlights that grace is a gift received through faith, not by works, underscoring that salvation cannot be earned by human effort. This understanding promotes a relationship with God based on trust and divine mercy rather than rigid rule-keeping or self-righteousness.
What is Legalism? Key Characteristics
Legalism is a theological concept emphasizing strict adherence to laws or rules as the primary means of achieving righteousness and favor with God. Key characteristics include reliance on human effort, strict observance of religious codes, and judgment based on external compliance rather than internal faith or grace. This approach often leads to self-righteousness and a lack of emphasis on forgiveness and transformation through divine grace.
Grace vs Legalism: Core Differences
Grace emphasizes forgiveness, unearned mercy, and the transformative power of God's love, while legalism prioritizes strict adherence to laws and human effort for righteousness. Grace promotes faith and relationship with God as the path to salvation, contrasting legalism's focus on rule-keeping and external behavior. The core difference lies in grace offering freedom through divine acceptance, whereas legalism imposes bondage through obligation and judgment.
Biblical Examples of Grace and Legalism
Paul's letters in the New Testament emphasize grace over legalism, illustrating salvation through faith rather than adherence to the Law of Moses, as seen in Romans 6:14 where grace frees believers from sin's dominion. The Pharisees in Matthew 23 exemplify legalism through strict, ritualistic adherence to the law without understanding its spirit, contrasting Jesus' teachings on mercy and inner righteousness. The story of the Prodigal Son in Luke 15 highlights God's grace, welcoming repentant sinners without legalistic judgment.
The Impact of Legalism on Spiritual Life
Legalism imposes rigid rules that often lead to spiritual burnout and hinder genuine faith experience by prioritizing human effort over divine grace. This approach creates a culture of judgment and fear, discouraging authentic worship and personal growth in the believer's relationship with God. Embracing grace fosters freedom and transformation, allowing for spiritual development rooted in love rather than obligation.
The Transformative Power of Grace
Grace empowers believers to experience profound inner transformation by fostering forgiveness, compassion, and spiritual growth beyond rigid rule-following. Unlike legalism, which emphasizes strict adherence to laws, grace cultivates a heart-centered faith that motivates ethical behavior through love and gratitude. This transformative power of grace enables lasting change and genuine freedom in the Christian life.
Grace and Legalism in Modern Christianity
Grace in modern Christianity emphasizes unmerited favor and salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, promoting compassion and spiritual freedom. Legalism, by contrast, stresses strict adherence to rules and moral codes as necessary for righteousness, often leading to judgment and spiritual burden. The ongoing tension between grace and legalism shapes contemporary Christian communities, influencing theological interpretations and personal faith experiences.
How to Recognize Legalism in the Church
Legalism in the church can be recognized by an overemphasis on strict rule-following and external behaviors rather than the transformational work of grace in a believer's heart. It often manifests through judgmental attitudes, rigid traditions, and the belief that salvation or favor with God is earned through human efforts. Congregations struggling with legalism typically prioritize rules and performance over faith, love, and the freedom offered by the gospel of grace.
Walking in Grace: Practical Steps
Walking in grace involves embracing forgiveness and extending mercy rather than adhering to strict legalistic rules. Practical steps include daily reflection on God's unmerited favor, cultivating humility to recognize personal shortcomings, and fostering a spirit of love that prioritizes relational restoration over judgment. This approach promotes spiritual growth by emphasizing internal transformation through faith instead of external compliance with the law.
Embracing Freedom: Moving Beyond Legalism
Embracing freedom in Christian life involves transcending legalism by focusing on the grace offered through faith in Christ, which liberates believers from rigid, rule-based righteousness. This shift emphasizes a transformational relationship with God rather than adherence to the Mosaic Law or human traditions. Living in grace fosters spiritual growth, empowerment by the Holy Spirit, and an authentic expression of love, moving beyond the constraints of legalistic practices.
Grace Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com