Mysticism explores the direct experience of ultimate reality beyond ordinary perception, often emphasizing spiritual union and inner transformation. Practices such as meditation, contemplation, and prayer are common paths to attaining mystical insights across various traditions. Discover how mysticism can deepen your understanding of existence and elevate your spiritual journey in the full article.
Table of Comparison
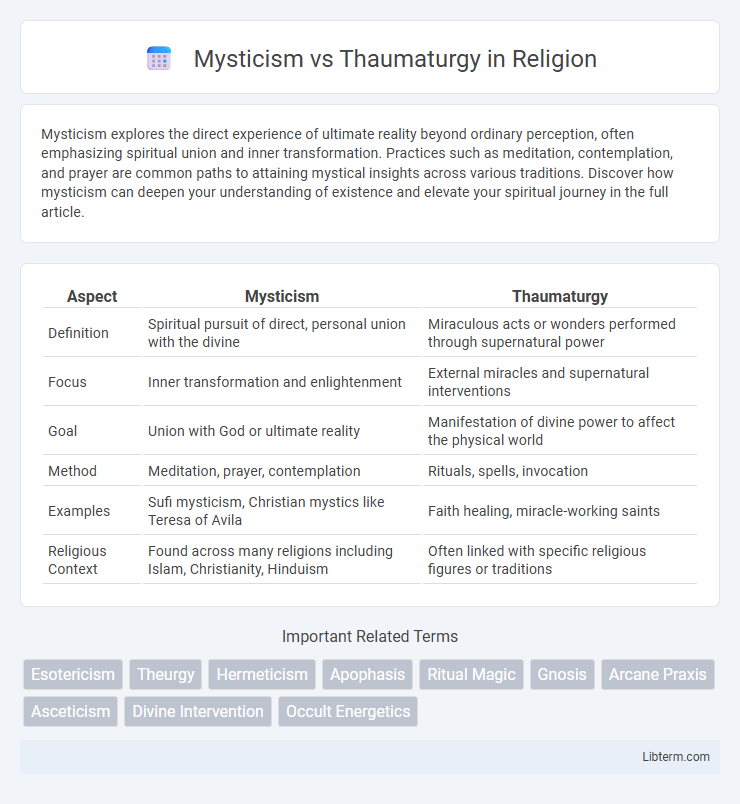
| Aspect | Mysticism | Thaumaturgy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual pursuit of direct, personal union with the divine | Miraculous acts or wonders performed through supernatural power |
| Focus | Inner transformation and enlightenment | External miracles and supernatural interventions |
| Goal | Union with God or ultimate reality | Manifestation of divine power to affect the physical world |
| Method | Meditation, prayer, contemplation | Rituals, spells, invocation |
| Examples | Sufi mysticism, Christian mystics like Teresa of Avila | Faith healing, miracle-working saints |
| Religious Context | Found across many religions including Islam, Christianity, Hinduism | Often linked with specific religious figures or traditions |
Defining Mysticism: A Journey Inward
Mysticism centers on the inner experience of connecting with ultimate reality, emphasizing personal spiritual growth and transcendent awareness beyond ordinary perception. It involves practices such as meditation, contemplation, and prayer aimed at achieving unity with the divine or higher consciousness. Unlike thaumaturgy, which focuses on external miracles and supernatural feats, mysticism prioritizes the inward journey and transformative self-realization.
Thaumaturgy Explained: The Art of Manifestation
Thaumaturgy refers to the art of manifestation through supernatural means, often involving rituals and symbolic acts to influence natural or spiritual forces. Unlike mysticism, which emphasizes internal spiritual experience and union with the divine, thaumaturgy focuses on external results such as healing, protection, or material transformation. As a practice rooted in esoteric traditions, thaumaturgy employs specific techniques and incantations designed to bring about tangible effects in the physical world.
Historical Roots: Mysticism and Thaumaturgy Through Ages
Mysticism traces its historical roots to ancient spiritual traditions such as Neoplatonism, Vedanta, and Sufism, emphasizing inner knowledge and union with the divine through contemplative practices. Thaumaturgy, historically linked to miracle-working and magical feats, appears in diverse contexts from ancient shamanism and alchemy to medieval Christian miracle accounts and Renaissance occultism. Both mysticism and thaumaturgy evolved through cultural exchanges, shaping religious and esoteric systems that influenced medieval mystics, early modern occultists, and contemporary spiritual movements.
Key Philosophical Differences
Mysticism centers on the pursuit of direct, personal union with a transcendent reality through inner spiritual experience, emphasizing introspection and transformative enlightenment. Thaumaturgy involves the performance of miracles or supernatural acts to alter external realities, prioritizing observable effects over internal spiritual change. The key philosophical difference lies in mysticism's inward focus on achieving ultimate reality through consciousness, while thaumaturgy operates outwardly, manipulating physical phenomena through esoteric practices.
Practices and Rituals: Contrasting Approaches
Mysticism centers on inner spiritual experiences and meditation techniques aimed at achieving direct union with the divine, often emphasizing silence, contemplation, and personal revelation. Thaumaturgy involves performing external rituals, ceremonies, and magical acts intended to produce tangible, supernatural effects, guided by specific formulas and symbolic tools. While mysticism prioritizes inward transformation and enlightenment, thaumaturgy focuses on manipulating external forces through ritualistic actions to influence reality.
Perception of Power: Inner Wisdom vs External Miracles
Mysticism centers on the perception of power as an inner wisdom, emphasizing self-awareness, spiritual insight, and personal transformation. Thaumaturgy, by contrast, focuses on external miracles and the manipulation of supernatural forces to produce tangible effects in the physical world. This distinction highlights mysticism's inward journey toward enlightenment versus thaumaturgy's outward demonstration of power.
Notable Figures in Mysticism and Thaumaturgy
Notable figures in mysticism include Meister Eckhart, whose Christian mystical teachings significantly shaped medieval spirituality, and Rumi, whose Sufi poetry explores divine love and union. In thaumaturgy, Paracelsus stands out for his contributions to alchemy and early medicine, blending mystical practices with practical healing. Helena Blavatsky is also prominent, known for founding Theosophy and promoting esoteric knowledge and occult phenomena.
Influence on Modern Spirituality
Mysticism profoundly shapes modern spirituality through its emphasis on direct, personal experiences of the divine, fostering practices like meditation and contemplative prayer that encourage inner transformation and self-realization. Thaumaturgy influences contemporary spiritual practices by highlighting the role of ritual, symbols, and the invocation of supernatural forces to manifest change and healing in the physical world. Together, these traditions contribute to a diverse spiritual landscape that integrates experiential wisdom with pragmatic applications of spiritual power.
Debates and Misconceptions
Debates surrounding mysticism vs thaumaturgy often center on the distinction between spiritual experience and magical practice, with mysticism emphasizing internal transformation and thaumaturgy focusing on external miracle-working. Misconceptions arise when thaumaturgy is mistaken for mere magic tricks, obscuring its deeper religious or esoteric context, while mysticism is sometimes wrongly perceived as purely passive or abstract. Scholars highlight the overlapping but distinct goals: mysticism seeks union with the divine, whereas thaumaturgy aims at tangible supernatural intervention.
Choosing Your Path: Personal Growth and Transformation
Mysticism emphasizes inner personal growth through direct spiritual experiences and awakening higher consciousness, fostering deep self-transformation. Thaumaturgy focuses on manipulating external forces or performing miracles to influence reality, often appealing to those seeking tangible results and practical change. Choosing between mysticism and thaumaturgy depends on whether your path prioritizes profound inner enlightenment or external manifestations of power.
Mysticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com