Effective teaching methods can significantly enhance student engagement and knowledge retention by tailoring lessons to diverse learning styles. Incorporating interactive activities and real-world applications helps make complex concepts more relatable and easier to understand. Explore the rest of the article to discover proven strategies that can transform your teaching approach and enrich your students' learning experiences.
Table of Comparison
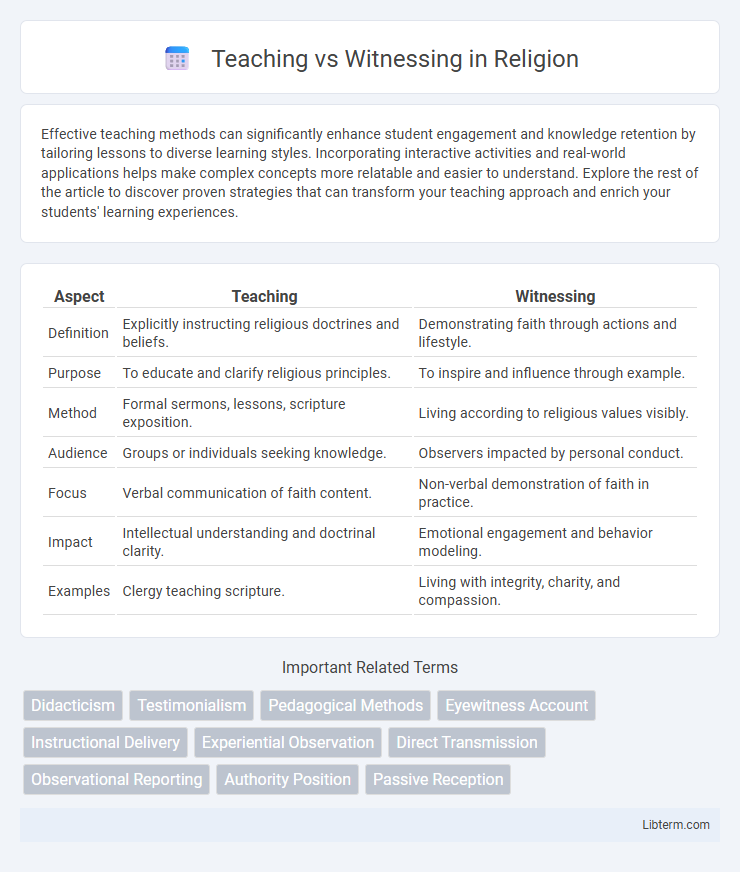
| Aspect | Teaching | Witnessing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explicitly instructing religious doctrines and beliefs. | Demonstrating faith through actions and lifestyle. |
| Purpose | To educate and clarify religious principles. | To inspire and influence through example. |
| Method | Formal sermons, lessons, scripture exposition. | Living according to religious values visibly. |
| Audience | Groups or individuals seeking knowledge. | Observers impacted by personal conduct. |
| Focus | Verbal communication of faith content. | Non-verbal demonstration of faith in practice. |
| Impact | Intellectual understanding and doctrinal clarity. | Emotional engagement and behavior modeling. |
| Examples | Clergy teaching scripture. | Living with integrity, charity, and compassion. |
Understanding Teaching and Witnessing
Teaching involves actively imparting knowledge or skills through structured methods like lectures, demonstrations, or discussions, aiming for learner comprehension and application. Witnessing focuses on observing events or behaviors to gain insight, often emphasizing personal interpretation and reflection rather than direct instruction. Understanding teaching requires recognizing its goal to facilitate learning outcomes, while witnessing centers on subjective experience and contextual awareness.
Core Concepts: Teaching vs Witnessing
Teaching involves actively imparting knowledge, skills, or beliefs through structured instruction or explanation, aiming to influence understanding or behavior. Witnessing centers on observing, experiencing, or testifying to events, truths, or realities without necessarily engaging in direct instruction. Core concepts distinguish teaching's intentional transfer of information from witnessing's passive or experiential acknowledgment of phenomena.
Roles and Responsibilities
Teaching involves actively imparting knowledge, structuring learning experiences, and assessing comprehension to facilitate student growth. Witnessing entails observing behaviors or events, providing validation, and offering reflective feedback without direct instruction. Roles in teaching require curriculum design and content delivery, while witnessing focuses on attentive observation and empathetic support.
Impact on Learners and Observers
Teaching actively shapes learners' understanding through direct instruction and feedback, promoting knowledge retention and skill development. Witnessing, characterized by observation without intervention, influences observers by modeling behaviors and attitudes, fostering implicit learning and reflection. The impact on learners is more immediate and measurable, whereas observers often experience subtler, long-term changes in perception and motivation.
Communication Styles Compared
Teaching communication style emphasizes clarity, structure, and the transmission of knowledge through explanations and demonstrations. Witnessing communication style prioritizes active listening, empathy, and non-judgmental observation to create a supportive environment for self-discovery. Effective communication balances directive teaching with open witnessing to foster understanding and personal growth.
Methods and Approaches
Teaching relies on structured methods such as lectures, demonstrations, and guided practice to transfer knowledge effectively, emphasizing clear objectives and measurable outcomes. Witnessing involves experiential approaches like observation, storytelling, and personal example, fostering deep understanding through immersion and emotional connection. Both approaches utilize interactive techniques, but teaching prioritizes curriculum design while witnessing centers on authentic engagement and reflection.
Advantages and Limitations
Teaching offers structured knowledge transfer and clear learning objectives, enabling learners to acquire specific skills and information efficiently. However, it may limit personal interpretation and spontaneity, often relying on a one-way communication model. Witnessing encourages experiential learning and emotional engagement, fostering deeper understanding but sometimes lacks systematic instruction and measurable outcomes.
Real-life Scenarios and Examples
Teaching involves actively imparting knowledge or skills through structured lessons, as seen in classroom settings where educators explain concepts and guide student learning. Witnessing occurs when individuals observe events or phenomena, providing firsthand accounts or testimonies, such as eyewitnesses recounting details of an accident or legal proceedings. Real-life examples include a teacher demonstrating a science experiment versus a bystander describing what they saw during a public incident.
Practical Tips for Effective Practice
Effective teaching involves clear communication, structured lesson plans, and active learner engagement to ensure knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Witnessing, particularly in mentorship or coaching, requires attentive listening, empathetic feedback, and modeling desired behaviors to inspire and guide learners. Combining both approaches with consistent practice and reflection enhances overall educational impact and facilitates deeper understanding.
Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing between teaching and witnessing depends on the learner's readiness and context; teaching provides structured knowledge transfer, while witnessing emphasizes personal experience and observation. Effective educators assess learners' needs to decide whether direct instruction or modeling behaviors will yield better understanding and engagement. Balancing these approaches enhances learning outcomes by integrating cognitive comprehension with real-life application.
Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com