Ibadah, or worship, is a fundamental practice in Islam encompassing acts of devotion, prayer, and obedience to God. It strengthens spiritual connection and guides ethical behavior in daily life. Discover how understanding ibadah can enhance your faith by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
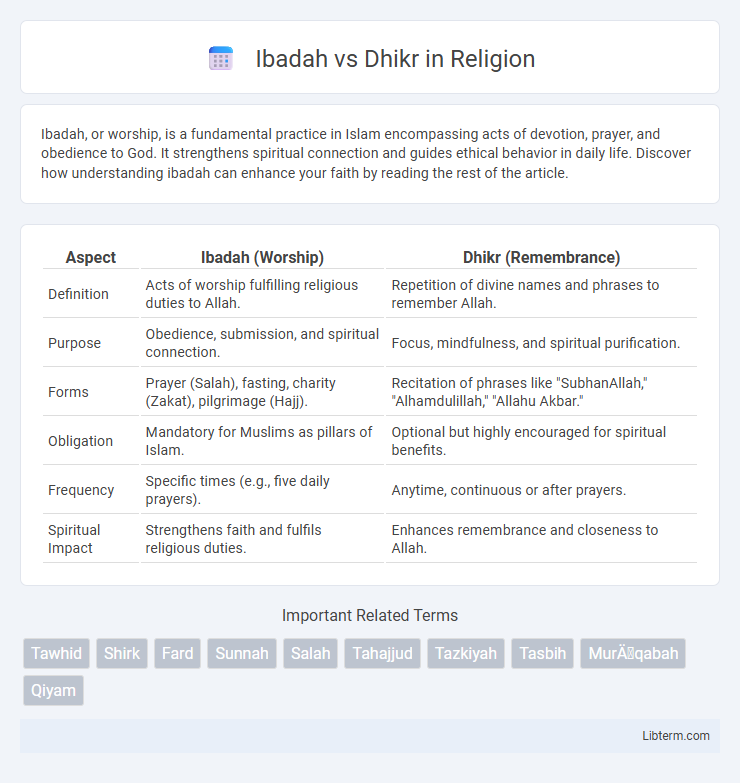
| Aspect | Ibadah (Worship) | Dhikr (Remembrance) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acts of worship fulfilling religious duties to Allah. | Repetition of divine names and phrases to remember Allah. |
| Purpose | Obedience, submission, and spiritual connection. | Focus, mindfulness, and spiritual purification. |
| Forms | Prayer (Salah), fasting, charity (Zakat), pilgrimage (Hajj). | Recitation of phrases like "SubhanAllah," "Alhamdulillah," "Allahu Akbar." |
| Obligation | Mandatory for Muslims as pillars of Islam. | Optional but highly encouraged for spiritual benefits. |
| Frequency | Specific times (e.g., five daily prayers). | Anytime, continuous or after prayers. |
| Spiritual Impact | Strengthens faith and fulfils religious duties. | Enhances remembrance and closeness to Allah. |
Understanding Ibadah: The Essence of Worship
Ibadah encompasses all acts of worship that demonstrate submission to Allah, including prayer, fasting, charity, and pilgrimage, reflecting the core essence of servitude in Islam. Dhikr, a vital component of Ibadah, involves the remembrance of Allah through repeated invocations, reinforcing spiritual mindfulness and connection with the Creator. Understanding Ibadah as the totality of worship highlights its role in cultivating devotion, obedience, and a continuous awareness of God's presence in every aspect of a believer's life.
Defining Dhikr: Remembrance in Islamic Practice
Dhikr, meaning "remembrance," is a central concept in Islamic practice involving the repeated invocation of Allah's names, phrases, and praises to maintain spiritual consciousness and foster a direct connection with the Divine. Unlike general Ibadah, which encompasses all acts of worship including prayer, fasting, and charity, Dhikr specifically targets the heart's awareness by constantly recalling Allah's presence through verbal or silent repetitions. This remembrance strengthens faith, purifies the soul, and serves as a continual spiritual practice that complements formal acts of Ibadah in a Muslim's daily life.
Core Differences Between Ibadah and Dhikr
Ibadah encompasses all acts of worship in Islam, including prayer, fasting, charity, and pilgrimage, aiming for obedience and submission to Allah. Dhikr specifically refers to the remembrance of Allah through repeated recitation of His names, phrases, or prayers to attain spiritual mindfulness and closeness. The core difference lies in Ibadah representing comprehensive worship practices, while Dhikr is a focused, devotional remembrance that can be part of Ibadah or practiced independently.
The Role of Intention in Ibadah and Dhikr
Intention (Niyyah) plays a pivotal role in both Ibadah and Dhikr, determining the sincerity and spiritual value of these acts of worship. In Ibadah, a pure intention aligns actions with seeking Allah's pleasure, transforming routine practices into meaningful devotion. Similarly, in Dhikr, the mindfulness and focus driven by sincere intention enhance the remembrance of Allah, deepening the believer's connection and spiritual awareness.
Forms of Ibadah: Beyond Ritual Acts
Forms of Ibadah extend beyond ritual acts to encompass everyday behavior and intentions aligned with Islamic principles. While Dhikr specifically refers to the remembrance of Allah through phrases and prayers, Ibadah includes acts such as charity, ethical conduct, and seeking knowledge. This broader understanding highlights the integration of faith in all aspects of life, reinforcing a holistic approach to worship in Islam.
Types and Methods of Dhikr
Dhikr, or remembrance of Allah, encompasses various types including verbal, silent, individual, and group recitations, each serving to deepen spiritual connection. Common methods involve repeating specific phrases such as "SubhanAllah," "Alhamdulillah," and "Allahu Akbar" using beads (tasbih) or mental repetition, facilitating mindfulness and tranquility. Unlike general acts of Ibadah, Dhikr emphasizes continual remembrance and reflection, often integrated within daily routines to reinforce faith and consciousness of God.
Spiritual Benefits of Ibadah
Ibadah encompasses a wide range of worship practices that cultivate a deep connection with Allah, fostering spiritual growth and inner peace through disciplined devotion. Engaging in Ibadah, such as prayer, fasting, and charity, purifies the heart, strengthens faith, and instills a sense of purpose and mindfulness in daily life. These acts of worship transform the believer's soul, promoting resilience against negative influences and enhancing overall spiritual well-being.
Psychological and Emotional Effects of Dhikr
Dhikr, the Islamic practice of remembrance of God, induces profound psychological calm by reducing stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms through rhythmic repetition and focused mindfulness. Neuropsychological studies suggest that Dhikr activates parasympathetic nervous system pathways, promoting emotional regulation and increased resilience against mental fatigue. Unlike structured Ibadah rituals that encompass formal worship actions, Dhikr offers continuous, accessible spiritual engagement that enhances emotional stability and mental clarity throughout daily life.
Synergy Between Ibadah and Dhikr in Daily Life
Ibadah and Dhikr create a powerful synergy by integrating ritual worship with continuous remembrance of Allah, enhancing spiritual awareness throughout daily activities. Practicing Dhikr during mundane tasks deepens the impact of formal Ibadah, promoting mindfulness and strengthening the believer's connection to divine presence. This harmonious blend fosters inner peace, resilience, and a more consistent devotion in both sacred and routine moments.
Common Misconceptions about Ibadah and Dhikr
Many people mistakenly believe Ibadah is limited to formal acts of worship like prayer, while Dhikr is often misunderstood as mere repetitive chanting without deeper spiritual significance. In reality, Ibadah encompasses all acts done in obedience to Allah, including Dhikr, which serves as a means to maintain constant awareness of God throughout daily life. Both Ibadah and Dhikr are integral to a believer's spiritual framework, fostering mindfulness and connection beyond ritualistic practices.
Ibadah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com