Vivid descriptions create immersive experiences by engaging all your senses, allowing readers to visualize, hear, and feel the scene vividly. Mastering descriptive writing enhances storytelling, making narratives more compelling and memorable. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques that elevate your descriptive skills.
Table of Comparison
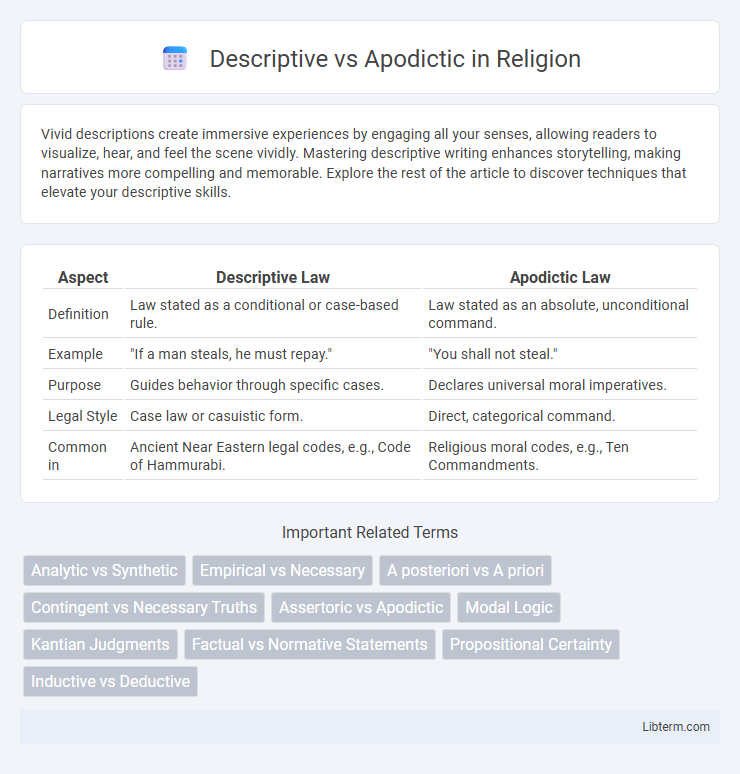
| Aspect | Descriptive Law | Apodictic Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law stated as a conditional or case-based rule. | Law stated as an absolute, unconditional command. |
| Example | "If a man steals, he must repay." | "You shall not steal." |
| Purpose | Guides behavior through specific cases. | Declares universal moral imperatives. |
| Legal Style | Case law or casuistic form. | Direct, categorical command. |
| Common in | Ancient Near Eastern legal codes, e.g., Code of Hammurabi. | Religious moral codes, e.g., Ten Commandments. |
Introduction to Descriptive and Apodictic
Descriptive statements convey observable facts and characteristics, providing detailed information without asserting absolute certainty. Apodictic statements express necessary truths or moral imperatives, characterized by undeniable certainty and authoritative tone. Understanding the distinction between descriptive and apodictic forms is crucial for interpreting legal texts, philosophical arguments, and linguistic expressions accurately.
Defining Descriptive Statements
Descriptive statements provide detailed observations or accounts of phenomena based on empirical evidence, focusing on what is or occurs without asserting necessity. These statements convey factual information about specific conditions, events, or characteristics, enabling clear understanding and analysis. Unlike apodictic statements, which express absolute certainty and logical necessity, descriptive statements remain open to verification and interpretation within their contextual framework.
Understanding Apodictic Assertions
Apodictic assertions represent statements grounded in absolute necessity and incontrovertible truth, commonly found in fields like mathematics and formal logic. Unlike descriptive assertions, which depict observations or facts subject to verification, apodictic assertions assert certainty that cannot be denied without contradiction. Understanding apodictic assertions enhances the ability to identify statements that are universally valid and foundational in deductive reasoning processes.
Key Differences Between Descriptive and Apodictic
Descriptive statements provide observational or factual information based on experience or evidence, emphasizing how things are or appear. Apodictic statements express necessary truths or absolute certainties, often used in logic or normative contexts to assert what must be true. The key difference lies in descriptive statements being contingent and empirical, while apodictic statements are categorical and a priori.
Examples of Descriptive vs Apodictic Statements
Descriptive statements convey information based on observation or experience, such as "The sky appears blue during a clear day," which reflects empirical evidence. Apodictic statements assert necessary, universally valid truths, exemplified by "All bachelors are unmarried men," indicating logical necessity. Understanding the distinction between these types clarifies how knowledge is communicated and validated across disciplines.
Roles in Philosophy and Logic
Descriptive statements in philosophy and logic convey observations about how things are, focusing on empirical or factual content that can be verified or falsified. Apodictic statements embody necessary truths or logical certainties, serving as foundational premises in deductive reasoning and philosophical arguments. Understanding the distinction highlights the roles of descriptive claims in forming hypotheses while apodictic claims provide irrefutable conclusions essential for rigorous logical analysis.
Importance in Critical Thinking
Descriptive statements convey factual information about how things are, providing essential context and evidence for critical thinking. Apodictic statements assert undeniable truths or logical necessities, serving as foundational premises in rigorous arguments. Distinguishing between these types enhances analytical clarity and strengthens the validity of conclusions in critical reasoning.
Common Misconceptions
Descriptive statements convey observations or facts based on empirical evidence, while apodictic statements express absolute, necessary truths with unquestionable certainty. A common misconception is that descriptive claims lack validity or importance compared to apodictic assertions, but descriptive knowledge often forms the foundation for scientific understanding and rational discourse. Another misunderstanding is equating apodictic statements with subjective opinion, despite their basis in logical necessity and formal proof.
Application in Everyday Language
Descriptive language provides factual details and observable information, making it essential for everyday communication such as giving directions or explaining concepts. Apodictic language, characterized by absolute certainty and authoritative statements, is commonly applied in legal, scientific, or instructional contexts where clear, definitive assertions are necessary. Understanding the balance between descriptive clarity and apodictic certainty improves effective communication across various daily interactions.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Descriptive and Apodictic
Choosing between descriptive and apodictic approaches depends on the context and purpose of communication; descriptive statements provide observations based on evidence, suitable for empirical analysis, while apodictic assertions convey absolute certainty, often reserved for logical or mathematical conclusions. Employing descriptive language fosters open inquiry and accommodates varying interpretations, whereas apodictic claims demand acceptance based on incontrovertible truth. Understanding the distinction ensures clarity and precision in argumentation, enhancing effective knowledge transmission and decision-making.
Descriptive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com