Doctrine serves as a fundamental framework guiding beliefs, principles, and practices within various religious, legal, and organizational contexts. It shapes the understanding and behavior of individuals and groups by establishing accepted standards and authoritative teachings. Discover how this concept influences your worldview and impacts different aspects of society by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
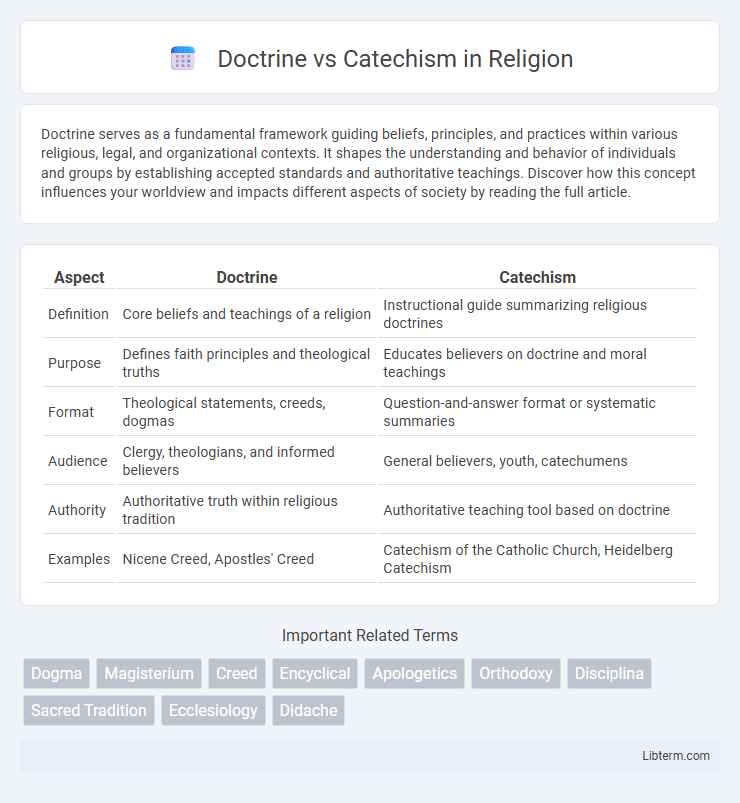
| Aspect | Doctrine | Catechism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core beliefs and teachings of a religion | Instructional guide summarizing religious doctrines |
| Purpose | Defines faith principles and theological truths | Educates believers on doctrine and moral teachings |
| Format | Theological statements, creeds, dogmas | Question-and-answer format or systematic summaries |
| Audience | Clergy, theologians, and informed believers | General believers, youth, catechumens |
| Authority | Authoritative truth within religious tradition | Authoritative teaching tool based on doctrine |
| Examples | Nicene Creed, Apostles' Creed | Catechism of the Catholic Church, Heidelberg Catechism |
Introduction to Doctrine and Catechism
Doctrine refers to the set of official teachings and principles held by a religious organization, providing foundational beliefs that guide faith and practice. Catechism is a structured summary or manual based on these doctrines, designed to teach and explain core doctrines through questions and answers for easier understanding. The introduction to doctrine focuses on defining essential truths, while the catechism introduces these truths in a systematic and pedagogical format for instruction.
Defining Doctrine: Core Beliefs Explained
Doctrine refers to the essential teachings and core beliefs held by a religious tradition, outlining its fundamental truths about God, salvation, and moral conduct. It functions as a framework that guides faith and practice, forming the theological foundation upon which other teachings are built. Unlike the Catechism, which systematically summarizes these beliefs in a question-and-answer format for instruction, doctrine encompasses the authoritative principles derived from sacred texts and ecclesiastical authority.
Understanding Catechism: Structured Faith Teaching
Catechism serves as a structured framework for imparting religious doctrine through organized questions and answers, designed to ensure clear comprehension of core beliefs and moral teachings. It systematically presents essential doctrines, facilitating catechumens' understanding of faith principles, sacraments, and commandments. As an educational tool, catechism emphasizes memorization and internalization, supporting consistent transmission of doctrine across generations.
Historical Origins of Doctrine and Catechism
The historical origins of doctrine trace back to early Church councils and theological debates, where core beliefs were formally defined to preserve apostolic teachings, such as the Nicene Creed established in 325 AD. Catechism, originating primarily in the post-Reformation period, developed as a systematic instructional tool designed to educate believers in these established doctrines through question-and-answer formats, exemplified by the Heidelberg Catechism (1563) and the Roman Catechism (1566). This distinction underlines doctrine as the foundational theological truths of Christianity, while catechism serves as the pedagogical method for communicating and reinforcing those principles to the faithful.
Key Differences Between Doctrine and Catechism
Doctrine refers to the core teachings and principles officially established by a religious tradition, representing authoritative beliefs that guide faith and practice. Catechism is a structured summary or instructional guide, often in question-and-answer format, designed to teach and explain these doctrines systematically to believers. The key difference lies in doctrine being the foundational truths themselves, while catechism serves as an educational tool to communicate and reinforce those doctrines.
Interdependence: How Doctrine Shapes Catechism
Doctrine forms the foundational theological truths that guide the development of the Catechism, ensuring its teachings align with core Christian beliefs. Catechism translates complex doctrinal principles into accessible, structured lessons for believers, facilitating understanding and practice of faith. This interdependence reinforces doctrinal integrity while promoting consistent religious education across generations.
Role in Religious Education and Formation
Doctrine provides the foundational beliefs and theological teachings essential for religious education, serving as the guiding framework for faith formation. The Catechism acts as a structured compendium of these doctrines, presenting them in a systematic and accessible format to facilitate understanding and memorization. Together, doctrine shapes the core content while the catechism organizes and communicates these teachings effectively for catechesis and spiritual development.
Examples in Major Christian Denominations
The Doctrine in Christianity refers to the formal teachings and beliefs upheld by various denominations, such as the Nicene Creed in Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy, which establishes foundational beliefs about the Trinity and Jesus Christ. The Catechism, like the Catholic Catechism of the Catholic Church or the Westminster Shorter Catechism in Reformed Christianity, serves as a structured educational tool, providing detailed explanations and guidance on these doctrines for teaching believers. Protestant denominations often emphasize sola scriptura doctrines summarized in catechisms like Luther's Small Catechism, while the Orthodox Church relies on oral traditions and catechetical instruction aligned with their doctrinal teachings.
Contemporary Relevance in Faith Communities
Doctrine constitutes the foundational teachings of a religion, providing the essential theological framework that shapes belief systems in contemporary faith communities. Catechism serves as a structured educational tool, translating complex doctrines into accessible questions and answers, facilitating religious instruction and spiritual formation across diverse age groups. Together, doctrine and catechism ensure the transmission of core beliefs while addressing modern challenges and fostering communal identity within evolving faith landscapes.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Doctrine and Catechism
Doctrine provides the foundational set of beliefs and principles that guide a faith community, offering a broad theological framework. Catechism serves as a practical instructional tool, delivering structured teachings designed for education and spiritual formation. Choosing between doctrine and catechism depends on the need for either deep theological understanding or accessible religious instruction tailored to different audiences.
Doctrine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com